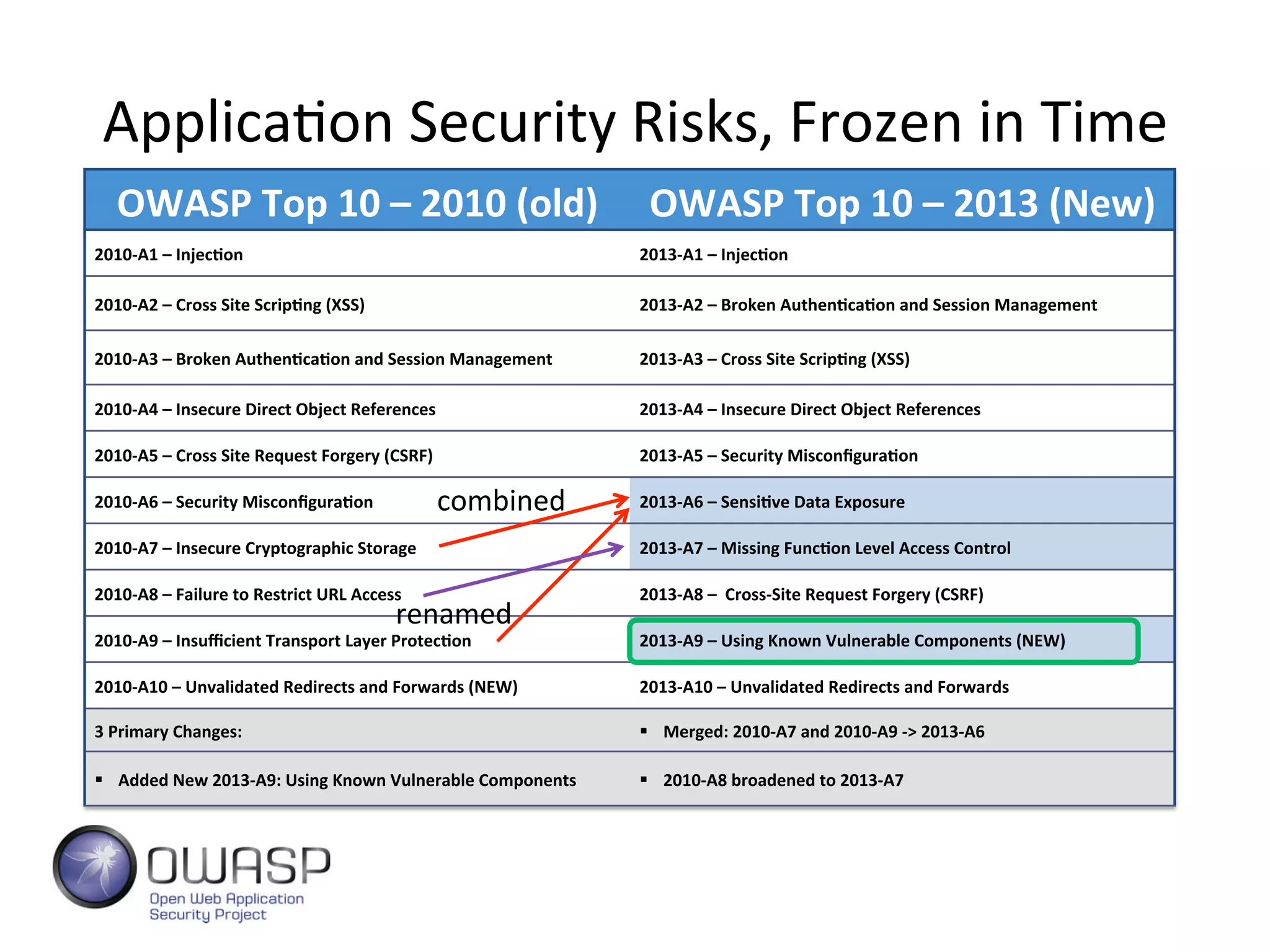
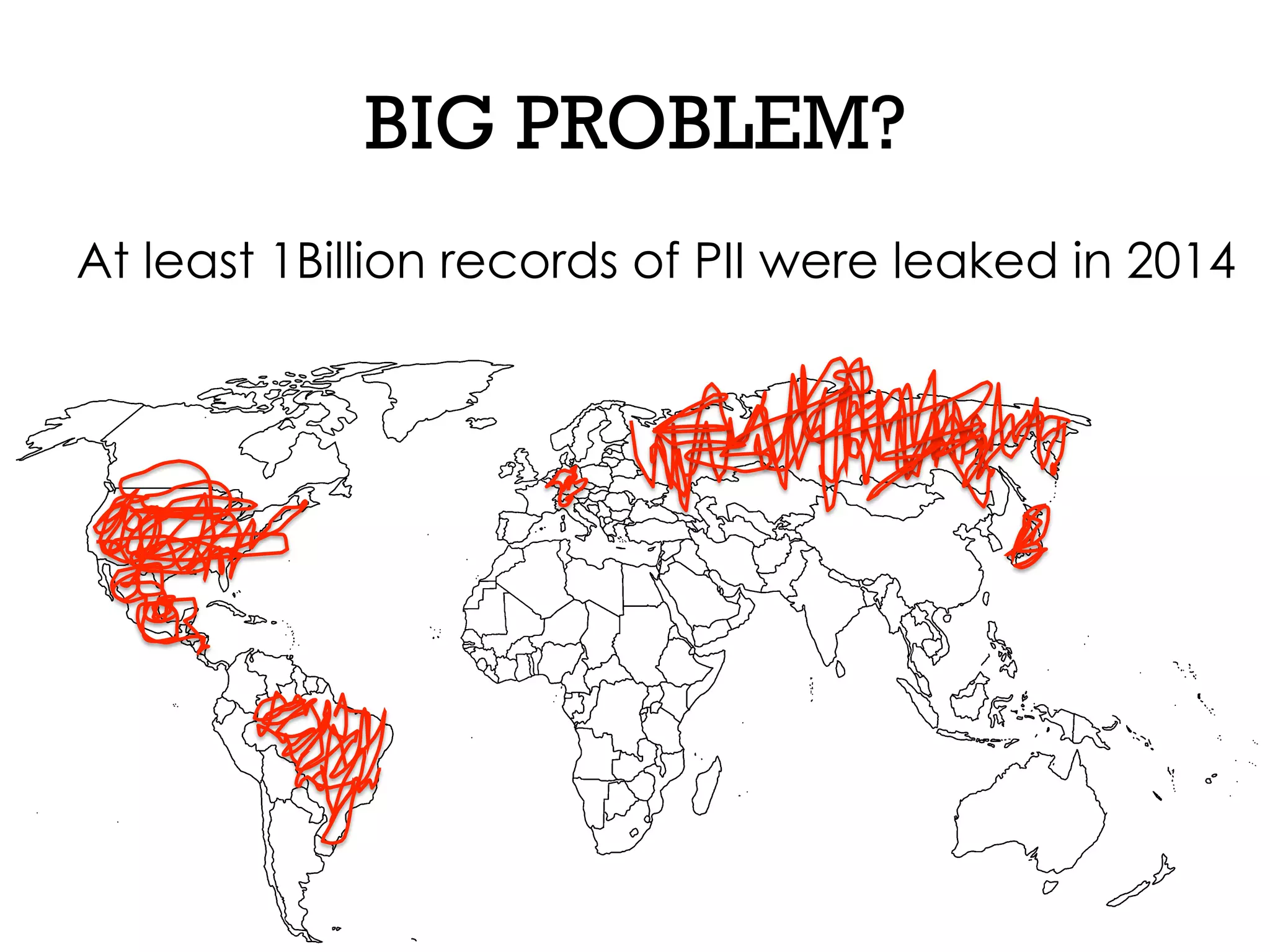
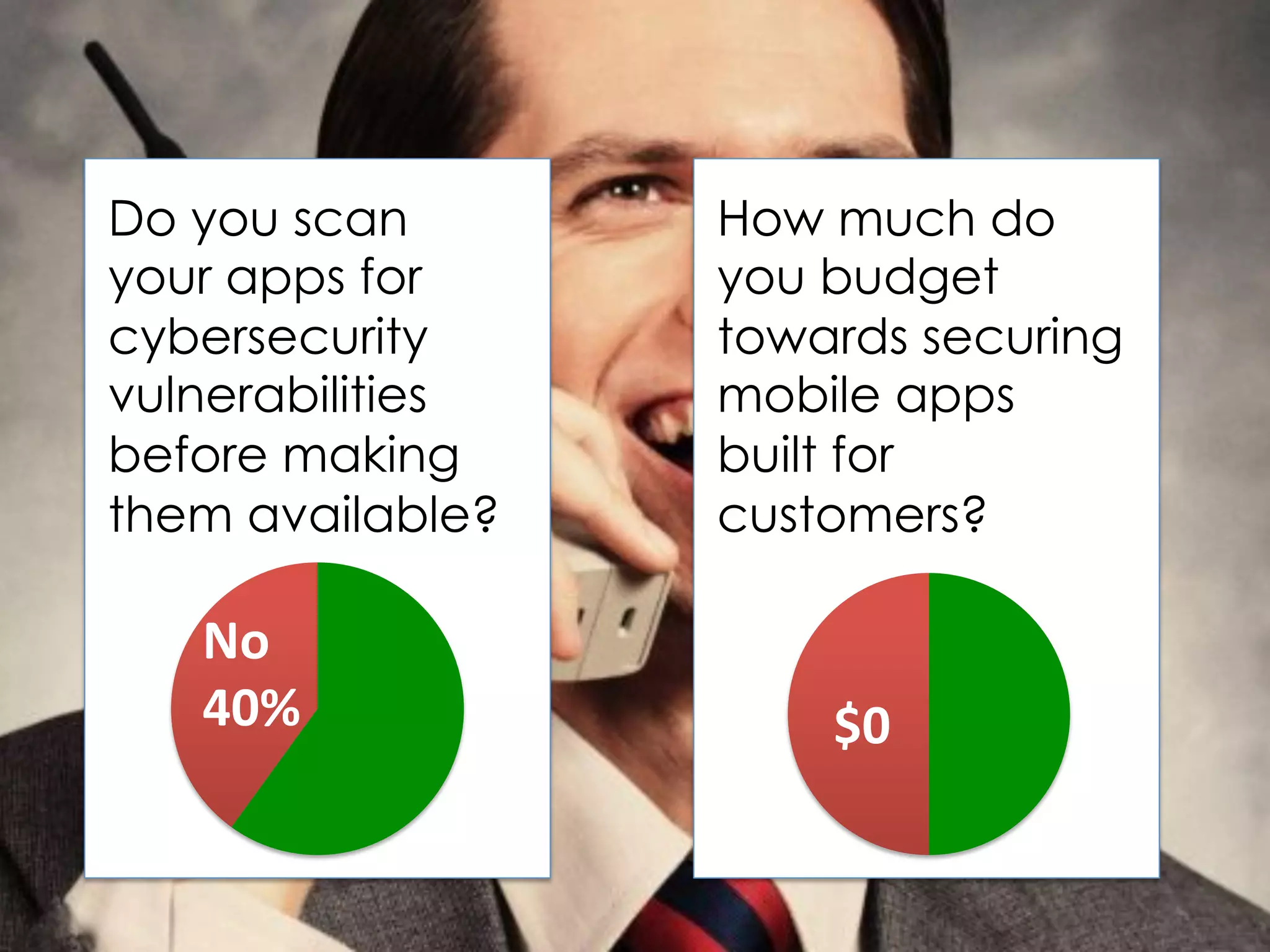
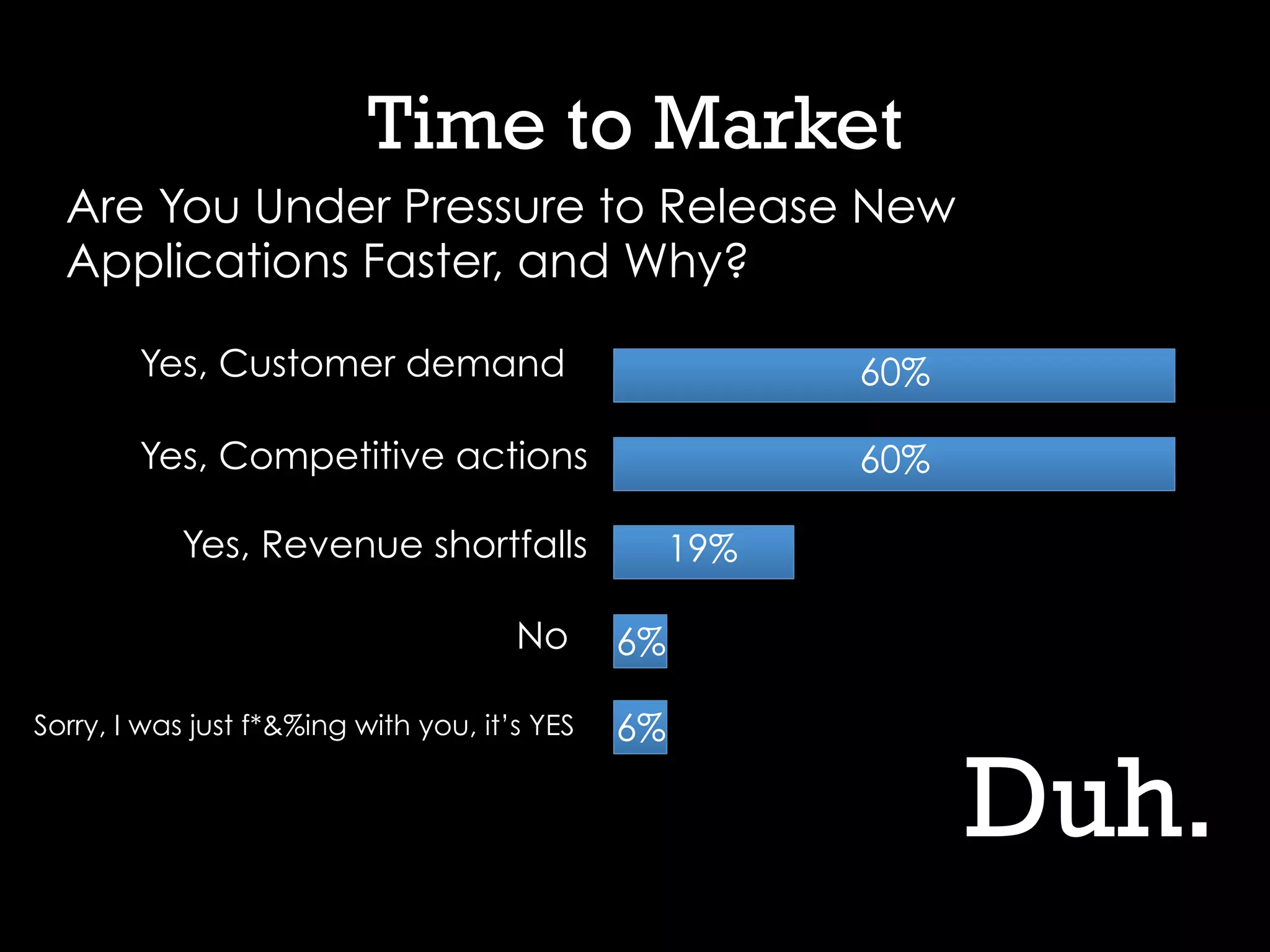
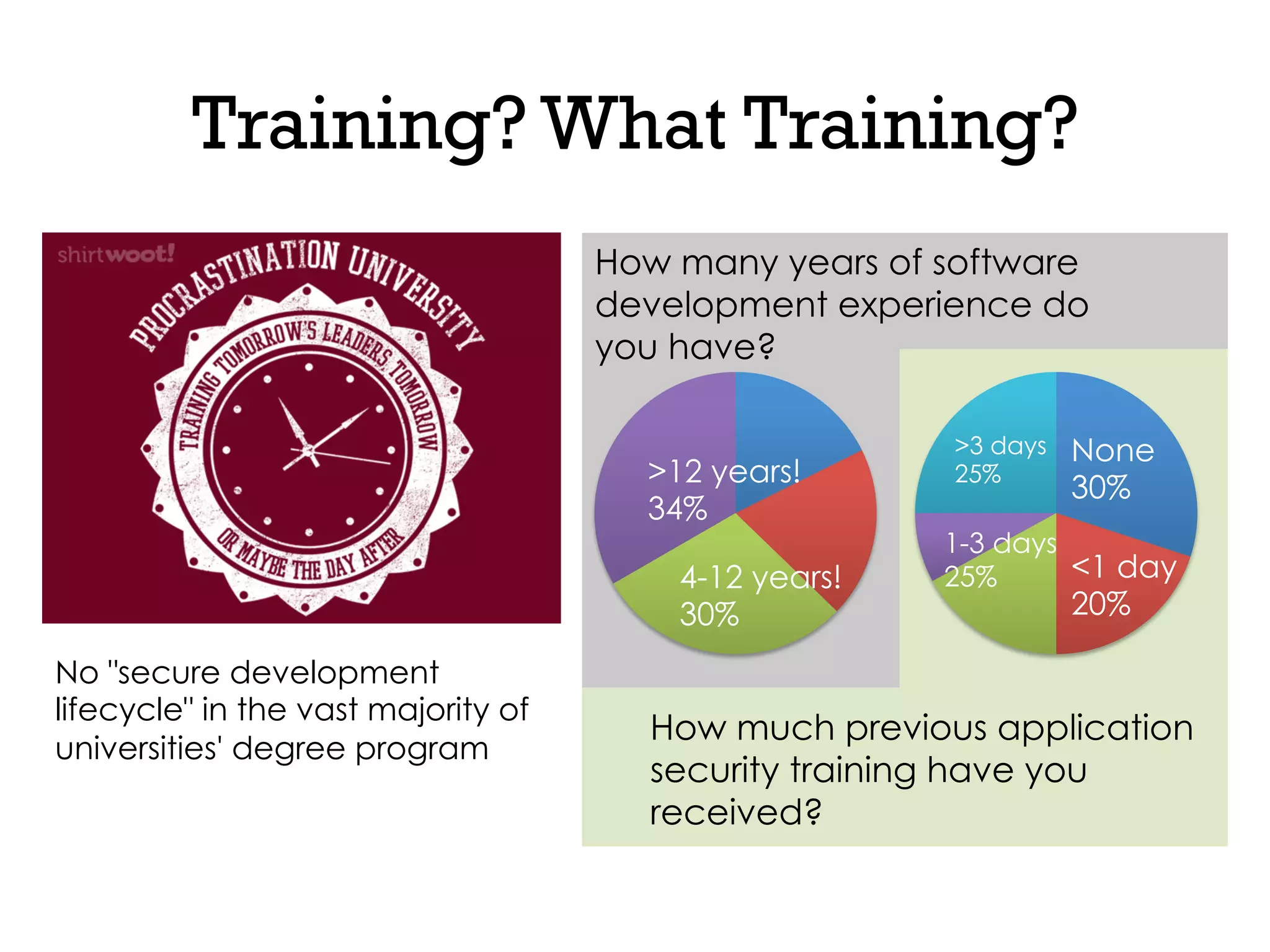
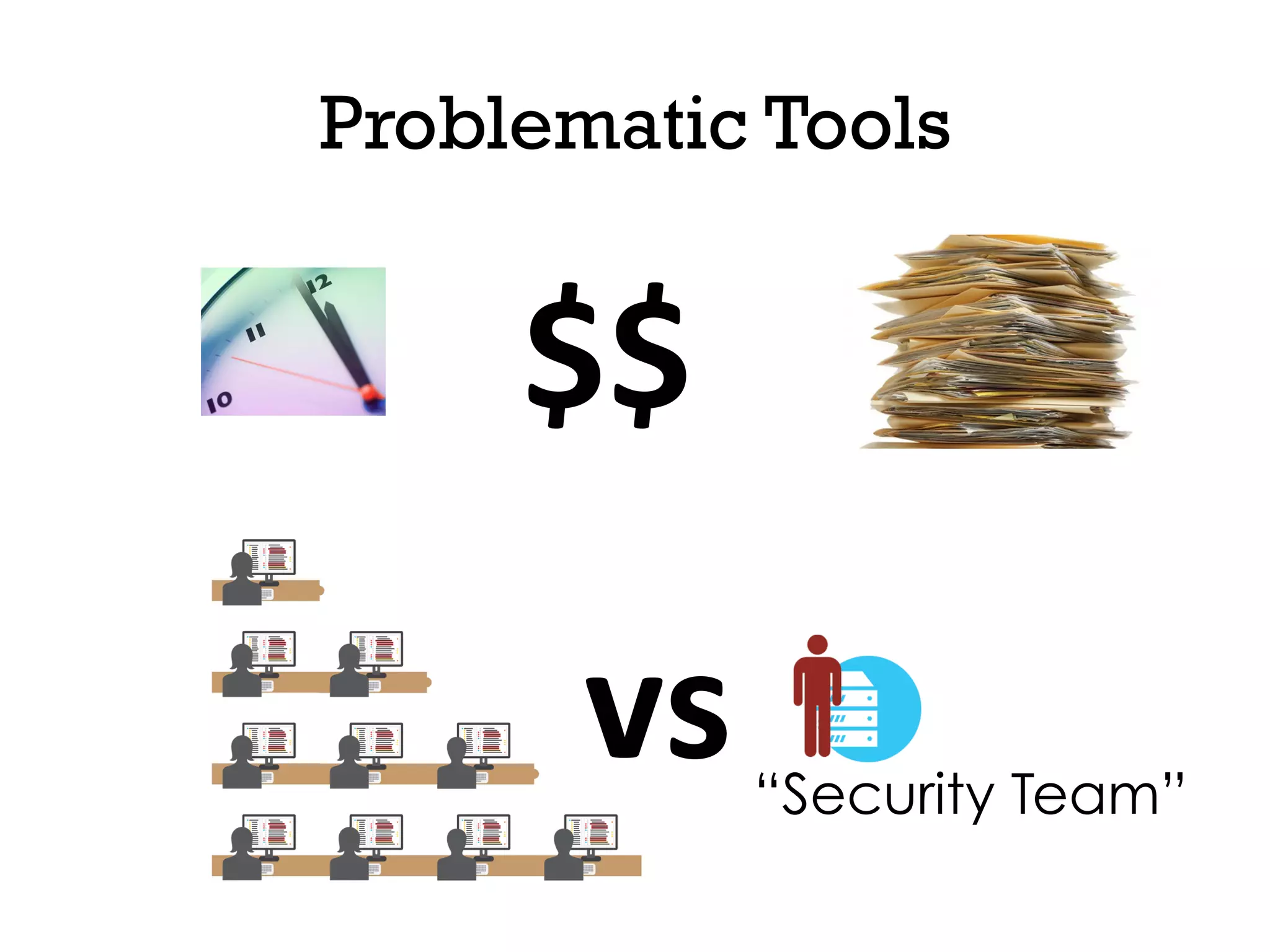
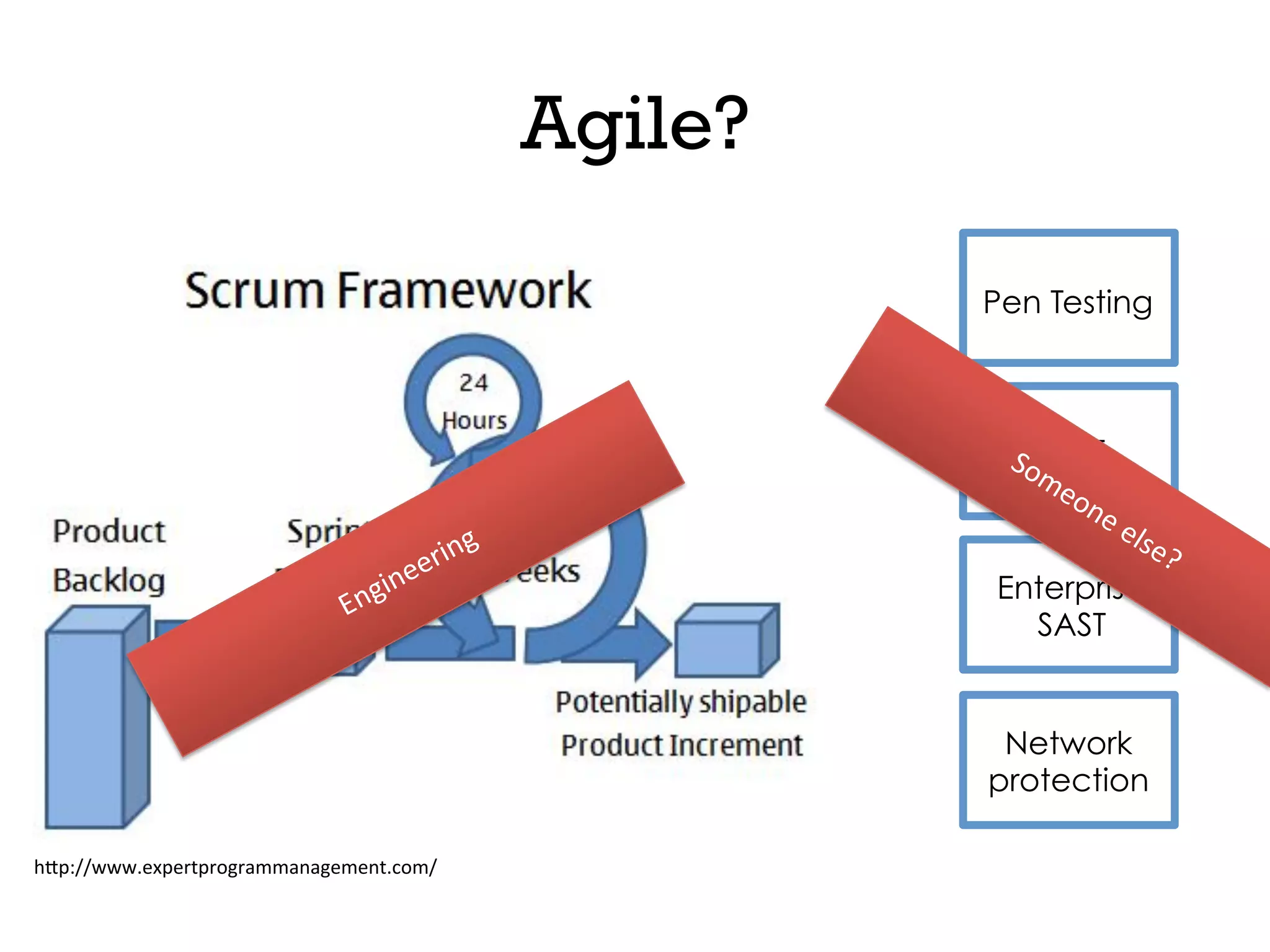
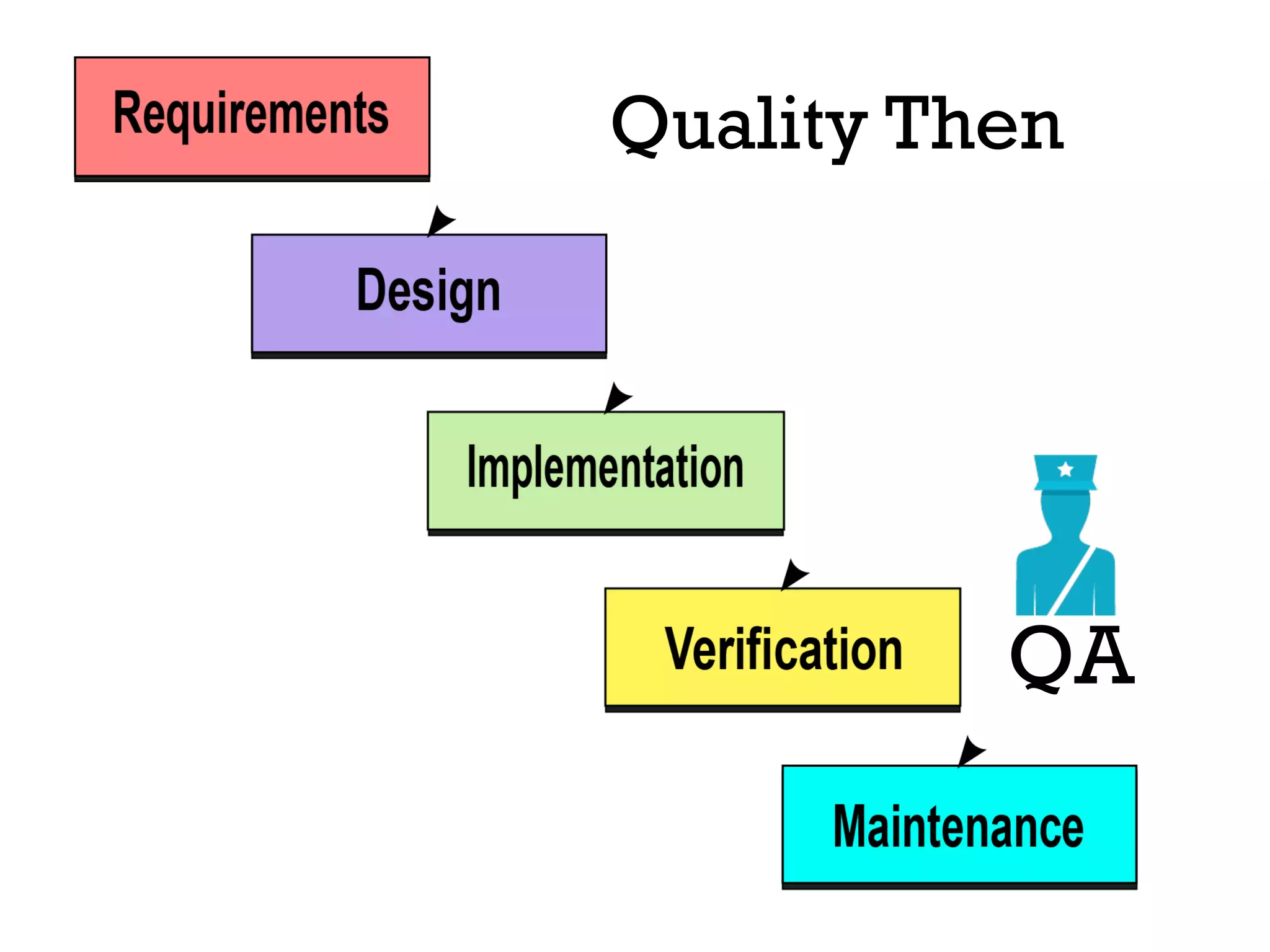
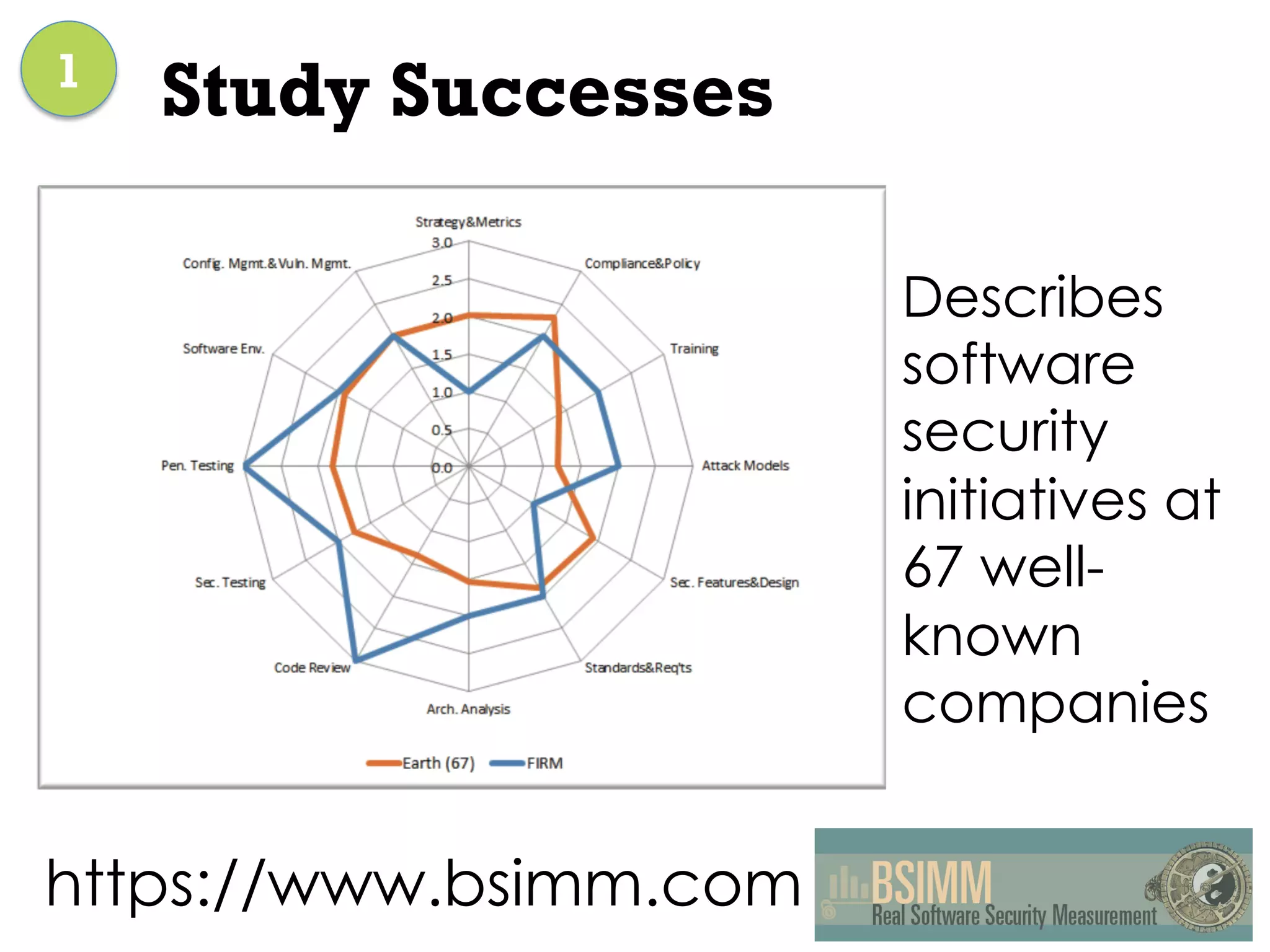
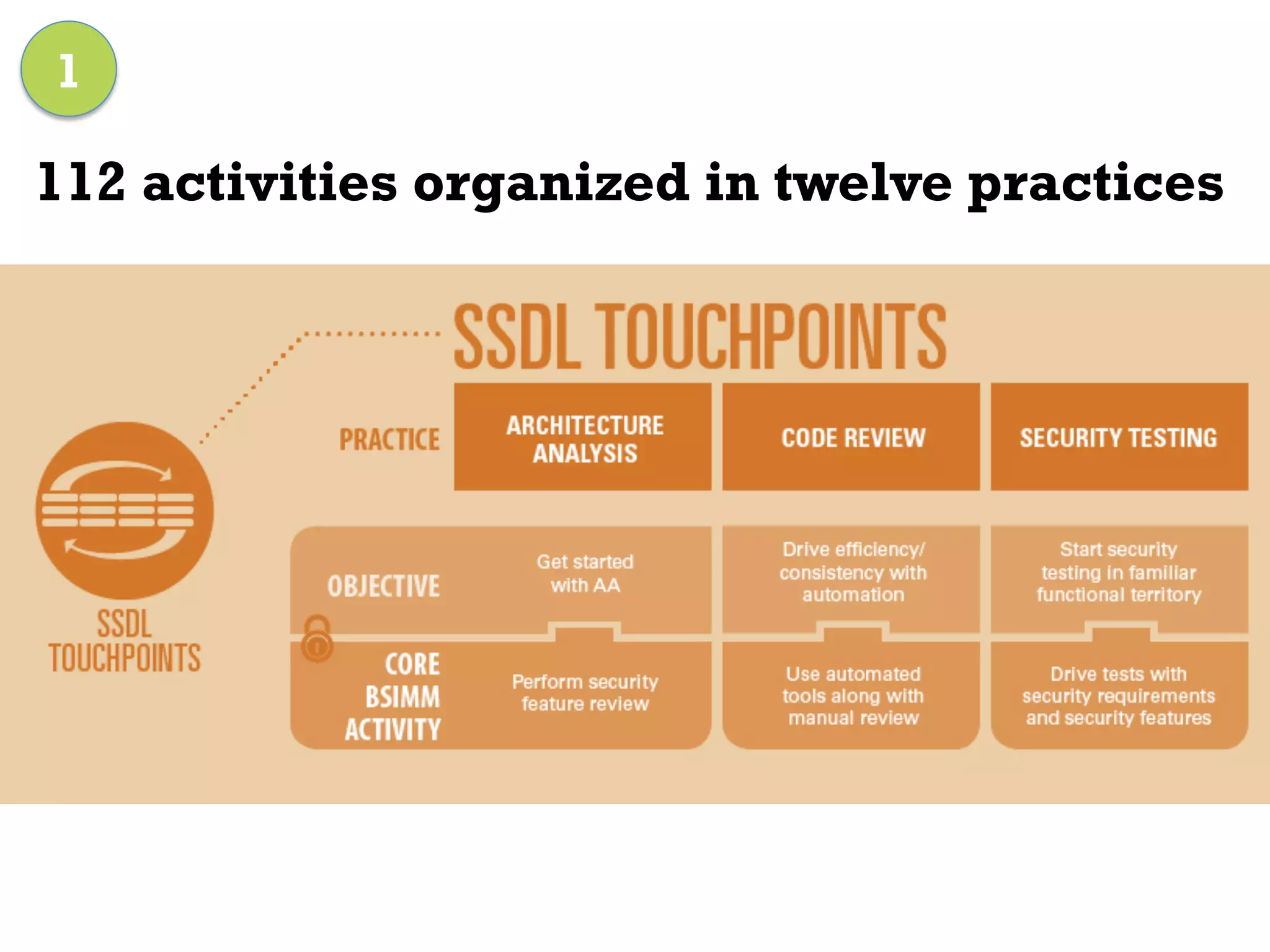
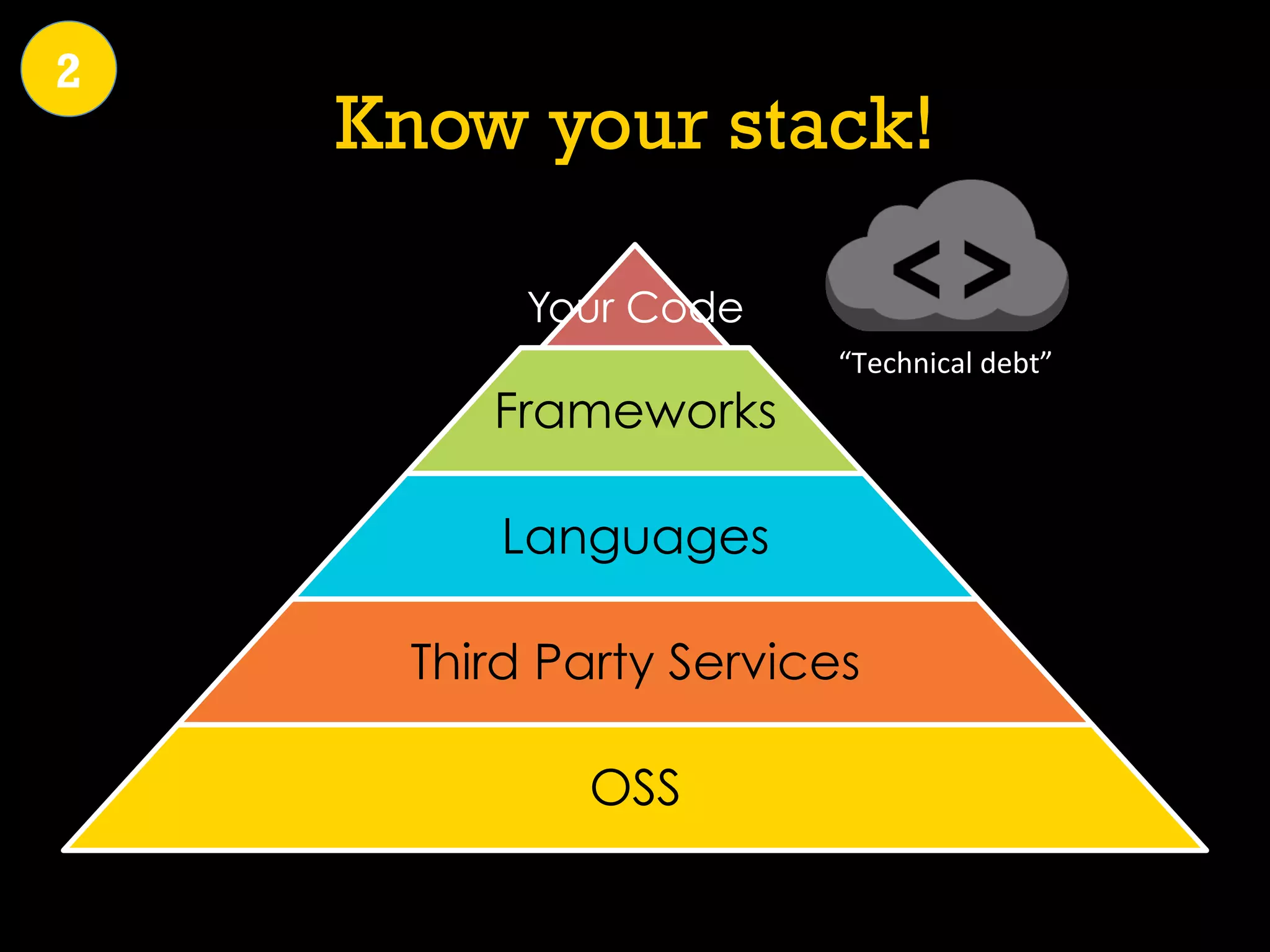
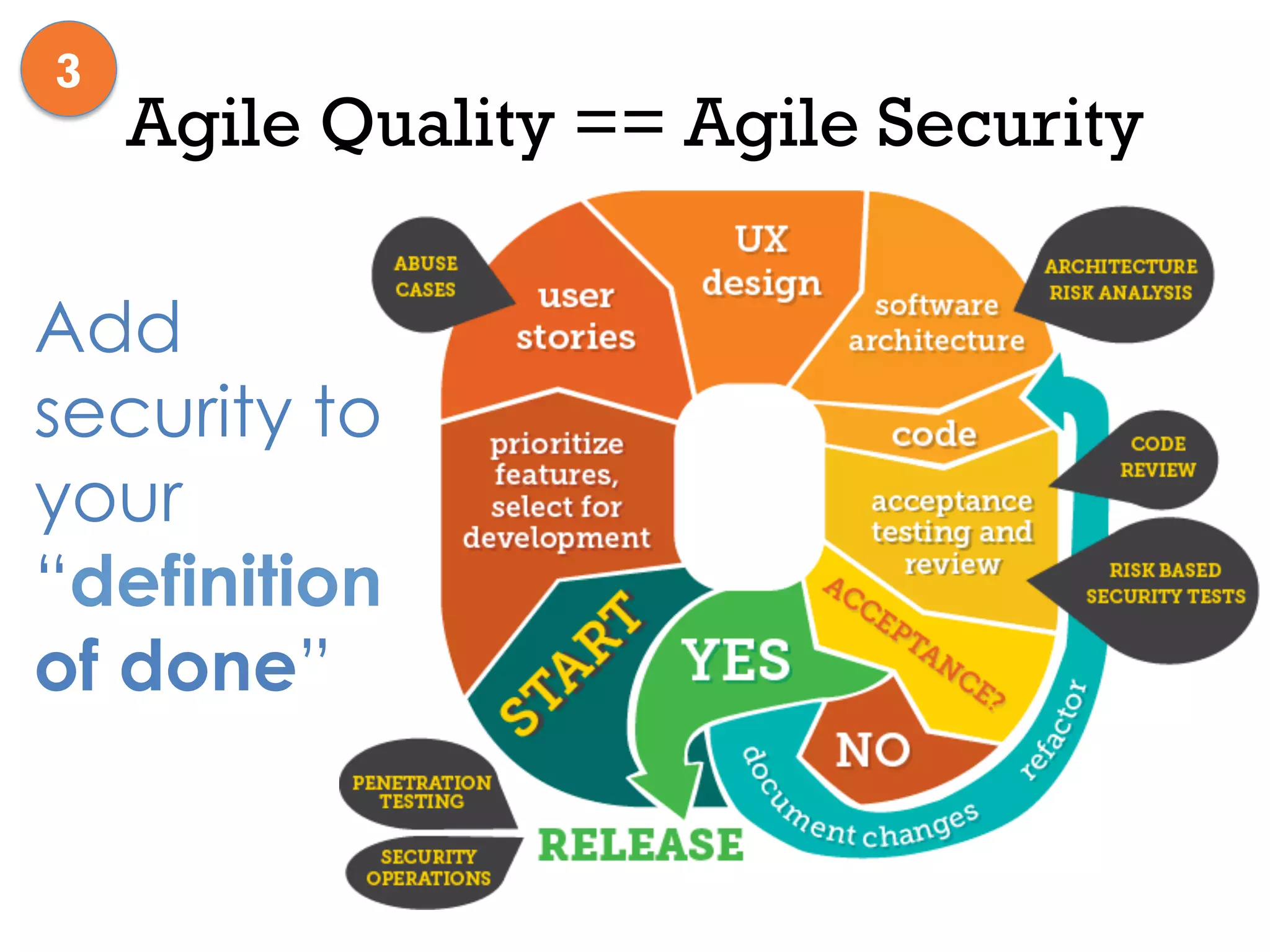
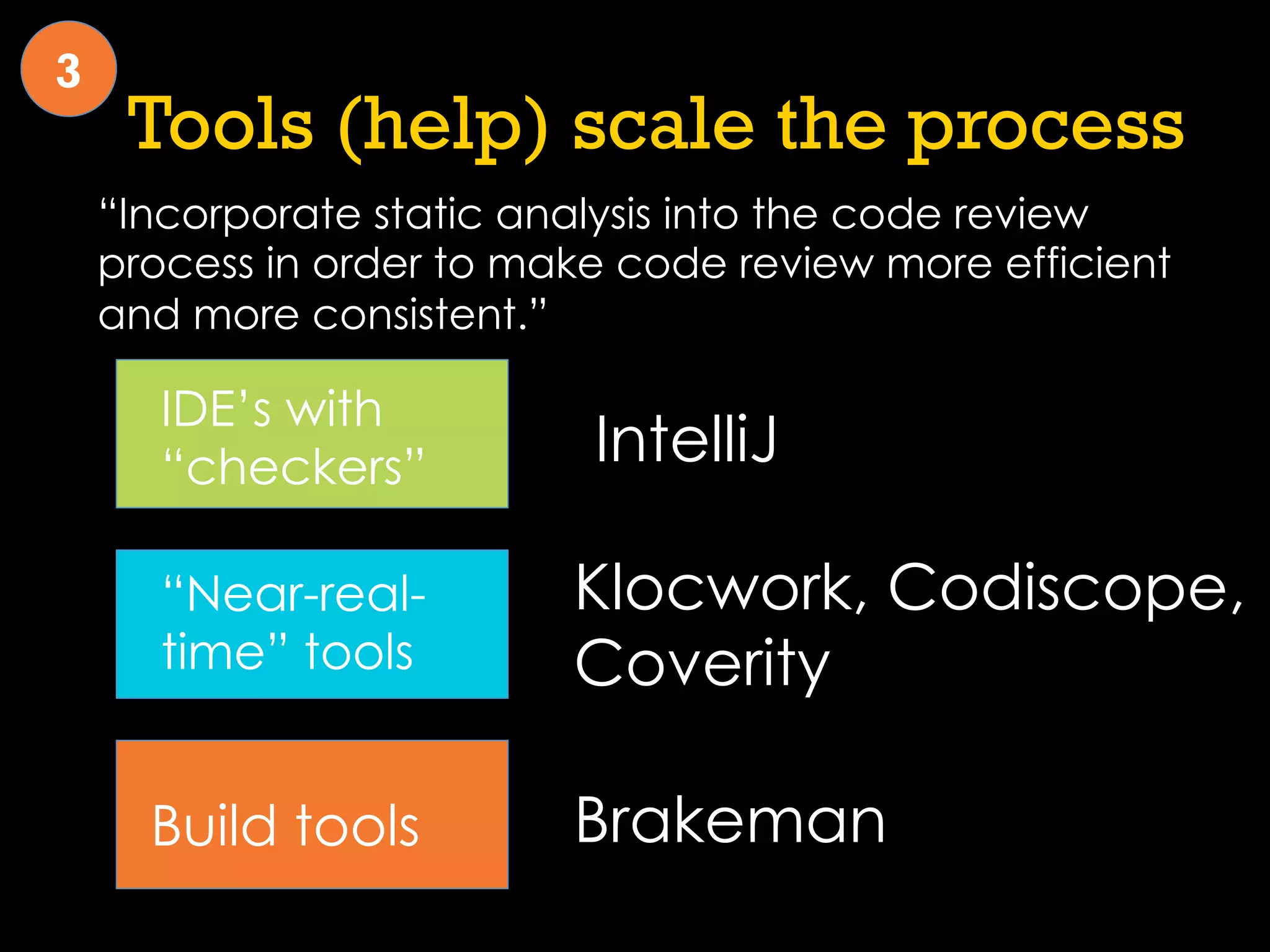
This document discusses software security and outlines a 4 step plan to improve it. It begins by recommending studying successful security initiatives at other companies. The second step is to inventory your own applications to understand what data and services they involve. The third step is to incorporate security practices into agile development processes and use tools to help scale this. The final step is to drive a security-focused culture change and have plans for incident response.