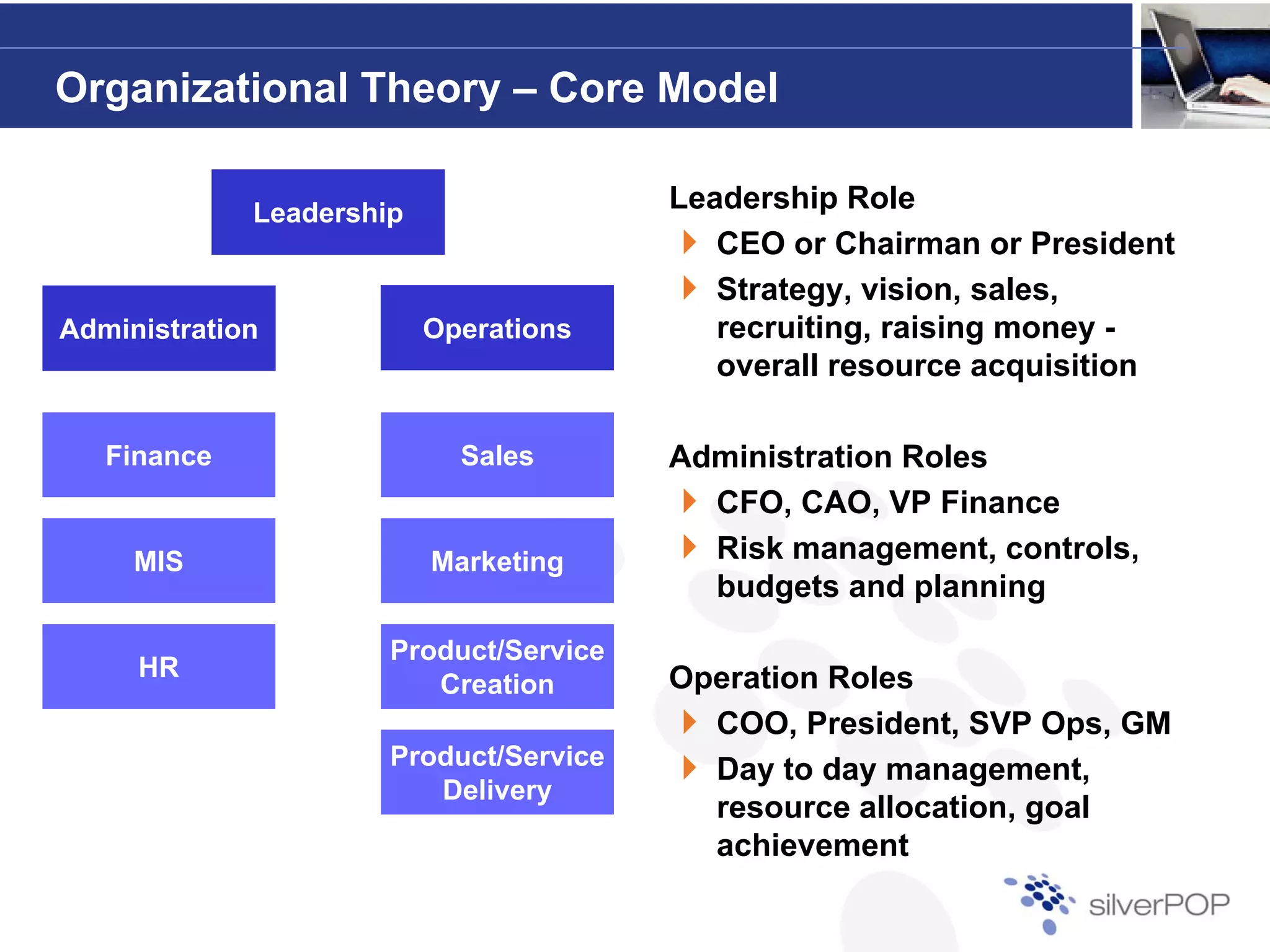
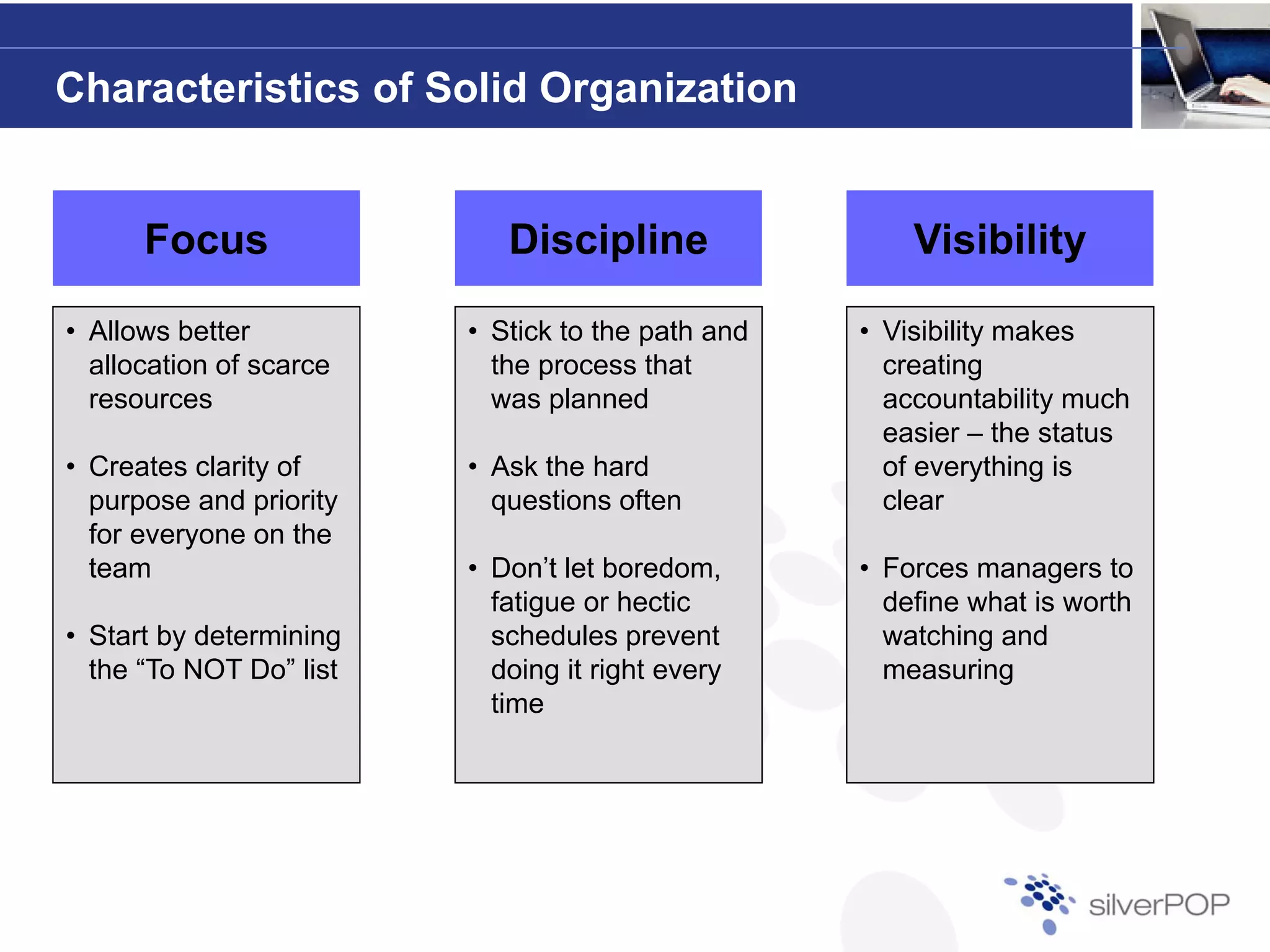
This document discusses the importance of flexibility in startups and how organizational structure should be tailored to each company's specific needs. Key elements to consider when designing an organization include leadership style, risk profile, and growth expectations. It emphasizes that successful organizations must integrate planning, people, processes, and performance management to effectively handle unexpected challenges.