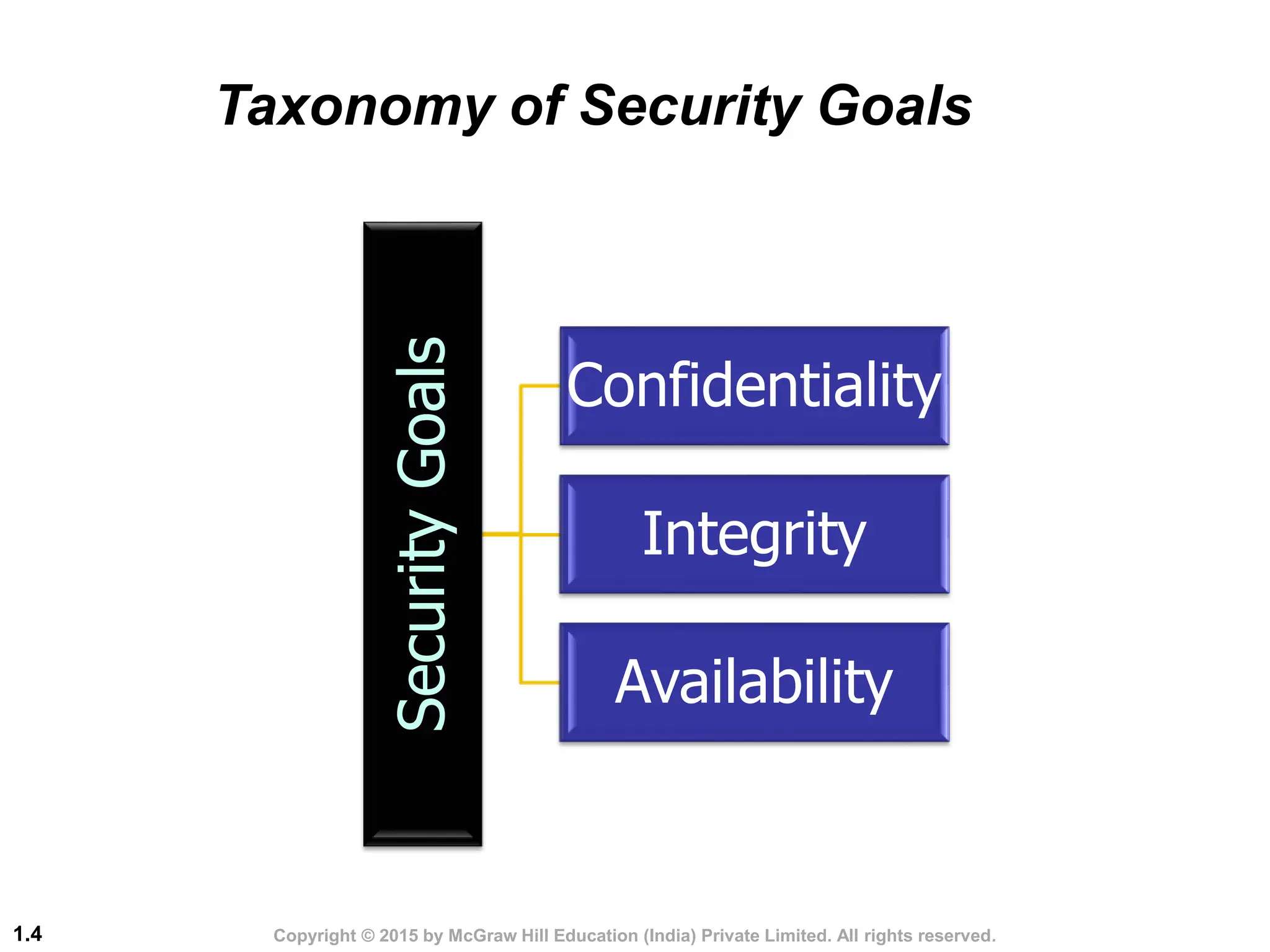
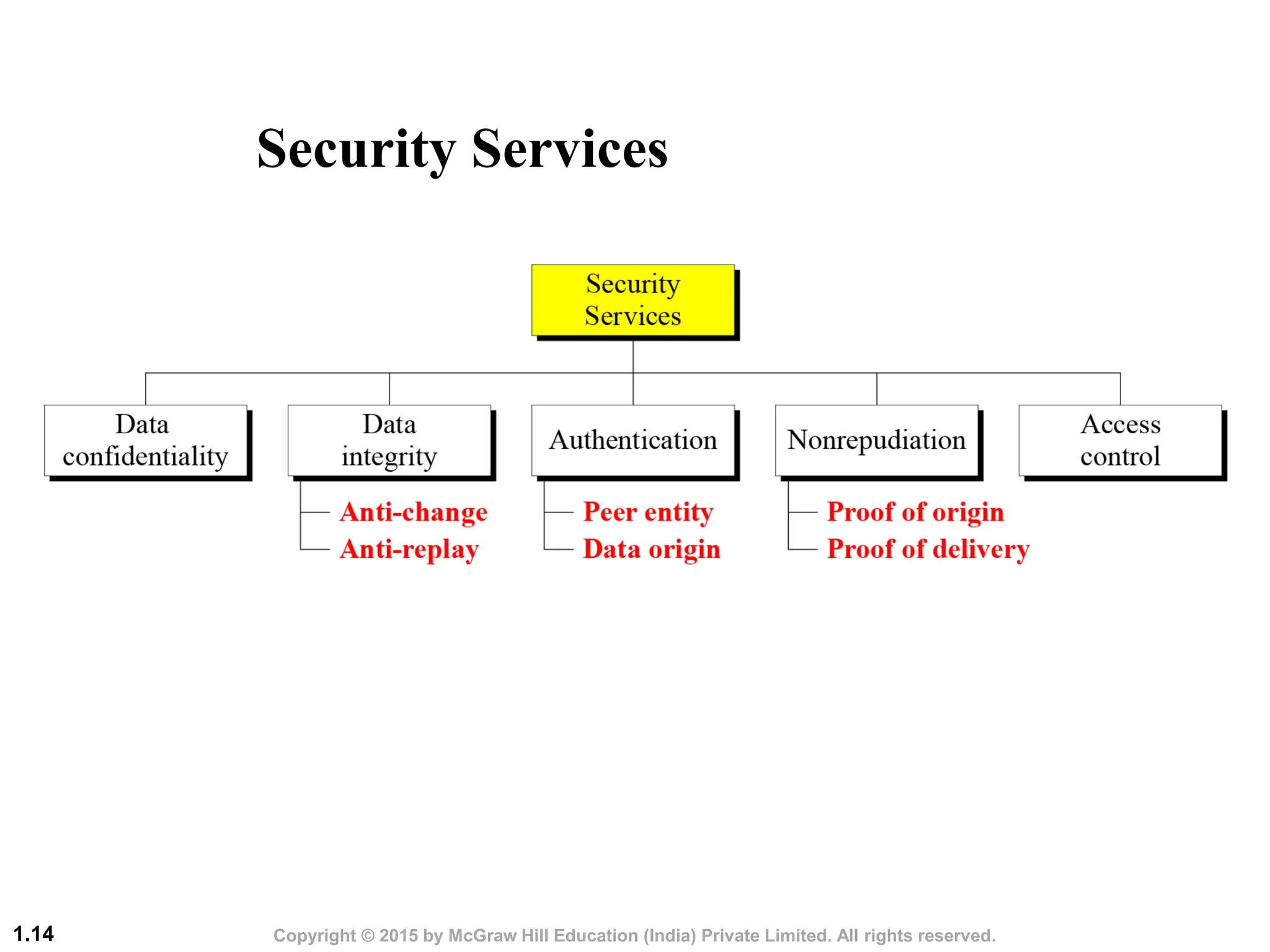
This document discusses cryptography and network security. It defines the three main security goals of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It describes different types of attacks that threaten each goal, such as snooping, modification, and denial of service attacks. It also categorizes attacks as passive or active. The document outlines security services like authentication, access control, and non-repudiation that can be provided through mechanisms like cryptography, digital signatures, and access control lists. Finally, it discusses cryptography and steganography as the main techniques used to implement security goals.