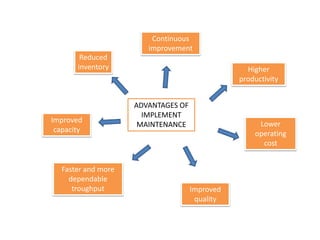
The document provides information on maintenance principles and procedures. It discusses the definition of maintenance as activities to keep systems functioning. The principles of maintenance are to achieve quality, maximize equipment life, and minimize interruptions. Planned maintenance includes activities like preventative maintenance to condition-based maintenance. Unplanned maintenance refers to emergency or breakdown maintenance. Maintenance aims to improve aspects like capacity, quality, and productivity while reducing costs and inventory. Workplace safety topics covered include personal protective equipment, lockout/tagout procedures, hazardous materials and energy, and the importance of inspecting hand tools and power tools.