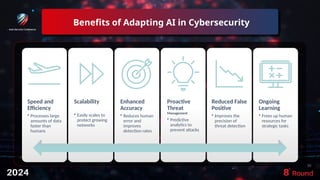
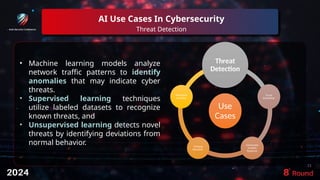
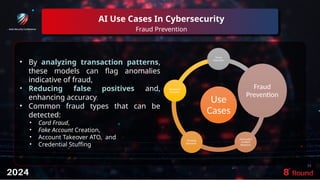
The document discusses the role of artificial intelligence (AI) in enhancing cybersecurity, highlighting its benefits such as improved speed, efficiency, and proactive threat management. It outlines various AI use cases, including threat detection, fraud prevention, and automated incident response, while also addressing concerns like bias and potential misuse. Future recommendations emphasize the need for training, data security, collaboration, and proactive threat mitigation to leverage AI effectively in cybersecurity.