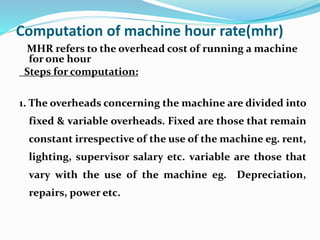
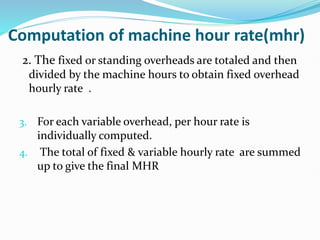
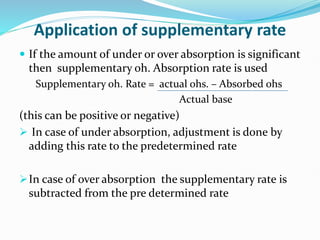
MHR refers to the overhead cost of running a machine for one hour. It is calculated by dividing fixed overheads by machine hours to get the fixed overhead rate, and calculating individual variable overhead rates. The total of fixed and variable rates gives the final MHR. Predetermined overhead rates are estimated in advance for costing, while actual rates are computed after the period. Under or over absorption of overheads can occur with predetermined rates and is treated by a supplementary rate, costing P&L, or carryover to next year.