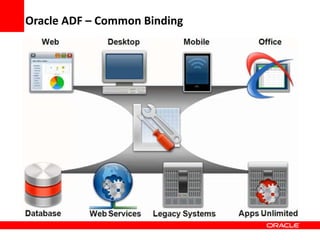
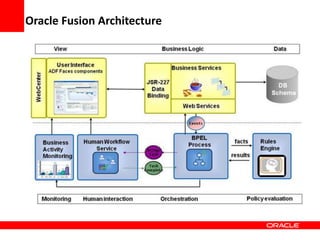
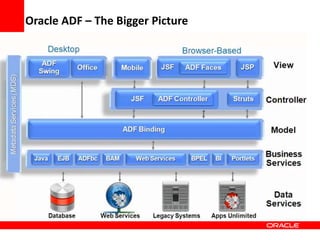
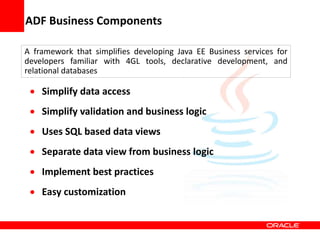
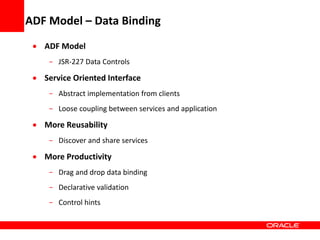
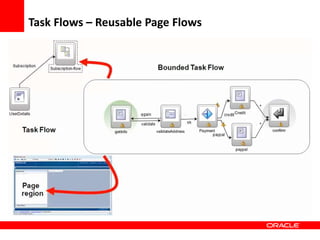
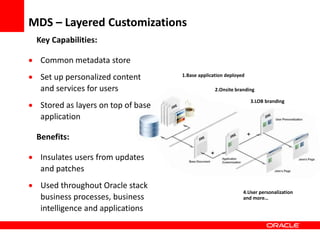
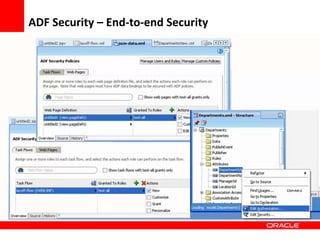
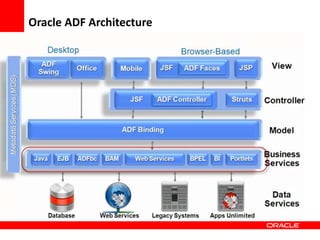
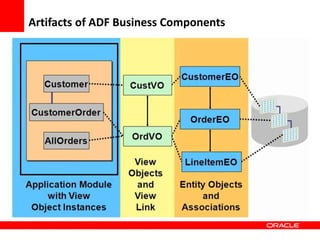
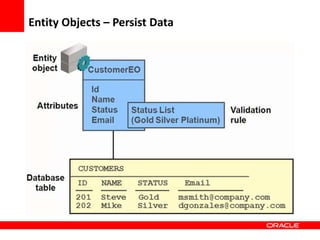
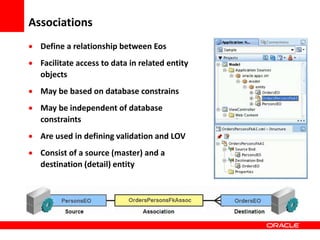
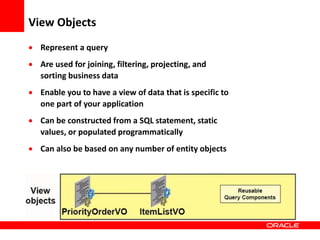
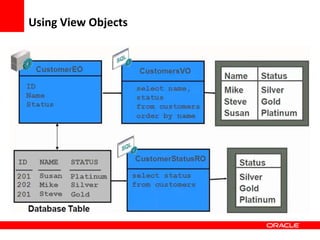
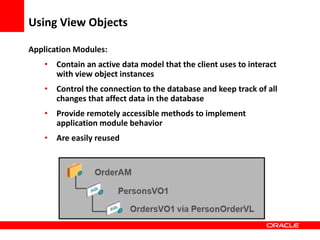
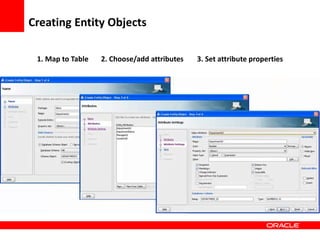
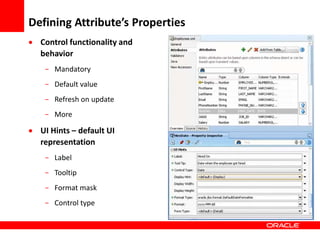
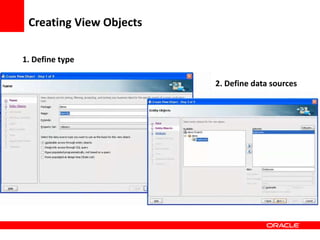
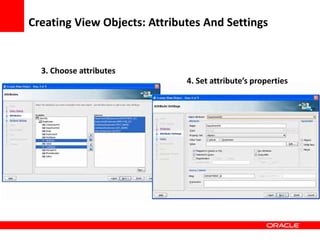
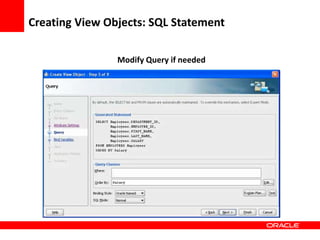
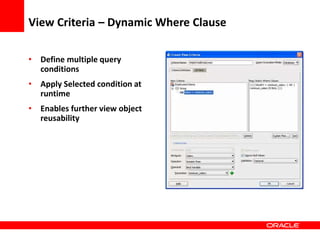
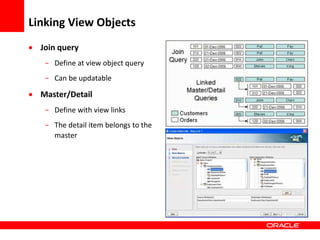
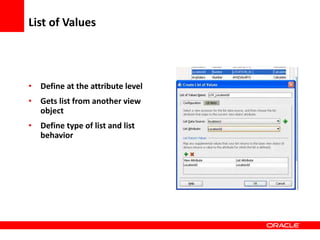
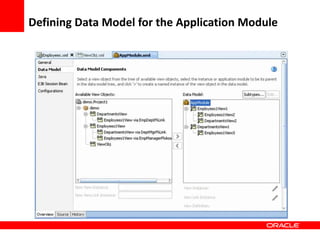
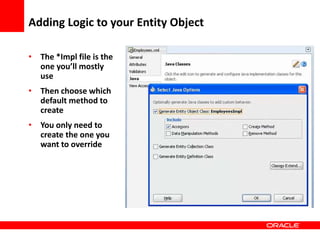
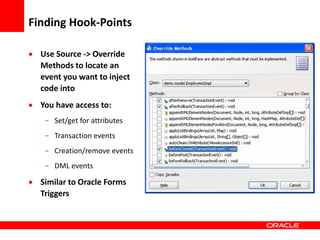
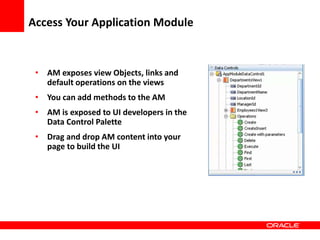
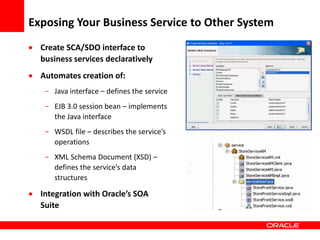
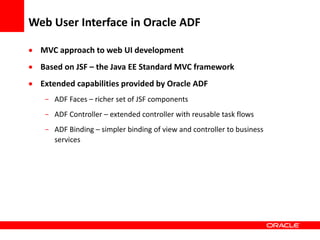
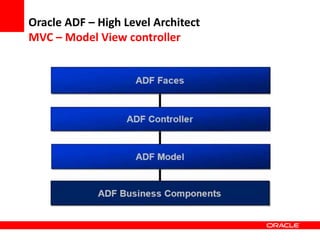
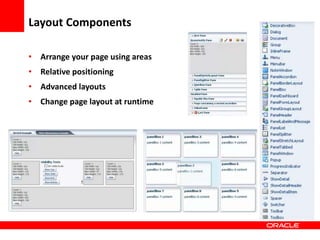
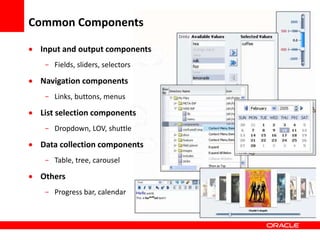
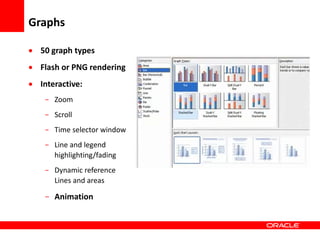
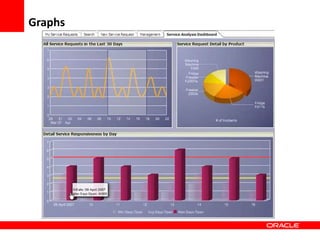
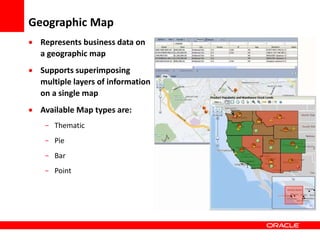
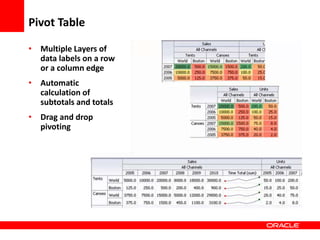
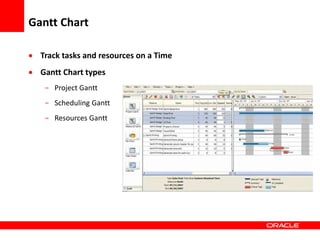
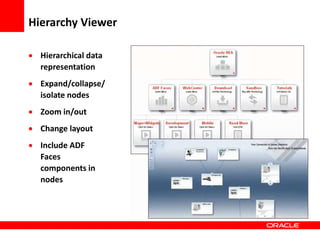
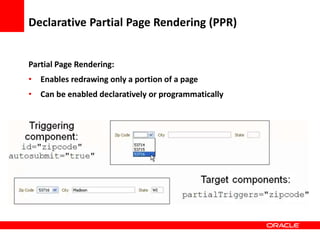
This document provides an overview of Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF). It discusses key capabilities including visual and declarative development, service-oriented architecture, and standards-based development. It describes various ADF artifacts like ADF Faces rich client components, ADF Business Components, ADF Model data binding, and ADF Controller for reusable page flows. The document also discusses how ADF promotes productivity, ease of use, and best practices for application development.