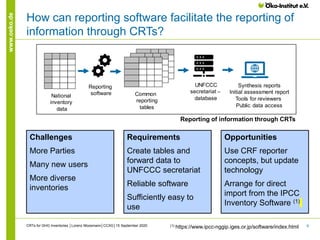
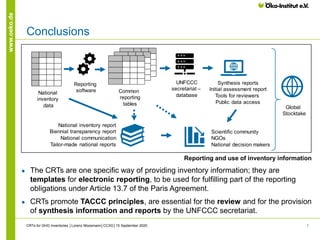
This presentation discusses improving common reporting tables (CRTs) for greenhouse gas inventories and the role of reporting software. It suggests that CRTs should promote transparency, accuracy, completeness, consistency over time, and comparability across parties. Reporting software could facilitate reporting by directly importing data from inventory software and generating tables for the UNFCCC. The current CRT format fulfills review needs but reporting software should be reliable, easy to use, and accommodate diverse inventories and more parties.