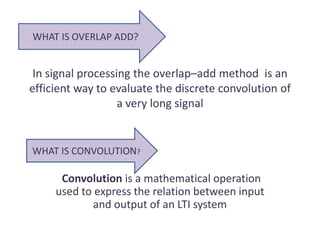
The overlap-add method is an efficient way to evaluate the discrete convolution of long signals using short blocks. It involves breaking the long signals into shorter blocks, zero-padding the blocks, convolving them, and adding the results. For example, an input signal of length N is broken into blocks of length M, with M-1 zeros added to each block. The blocks are convolved with the impulse response and added to produce the final output. This method was used to convolve an example input signal of length 10 with an impulse response of length 3.


![STEPS FOR OVERLAP ADD
METHOD
5
STEP-1:
Determine length ‘M’, which is the length of the
impulse response data sequences i.e. h[n] &
determine ‘M-1’.
STEP-2:
Given input sequence x[n] size is ‘N’. let assume,
N=5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-5-320.jpg)
![6
STEP-3:
Determine the length of the new data,
‘L’
STEP-4:
Pad ‘M-1’ zeros to xk[n]
Pad ‘L-1’ zeros to h[n]
xk[n] ‘M-1’ zeros
h[n] ‘L-1’ zeros](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-6-320.jpg)
![7
Input Data Sequence x[n]
x1[n]
x2[n]
x4[n]
x3[n]
M-1 zeros
M-1 zeros
M-1 zeros
M-1 zeros
L L L L](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-7-320.jpg)
![8
STEP-4:
Perform Convolution of h[n] & blocks of x[n]
i.e. y1[n]= x1[n]
y2[n]= x2[n]
y3[n]= x3[n]
y4[n]= x4[n]
N
N
h[n]
h[n]
N h[n]
h[n]
N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-8-320.jpg)
![9
y1[n]
y2[n]
y4[n]
y3[n]
M-1 data
M-1 data
M-1 data
Final Output Data Sequence y[n]
M-1 data
add
add
add](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-9-320.jpg)
![10
& h[n]={1,1,1}Ques. Given x[n]={3,-1,0,1,3,2,0,1,2,1}
Let, N=5
Length of h[n], M= 3
Therefore, M-1= 2
We know,
N=(L+M-1)
5=L+3-1
L=3
∴Pad L-1=2 zeros with h[n] i.e. h[n]={1,1,1,0,0}
SOLVED EXAMPLE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-10-320.jpg)
![11
3 -1 0 1 3 2 0 1 2 1
0 1 2
x2[n]
x4[n]
x3[n]
M-1(=2) no. of zeros
L(=3) no. of new data
3 -1 0 0 0
1 3 2 0 0
Input sequence x[n]
x1[n]
1 0 0 0 0
0 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-11-320.jpg)
![12
Performing yk[n]= xk[n] h[n], where k=1,2,3,4
1. y1[n]=
2. y2[n]=
3. y3[n]=
4. y4[n]=
{3,2,2,-1,0}
{1,4,6,5,2}
{0,1,3,3,2}
{1,1,1,0,0}
N](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-12-320.jpg)
![1 4 6 5 2
0 1
1 1 1 0 0
+=> add
n- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
3 2 2 -1 0
+ +
++
3 3 2
+ +
y[n] 3 2 2
30](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-13-320.jpg)
![1 4 6 5 2
0 1
1 1 1 0 0
+=> add
n- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
3 2 2 -1 0
+ +
++
3 3 2
+ +
y[n] 3 2 2 0 4 6
31](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-14-320.jpg)
![1 4 6 5 2
0 1
1 1 1 0 0
+=> add
n- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
3 2 2 -1 0
+ +
++
3 3 2
+ +
y[n] 3 2 2 0 4 6 5 3 3
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-15-320.jpg)
![1 4 6 5 2
0 1
1 1 1 0 0
+=> add
n- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
3 2 2 -1 0
+ +
++
3 3 2
+ +
y[n] 3 2 2 0 4 6 5 3 3 4 3
33](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-16-320.jpg)
![1 4 6 5 2
0 1
1 1 1 0 0
+=> add
n- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
3 2 2 -1 0
+ +
++
3 3 2
+ +
y[n] 3 2 2 0 4 6 5 3 3 4 3 1 0 0
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-17-320.jpg)
![1 4 6 5 2
0 1
1 1 1 0 0
+=> add
n- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
y1[n]
3 2 2 -1 0
+ +
++
3 3 2
+ +
y[n] 3 2 2 0 4 6 5 3 3 4 3 1 0 0
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/overlapadd-190423150517/85/Overlapadd-using-convolution-18-320.jpg)
