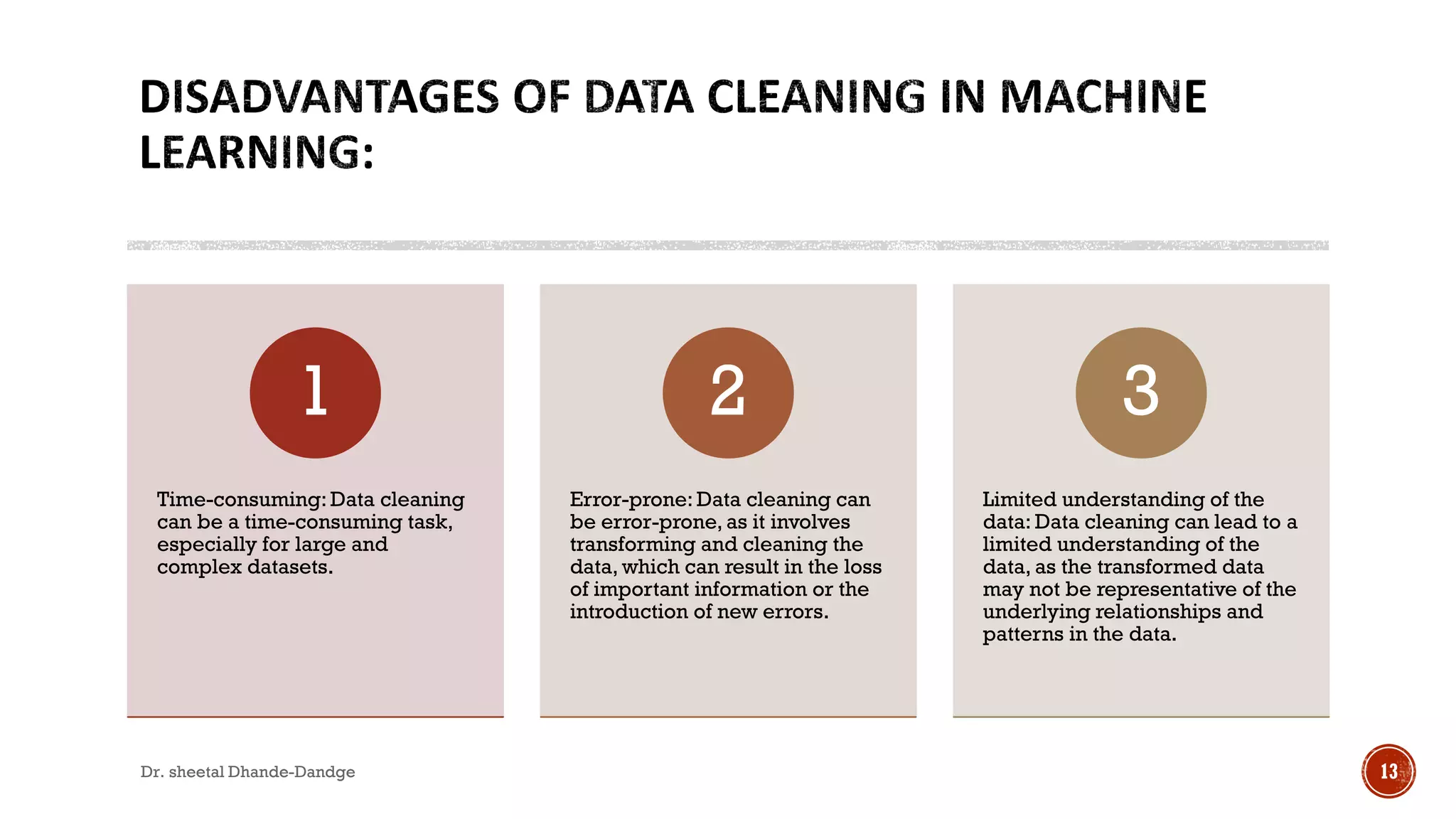
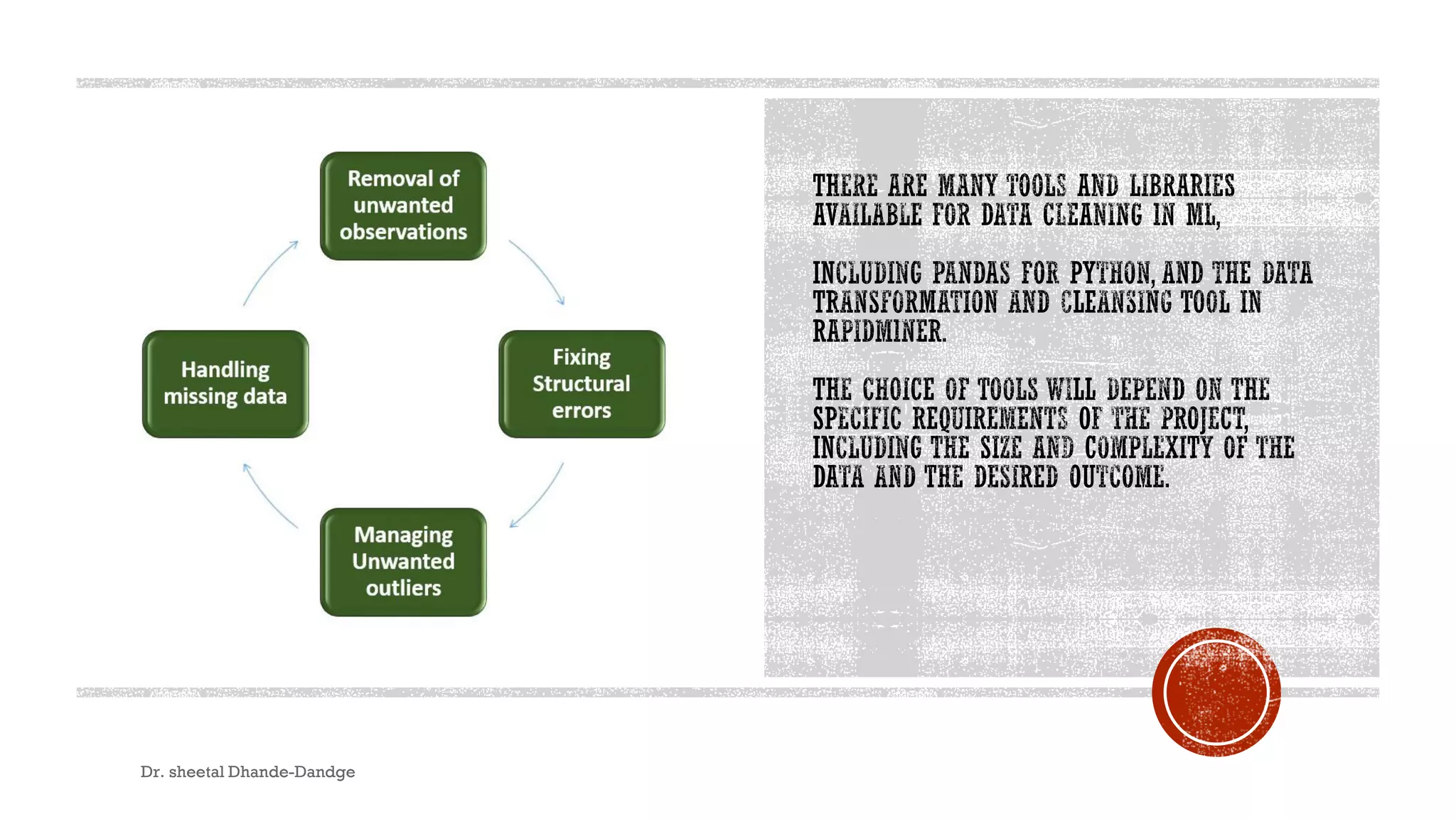
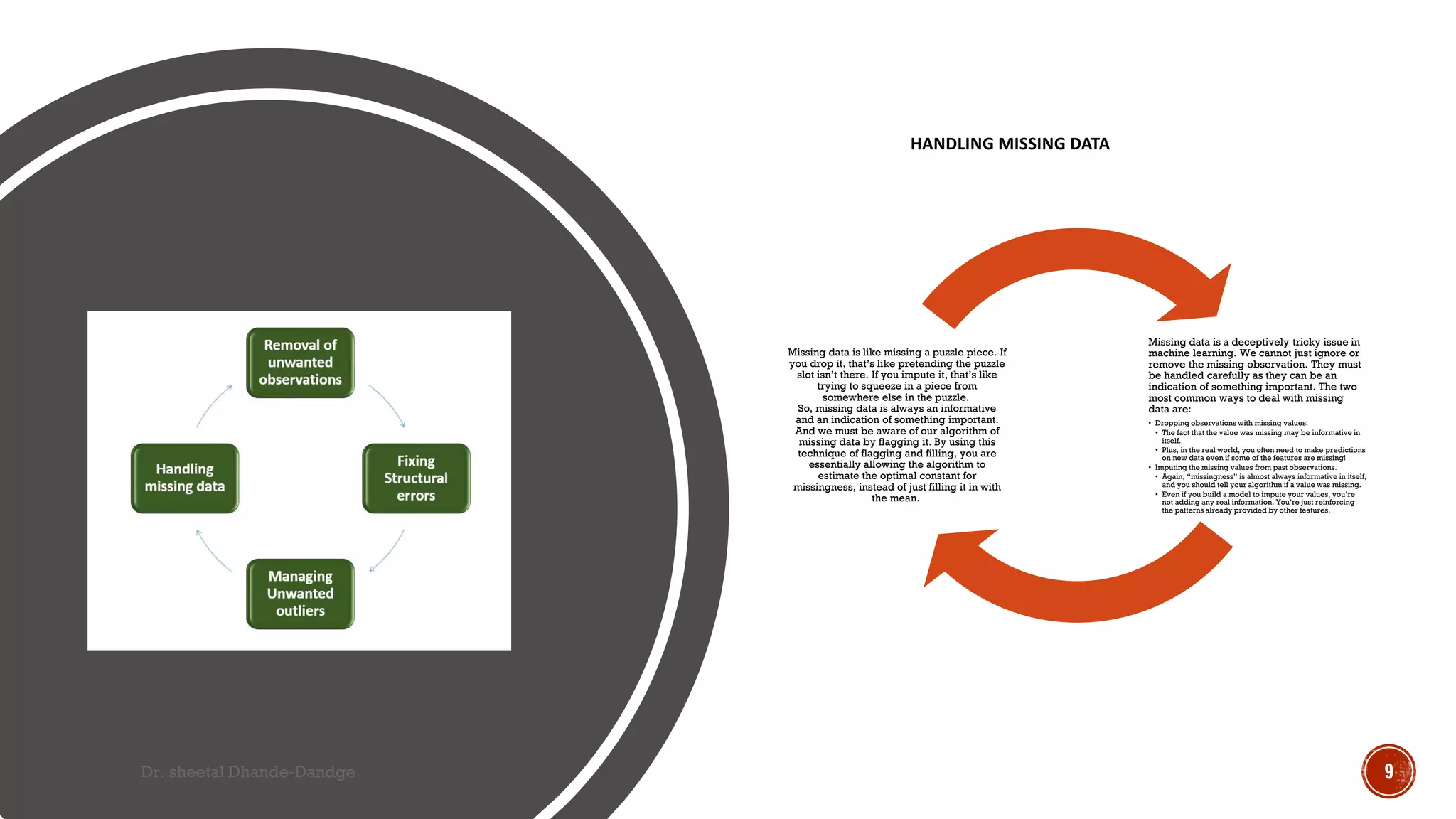
Data cleaning is a vital process in machine learning that ensures data accuracy and consistency, directly impacting model performance. It involves steps such as handling missing data, removing duplicates, correcting errors, and addressing outliers. While crucial, data cleaning can be time-consuming and may lead to errors if not conducted carefully, emphasizing the need for a systematic approach.








![ Here is a simple example of data cleaning in Python:
import pandas as pd
# Load the data
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv")
# Drop rows with missing values
df = df.dropna()
# Remove duplicate rows
df = df.drop_duplicates()
# Remove unnecessary columns
df = df.drop(columns=["col1", "col2"])
# Normalize numerical columns
df["col3"] = (df["col3"] - df["col3"].mean()) / df["col3"].std()
# Encode categorical columns
df["col4"] = pd.get_dummies(df["col4"])
# Save the cleaned data
df.to_csv("cleaned_data.csv", index=False)
The code I provided does not have any explicit output statements, so it
will not produce any output when it is run. Instead, it modifies the data
stored in the df DataFrame and saves it to a new CSV file.
If you want to see the cleaned data, you can print the df DataFrame or
read the saved CSV file. For example, you can add the following line at the
end of the code to print the cleaned data:
print(df)
Dr. sheetal Dhande-Dandge 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overviewofdatacleaning-230227115557-6514a4b9/75/Overview-of-Data-Cleaning-pdf-11-2048.jpg)