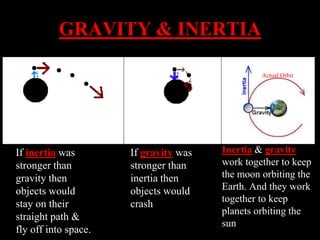
Our Solar System is part of the Milky Way galaxy, which contains billions of stars. The Solar System contains 8 planets that orbit the Sun, including Earth. The 4 inner planets are terrestrial and rocky, while the 4 outer planets are gas giants. Other objects in our Solar System include comets, asteroids, and meteoroids. Comets are icy bodies that develop tails as they near the Sun. Asteroids orbit the Sun in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Meteoroids are smaller pieces of asteroids and become meteors if they enter Earth's atmosphere or meteorites if they reach the ground. Gravity and inertia work together to keep objects like the planets and Moon in orbit around other larger bodies.