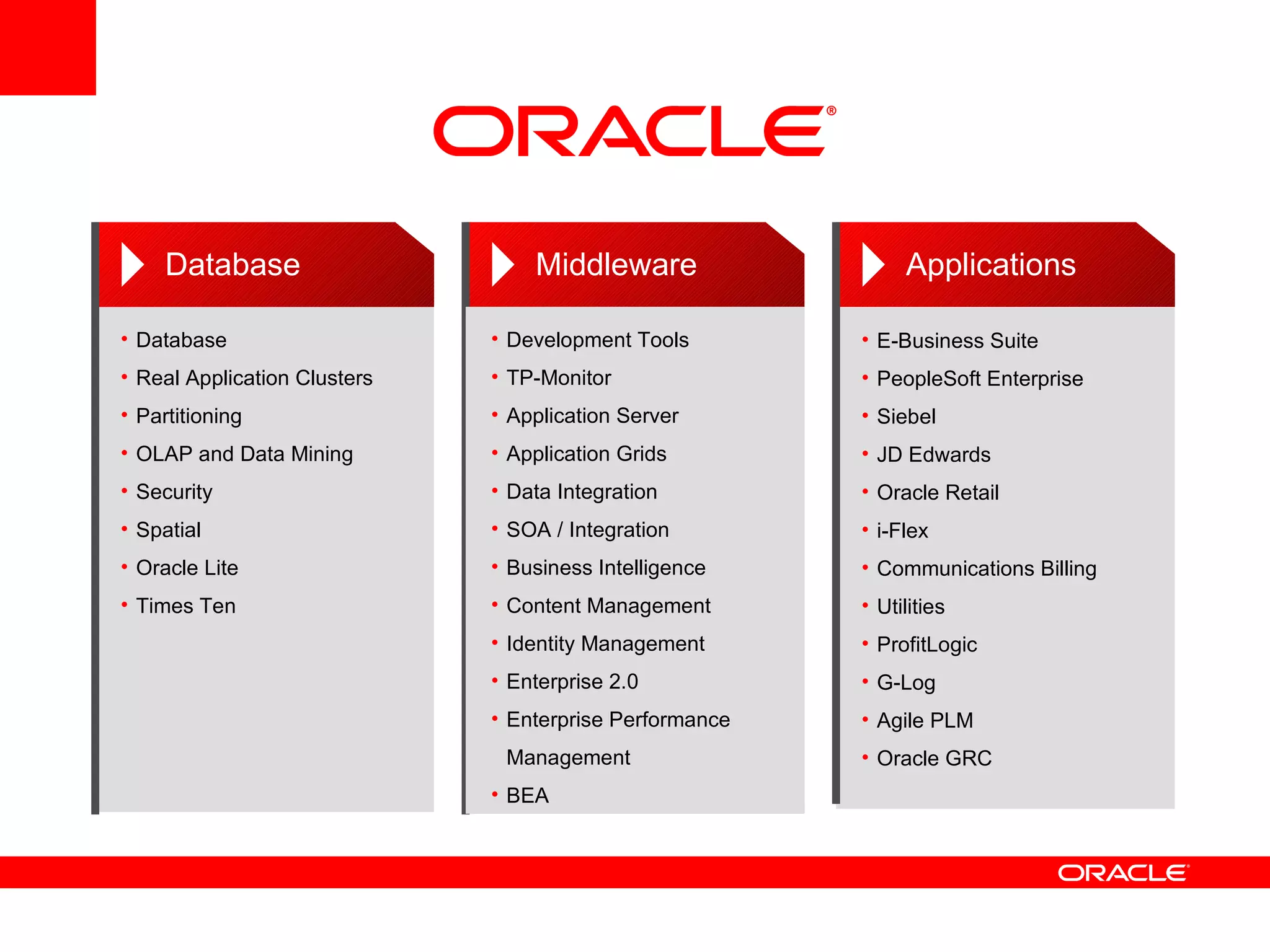
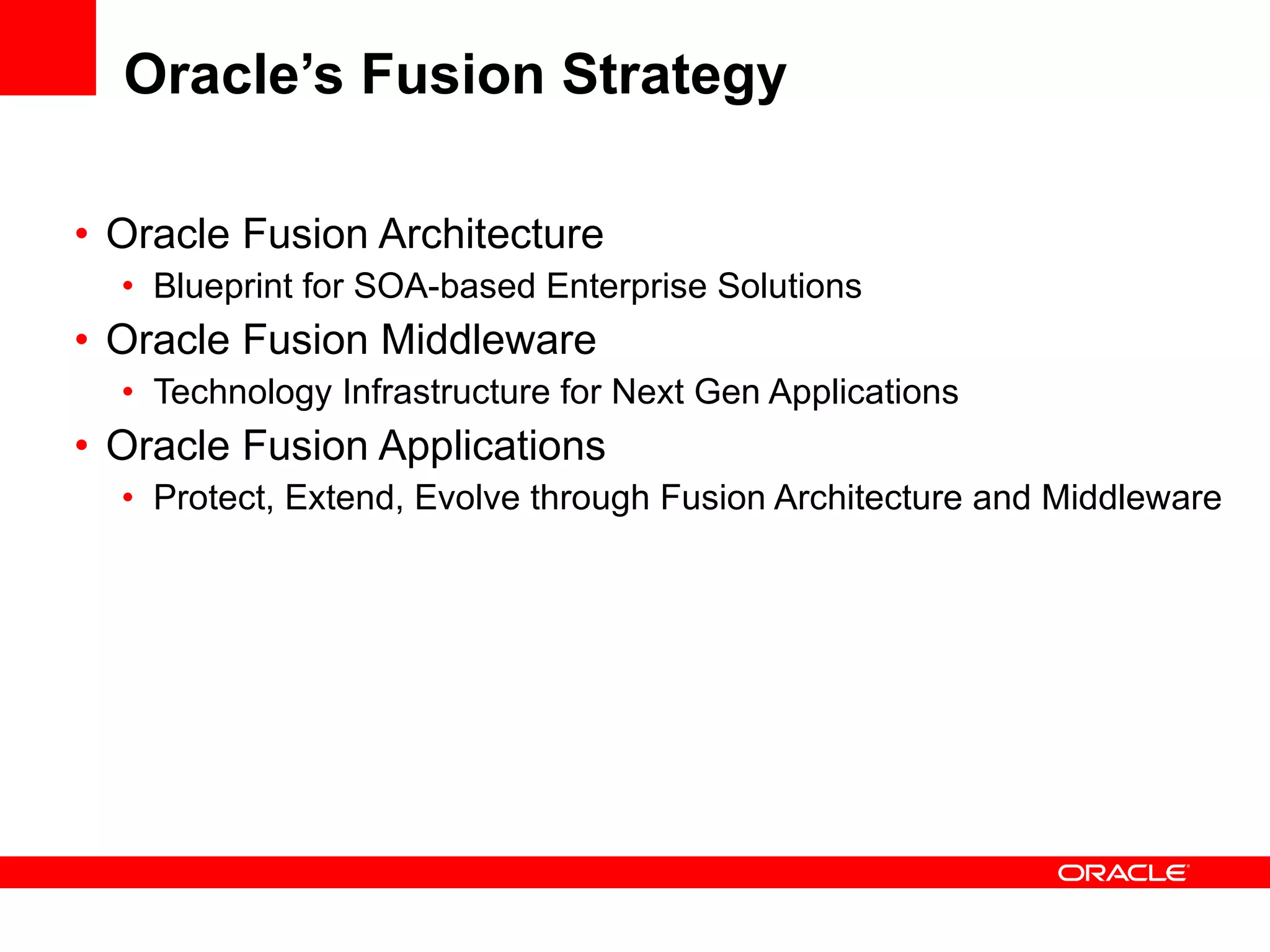
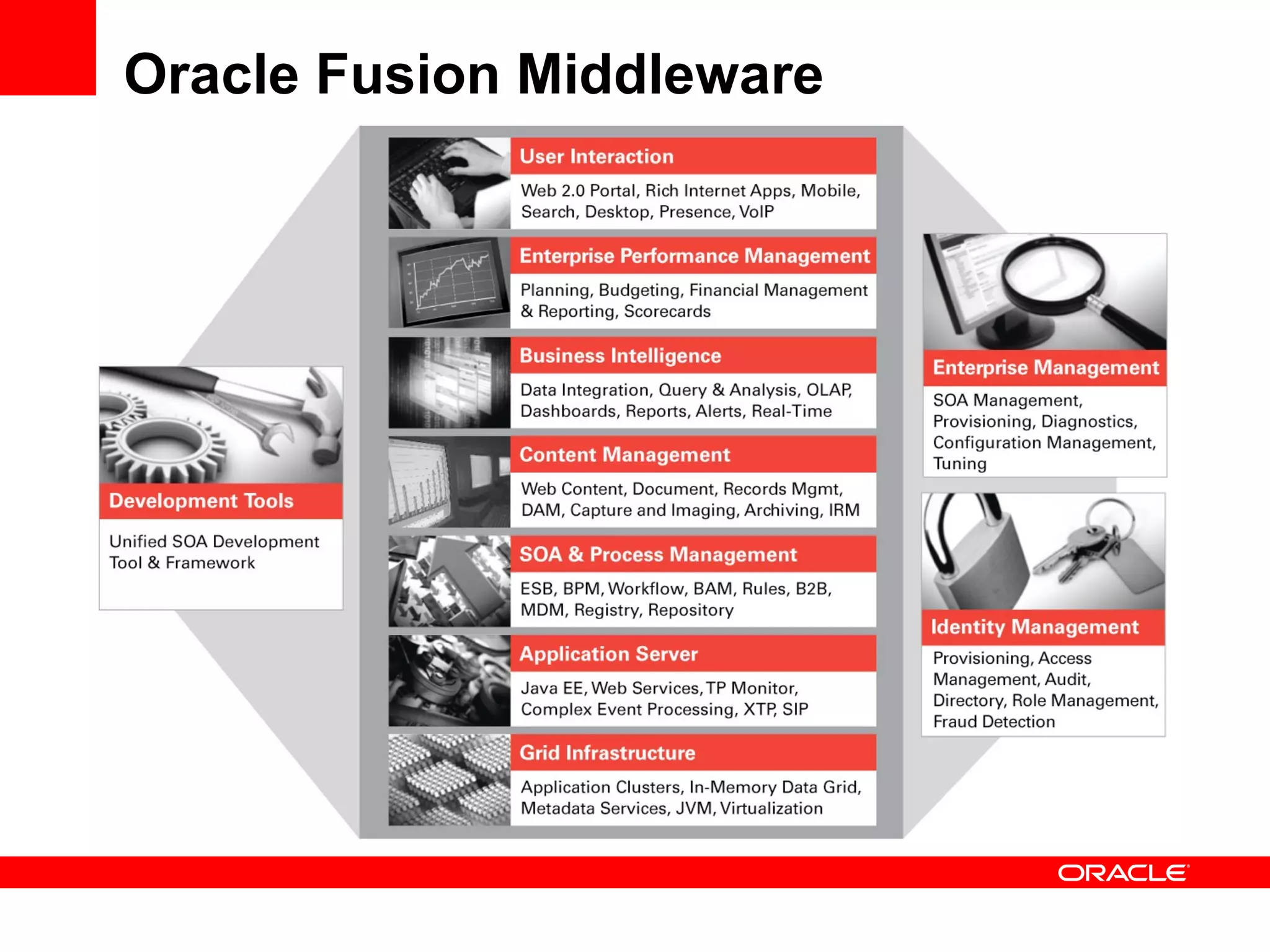
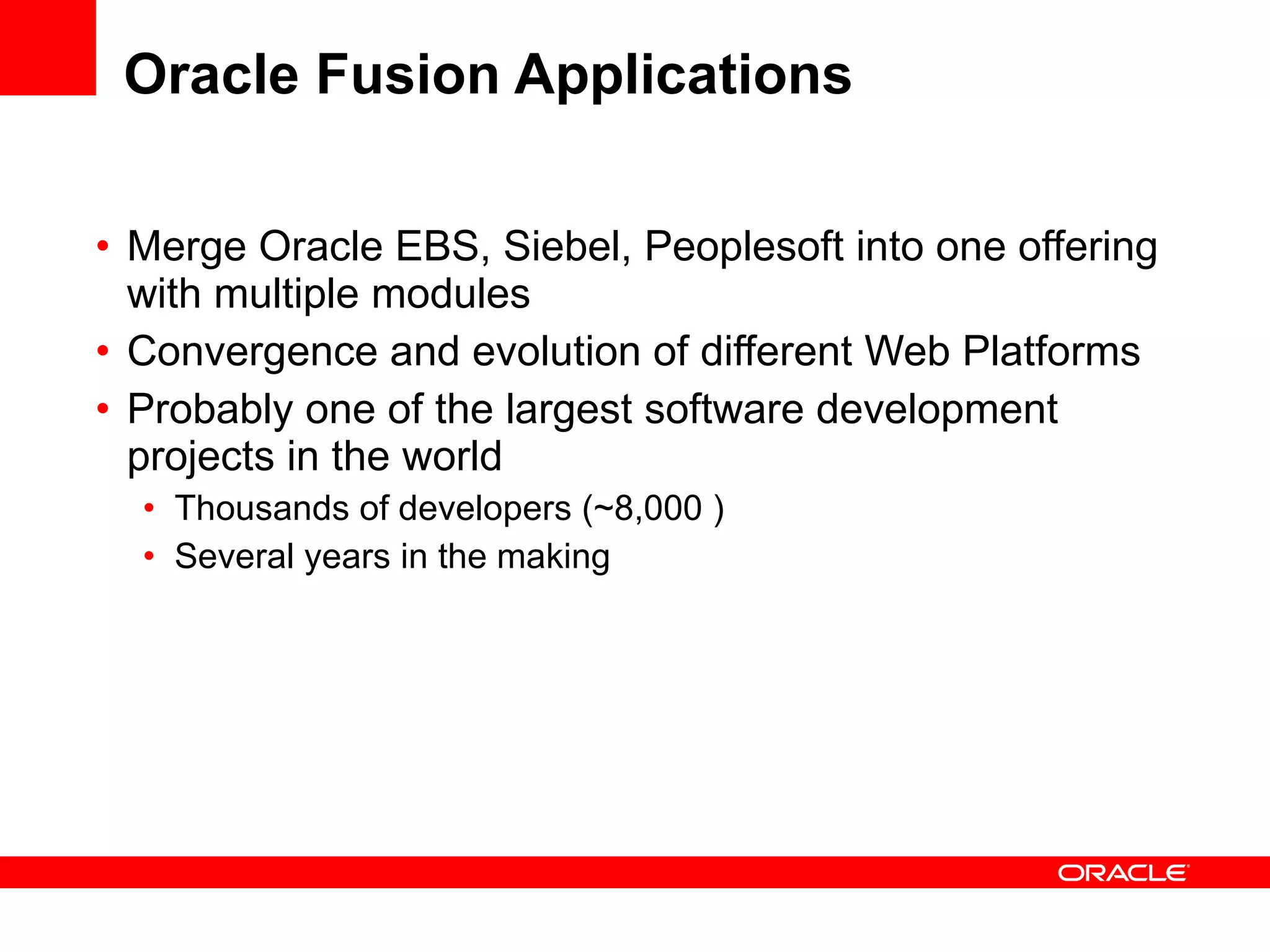
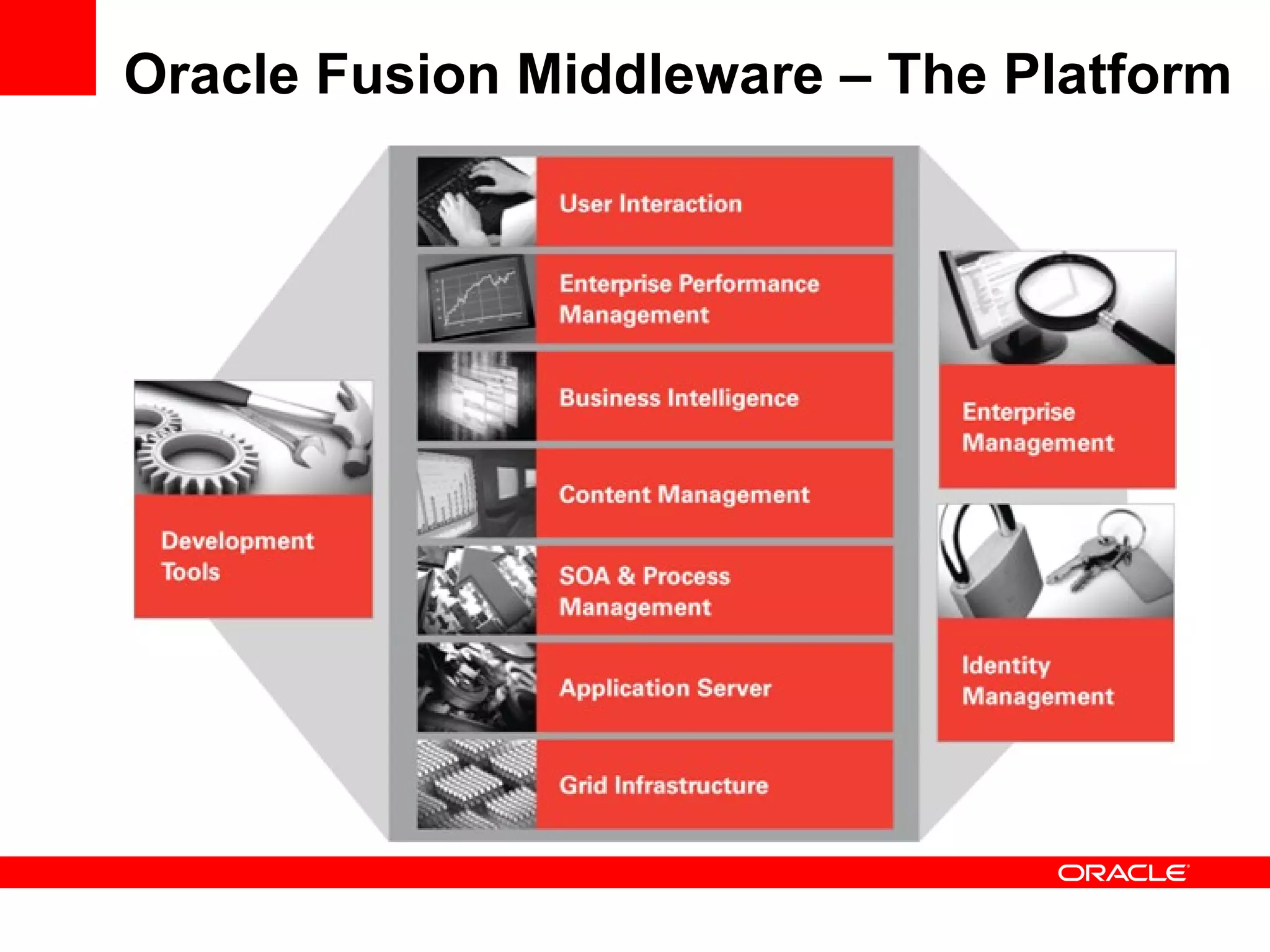
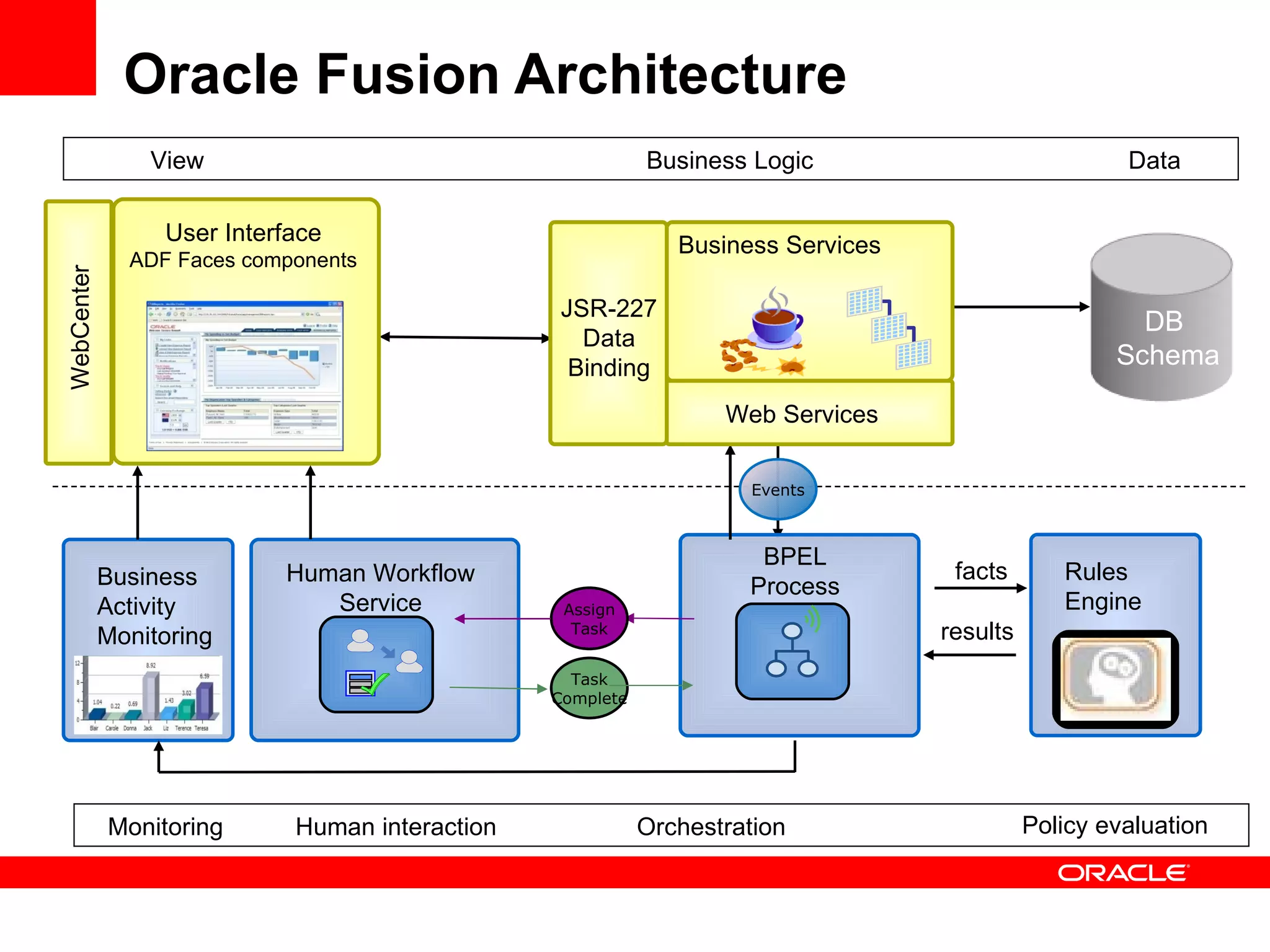
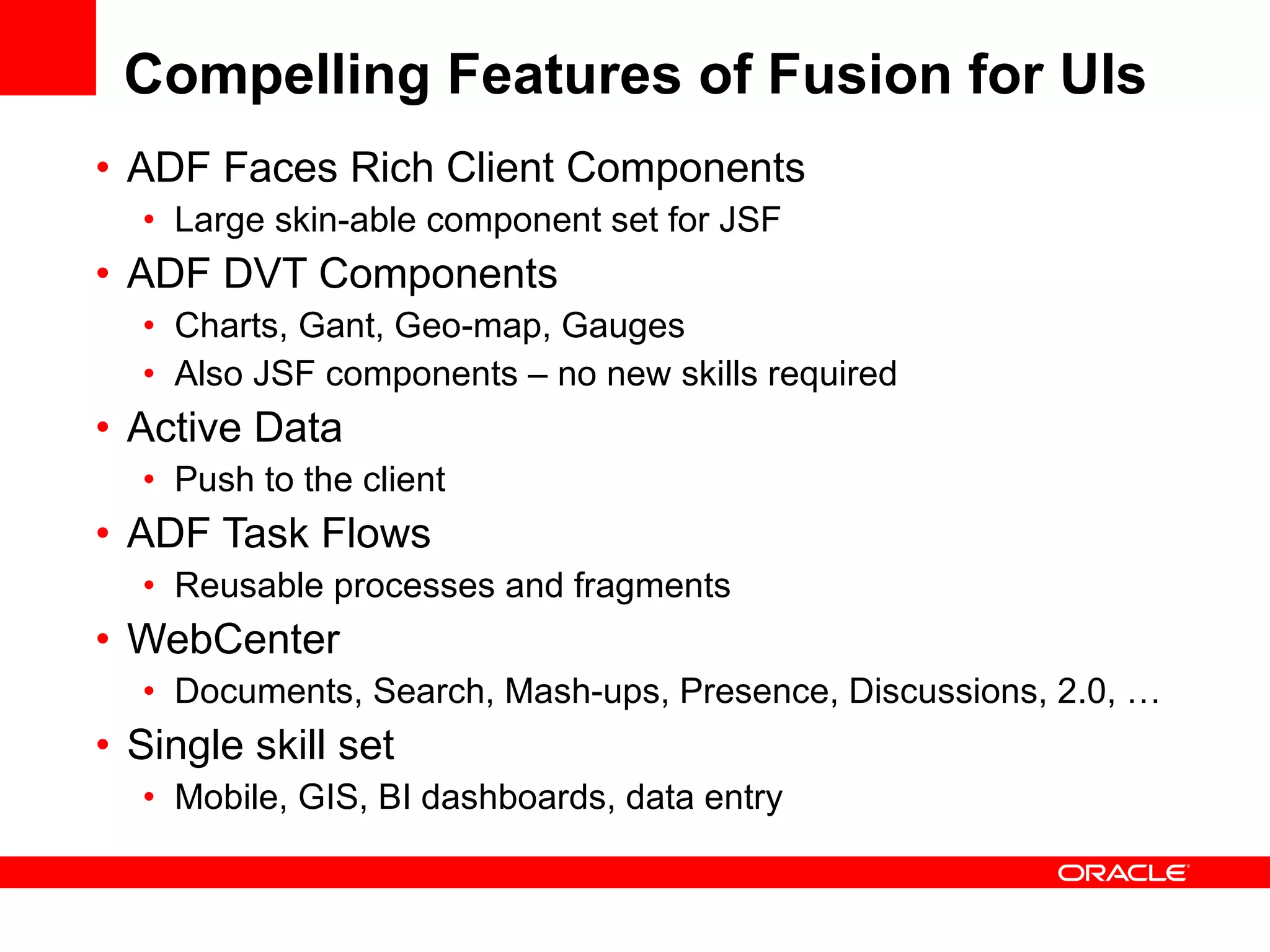
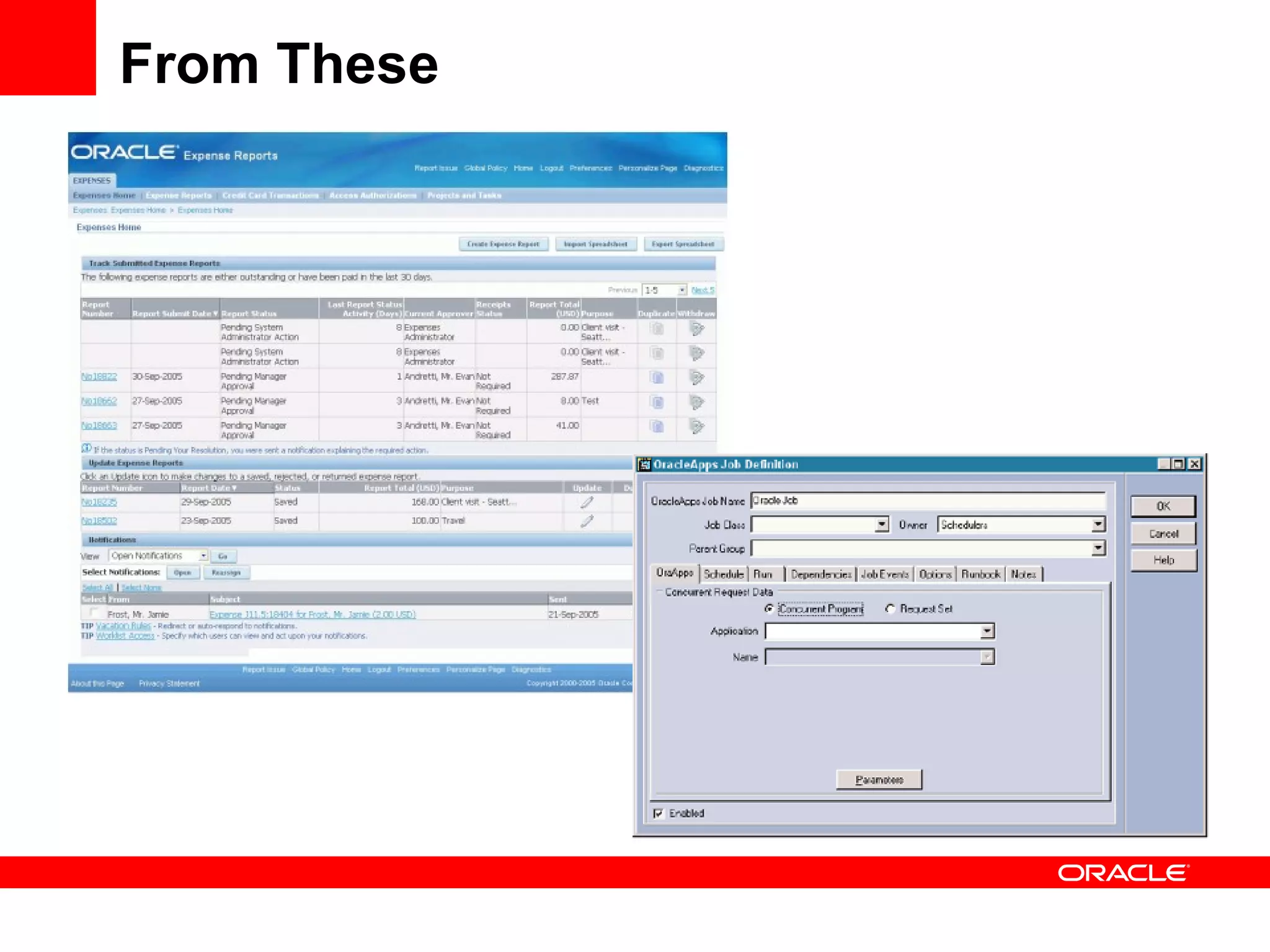
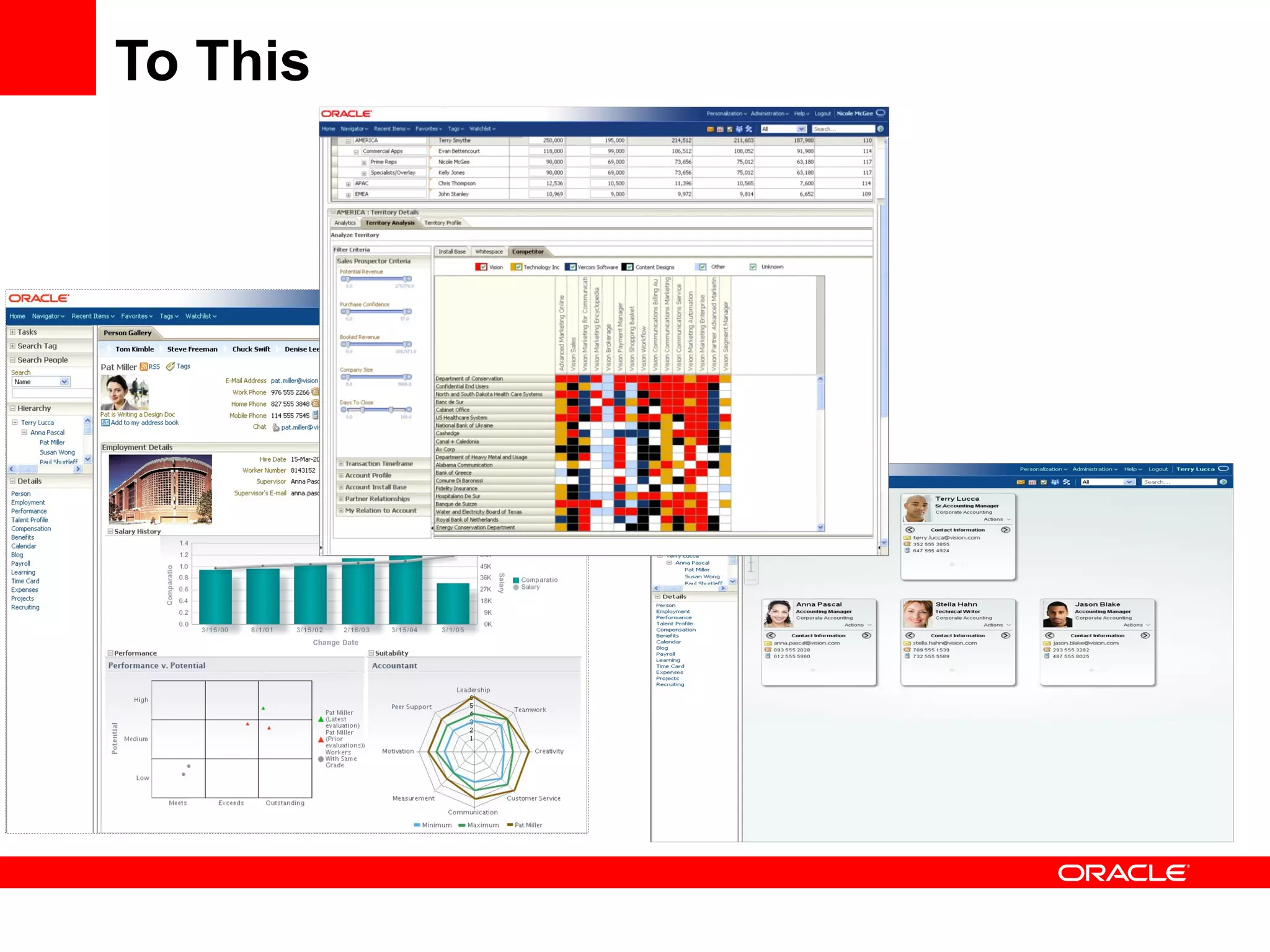
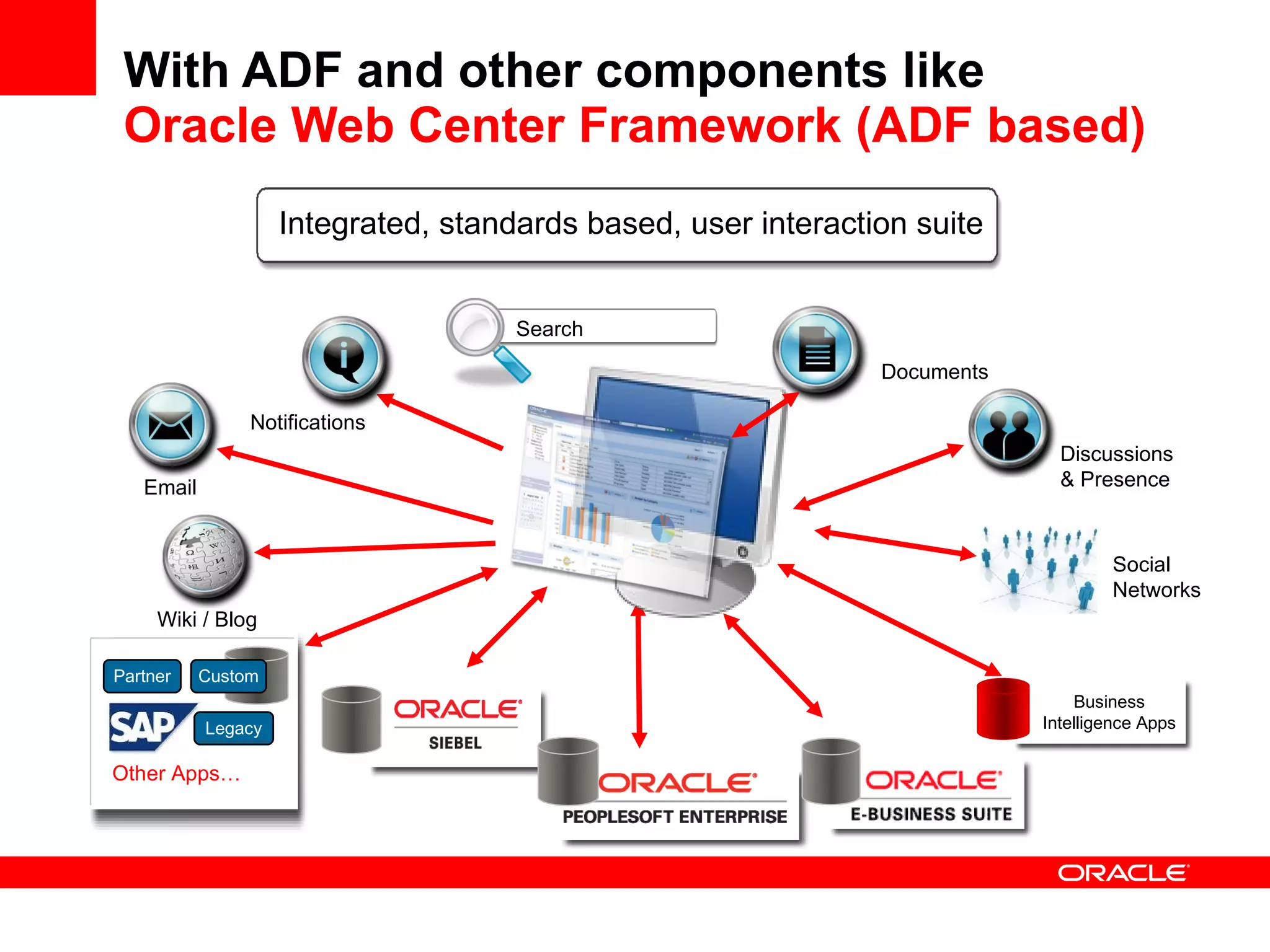
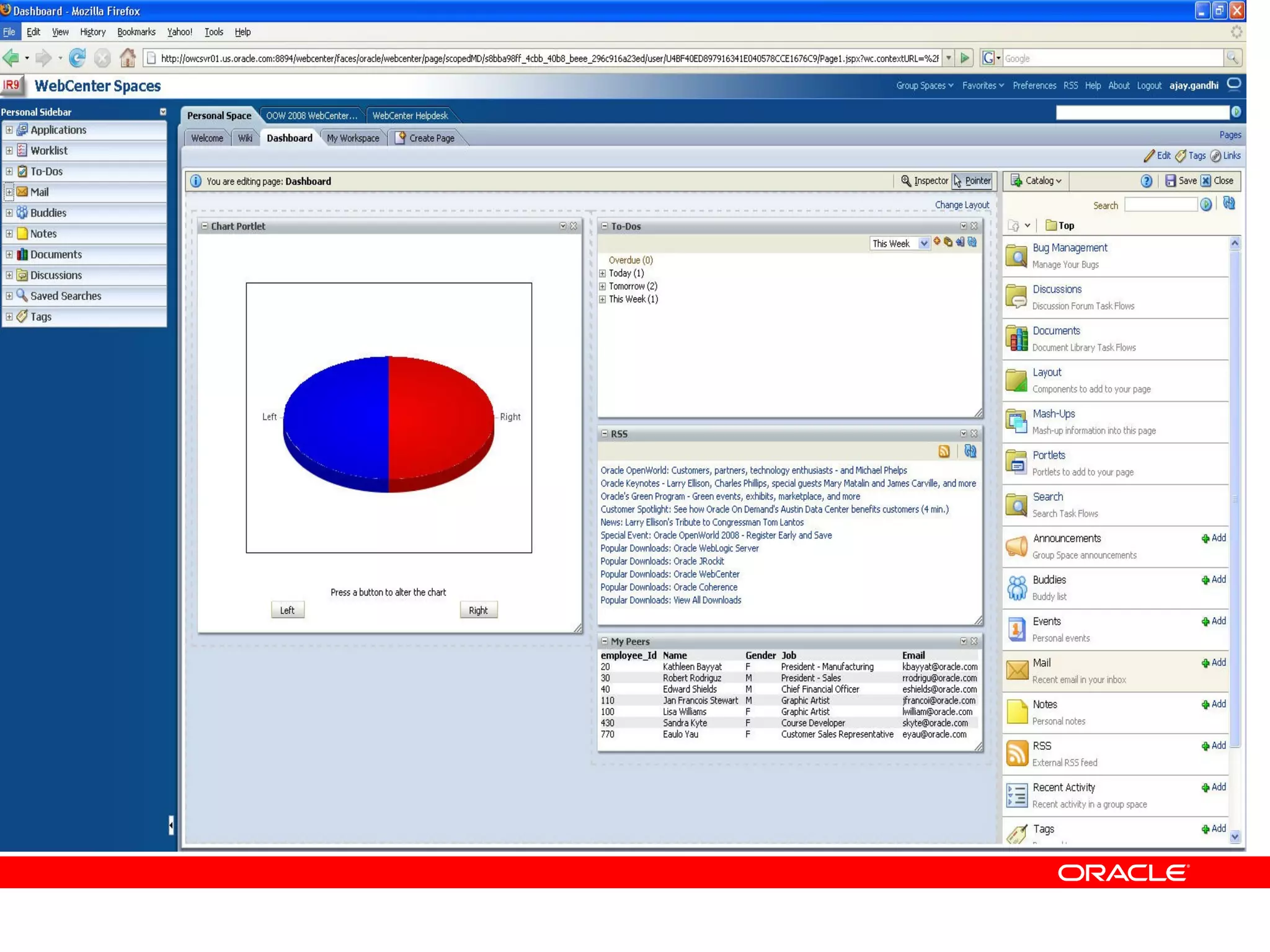
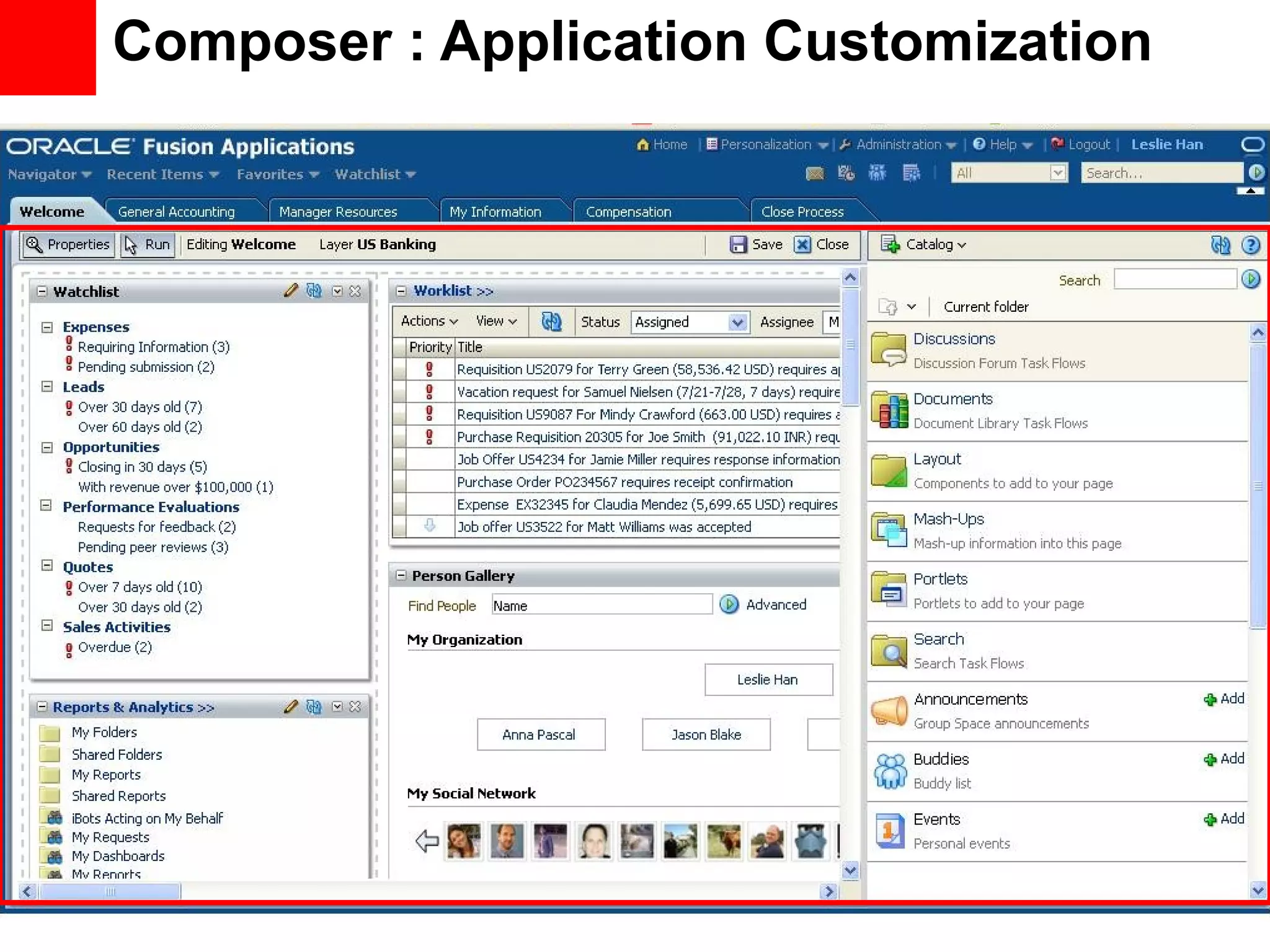
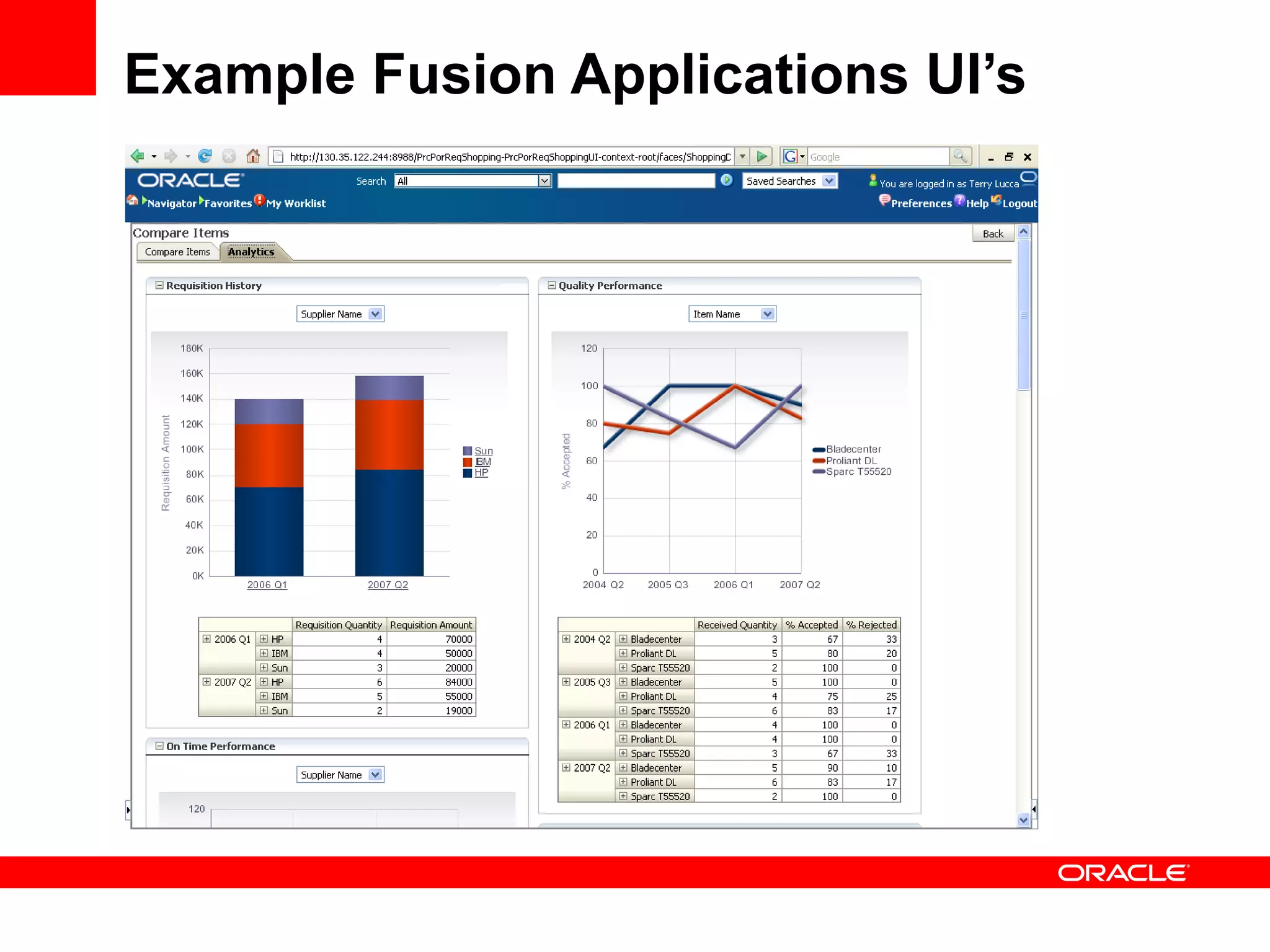
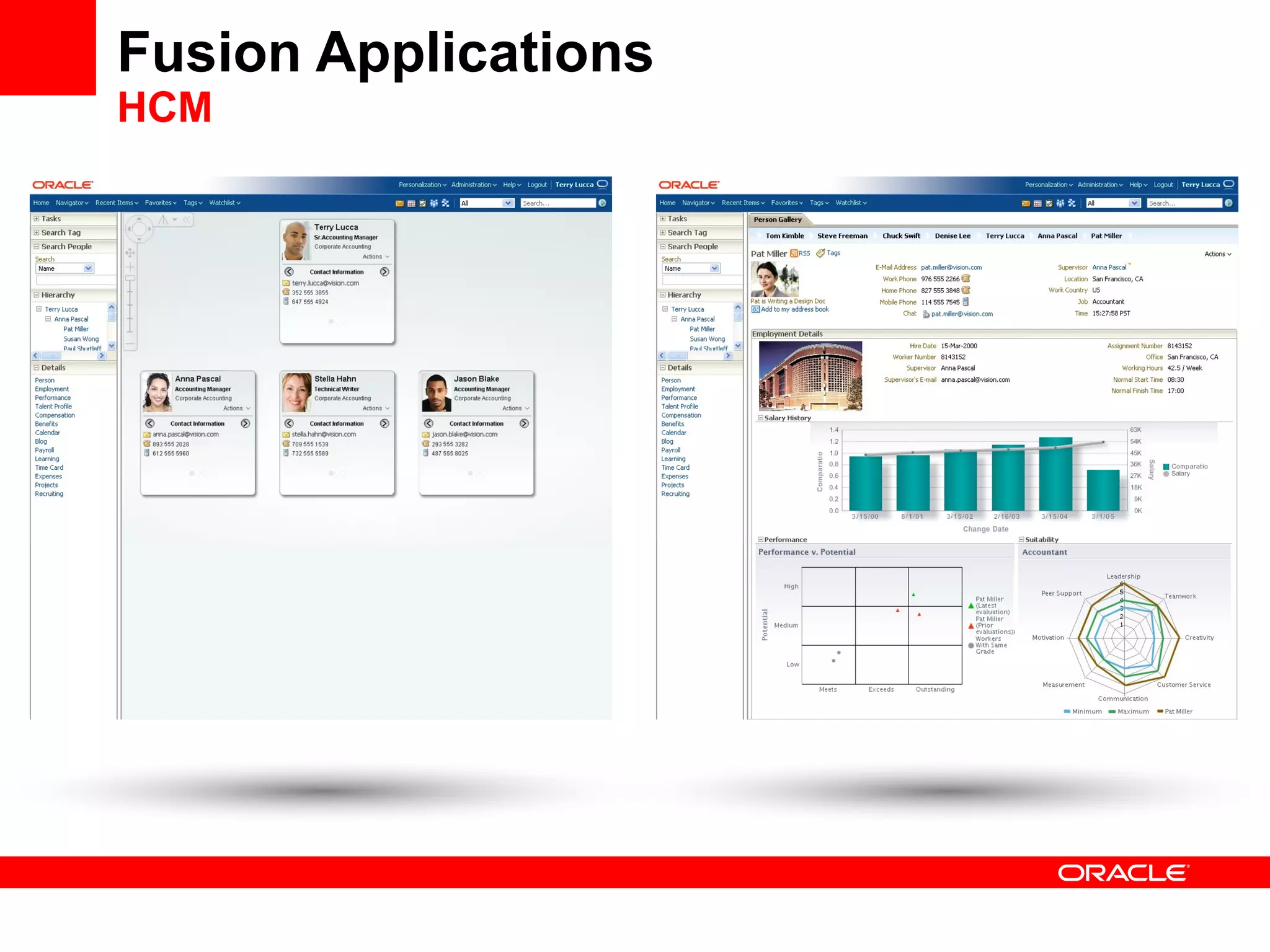
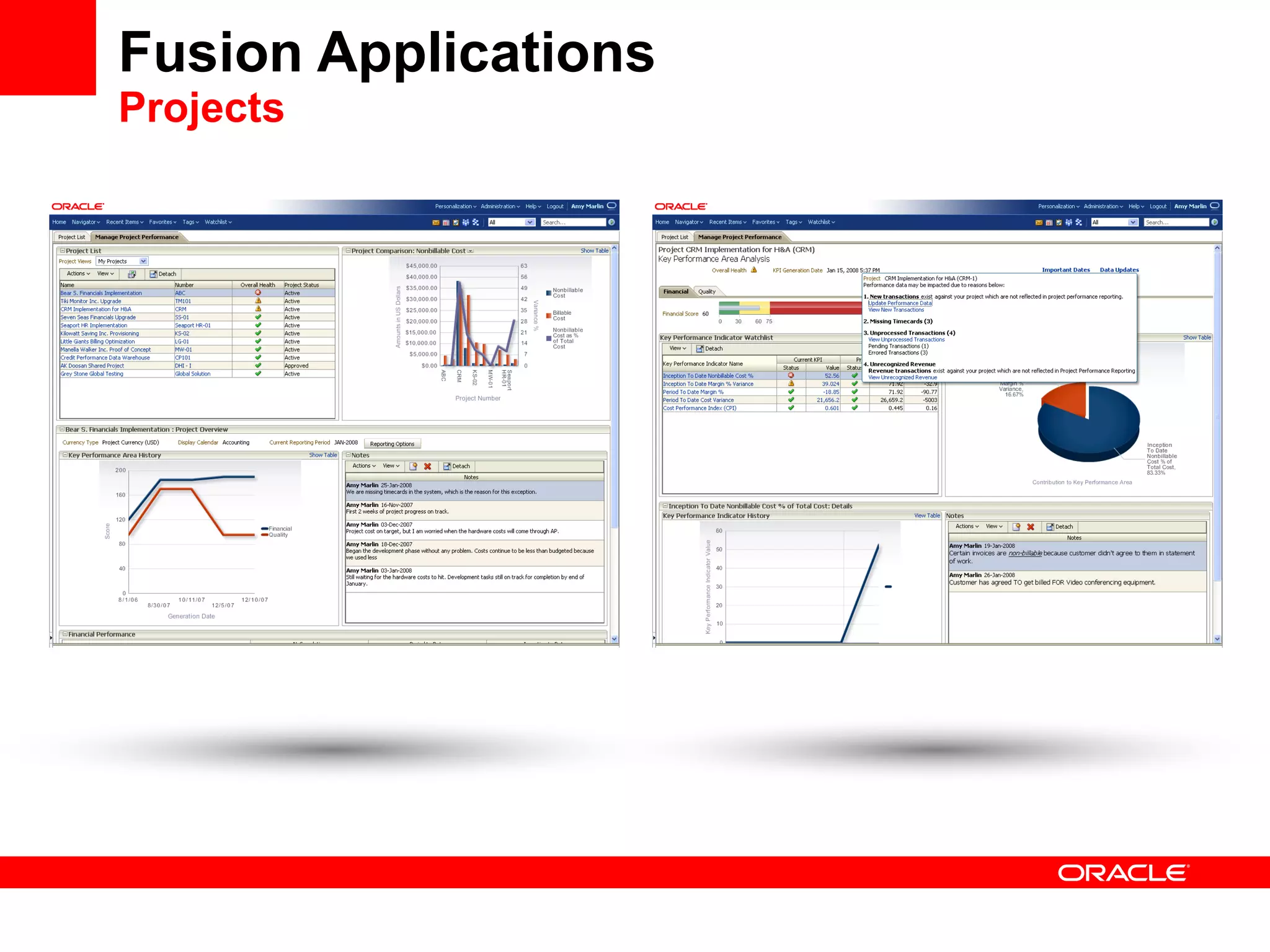
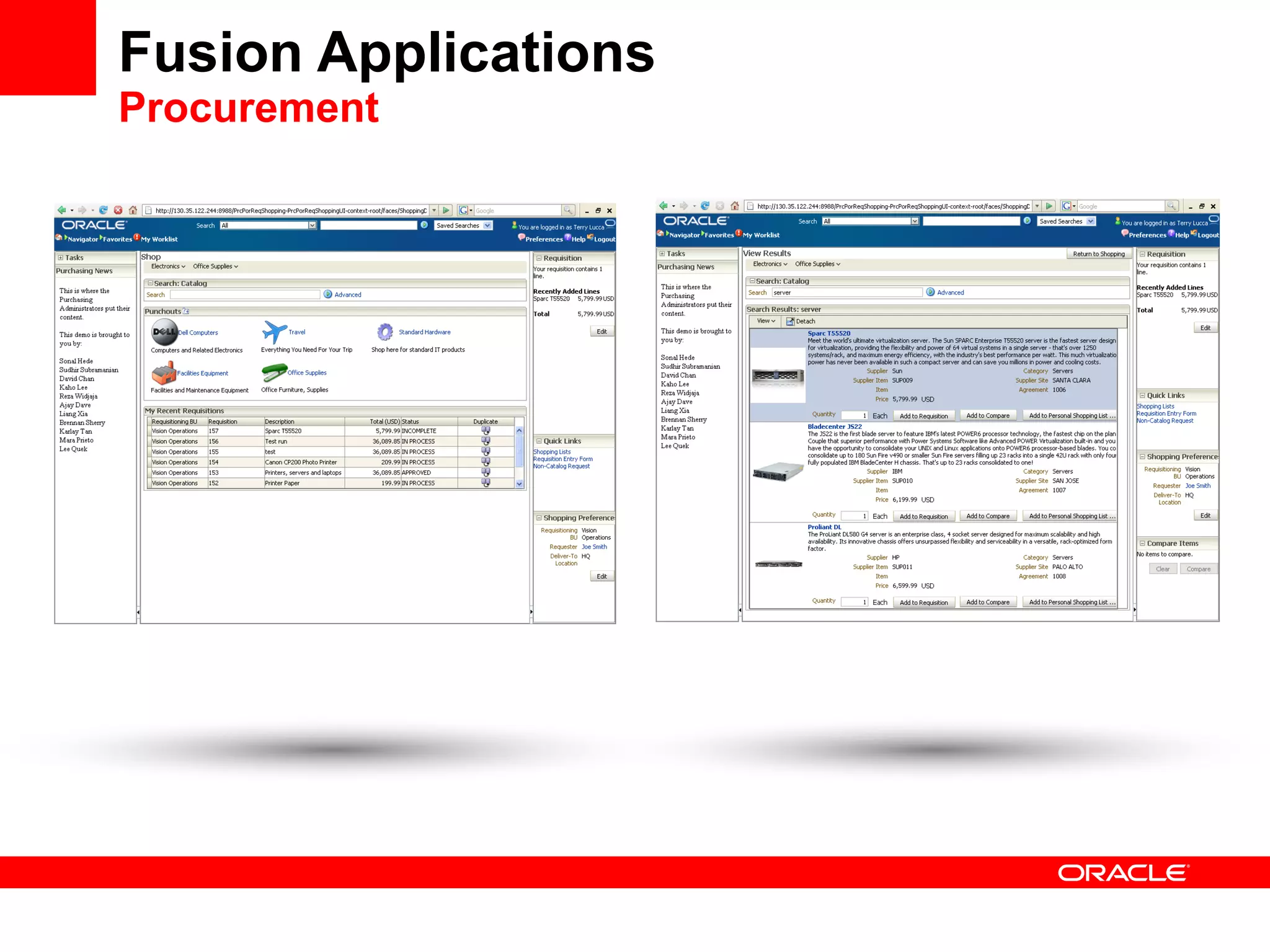
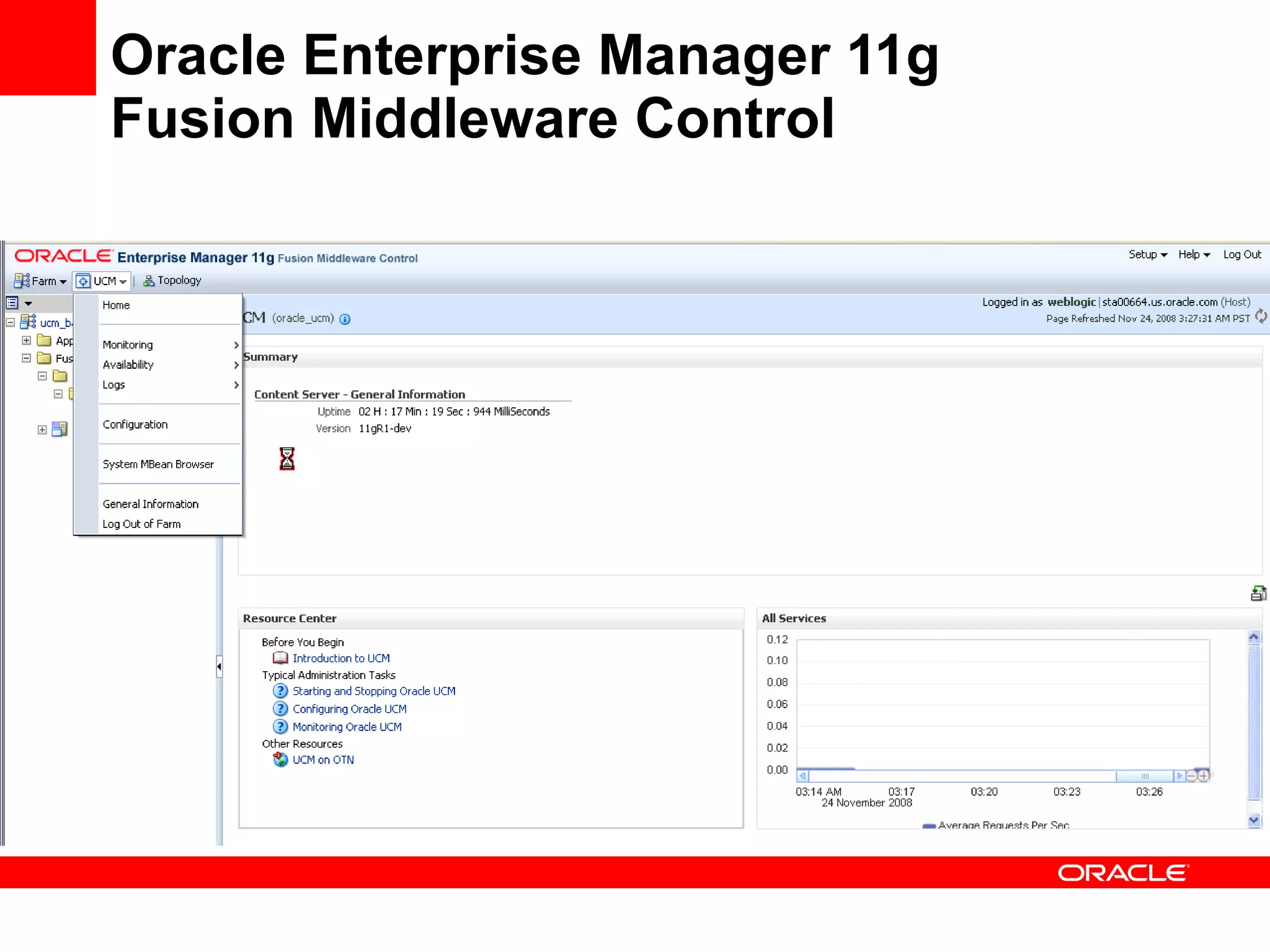
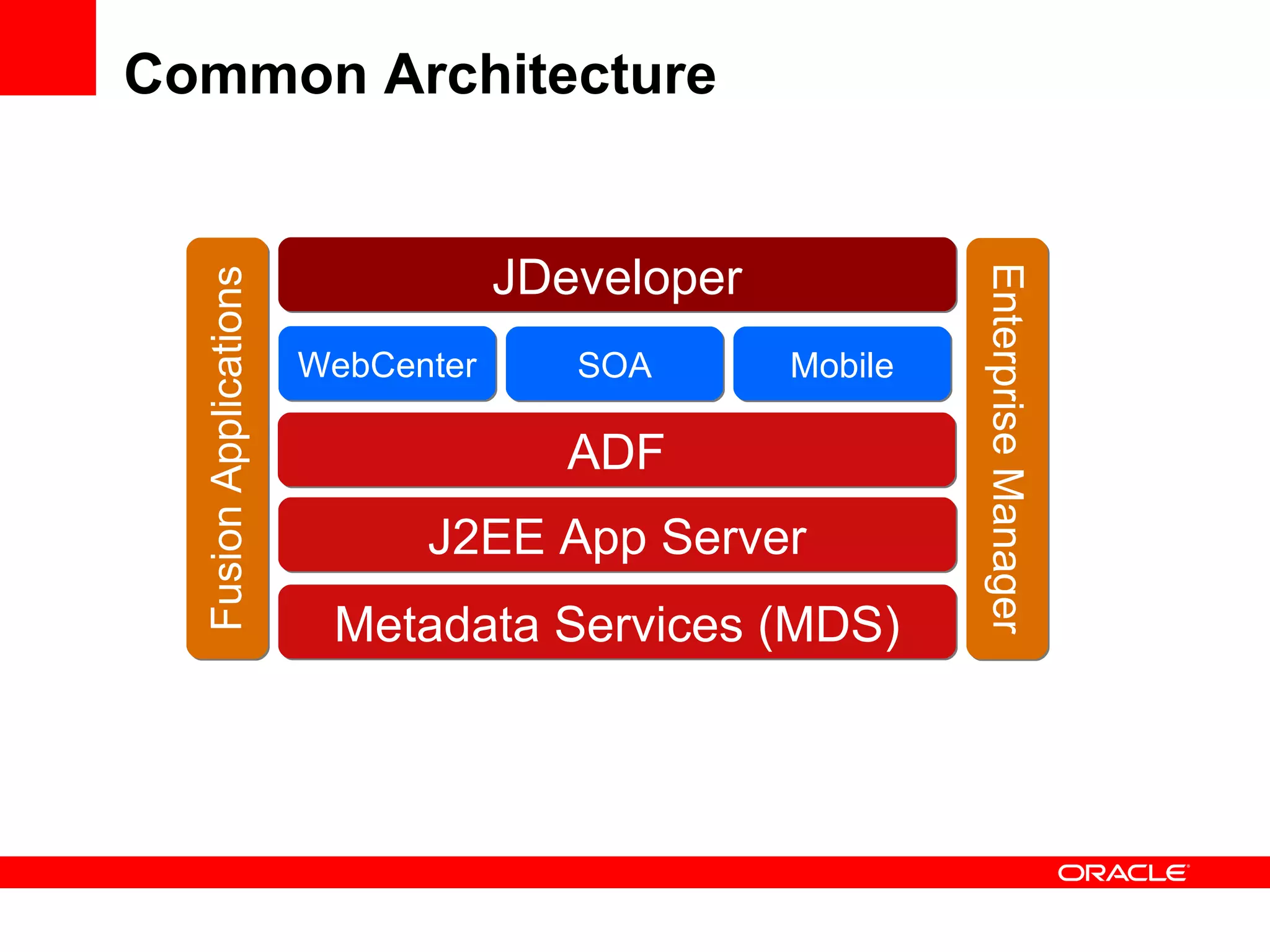
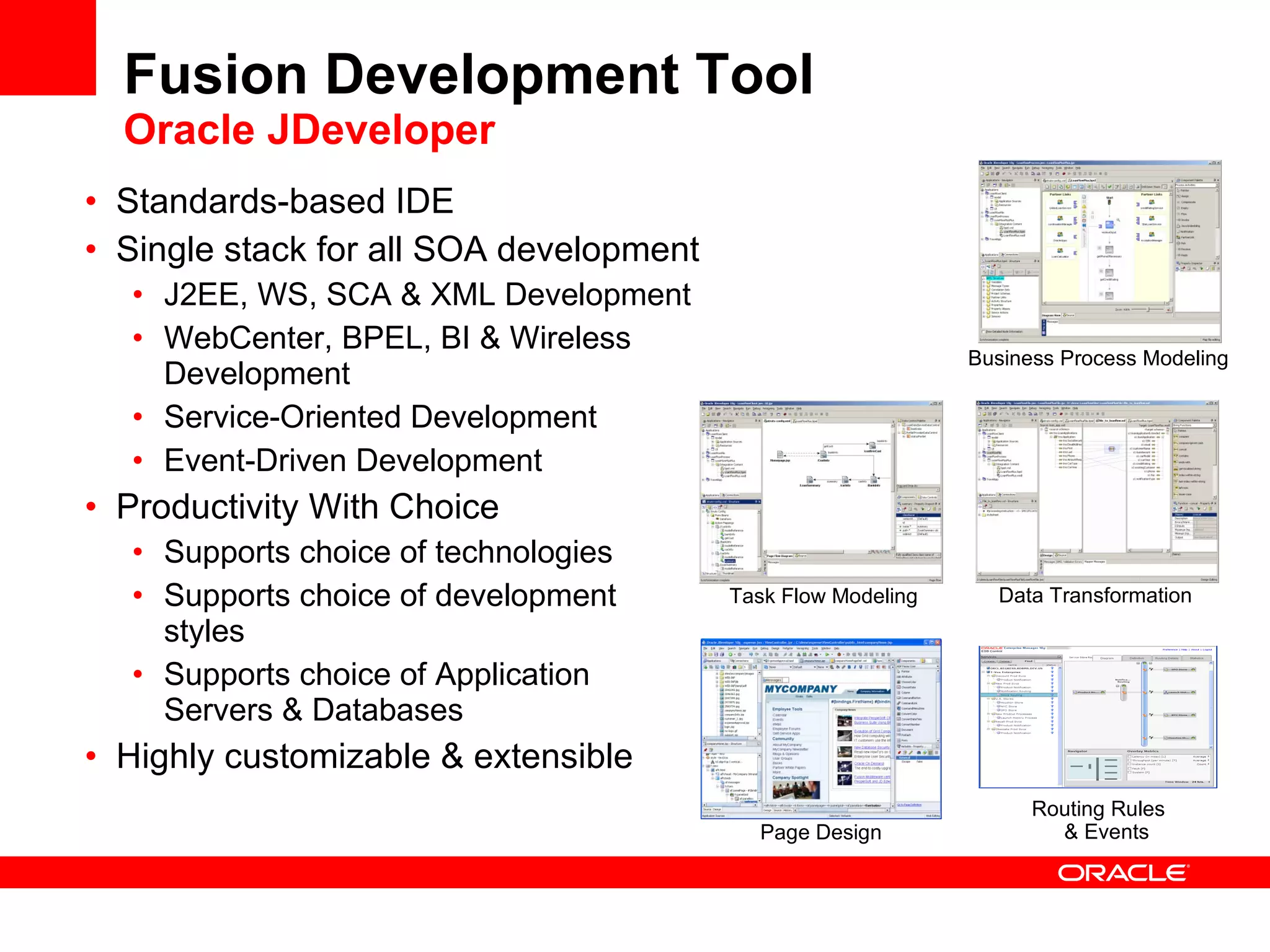
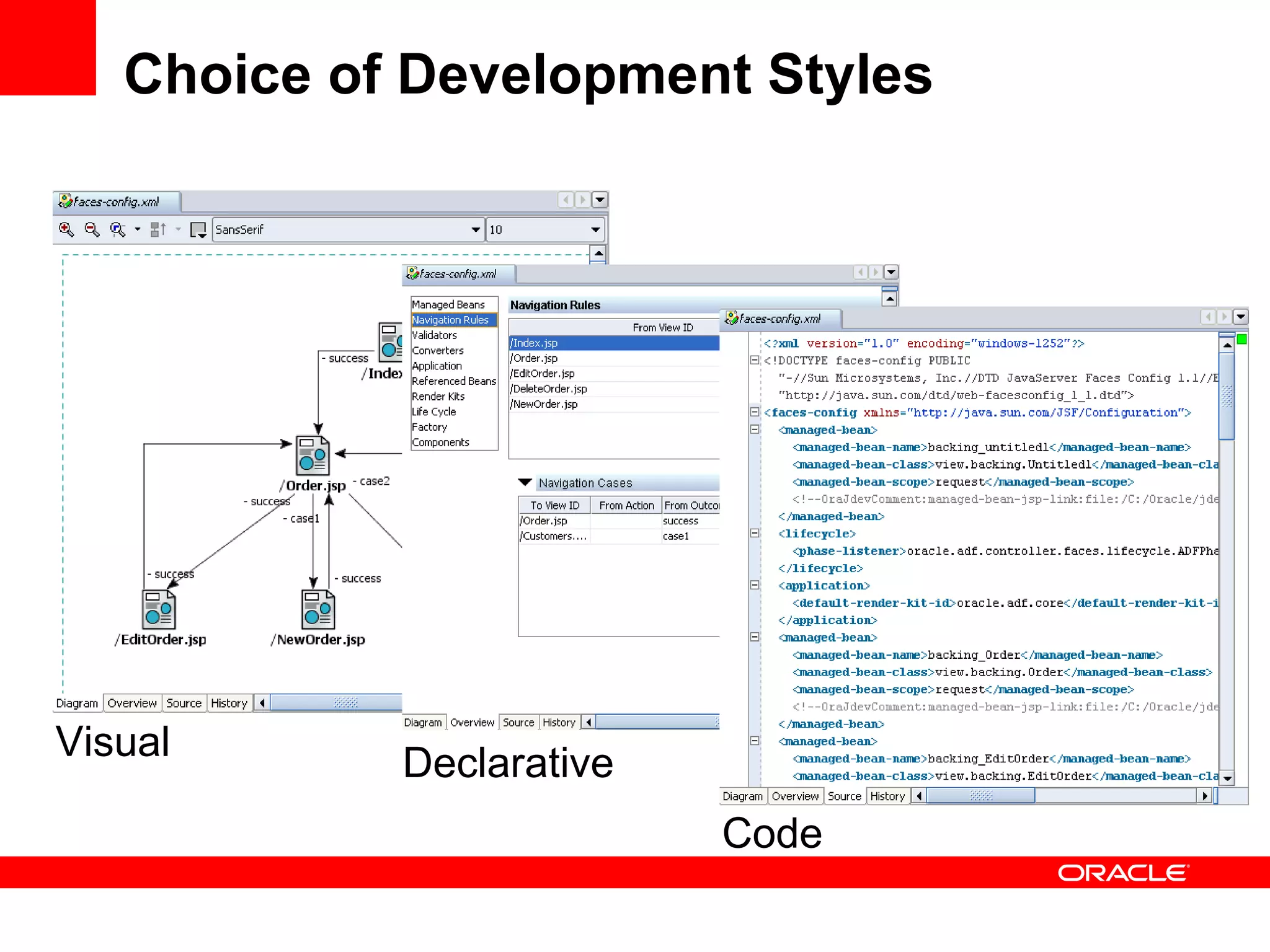
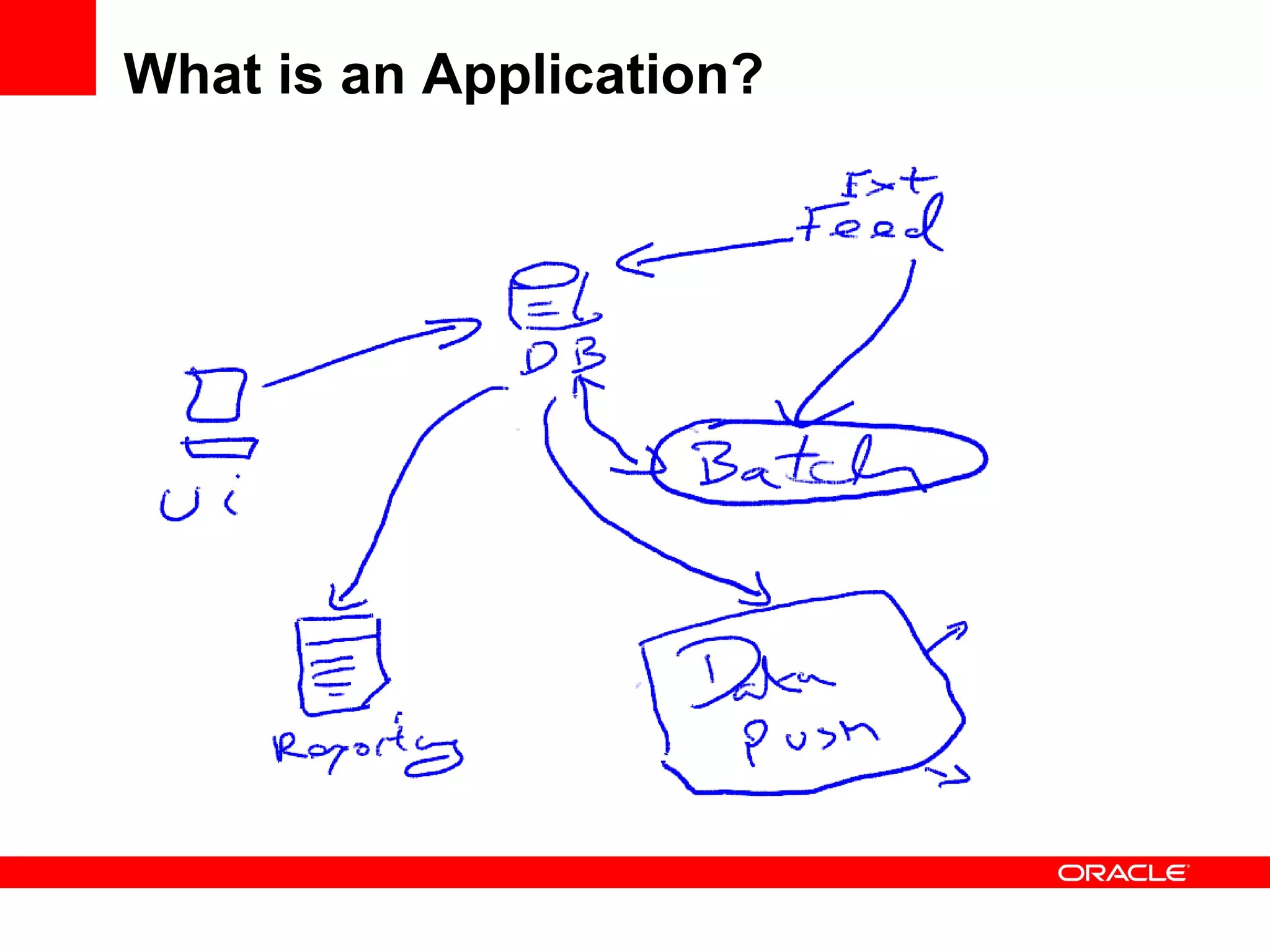
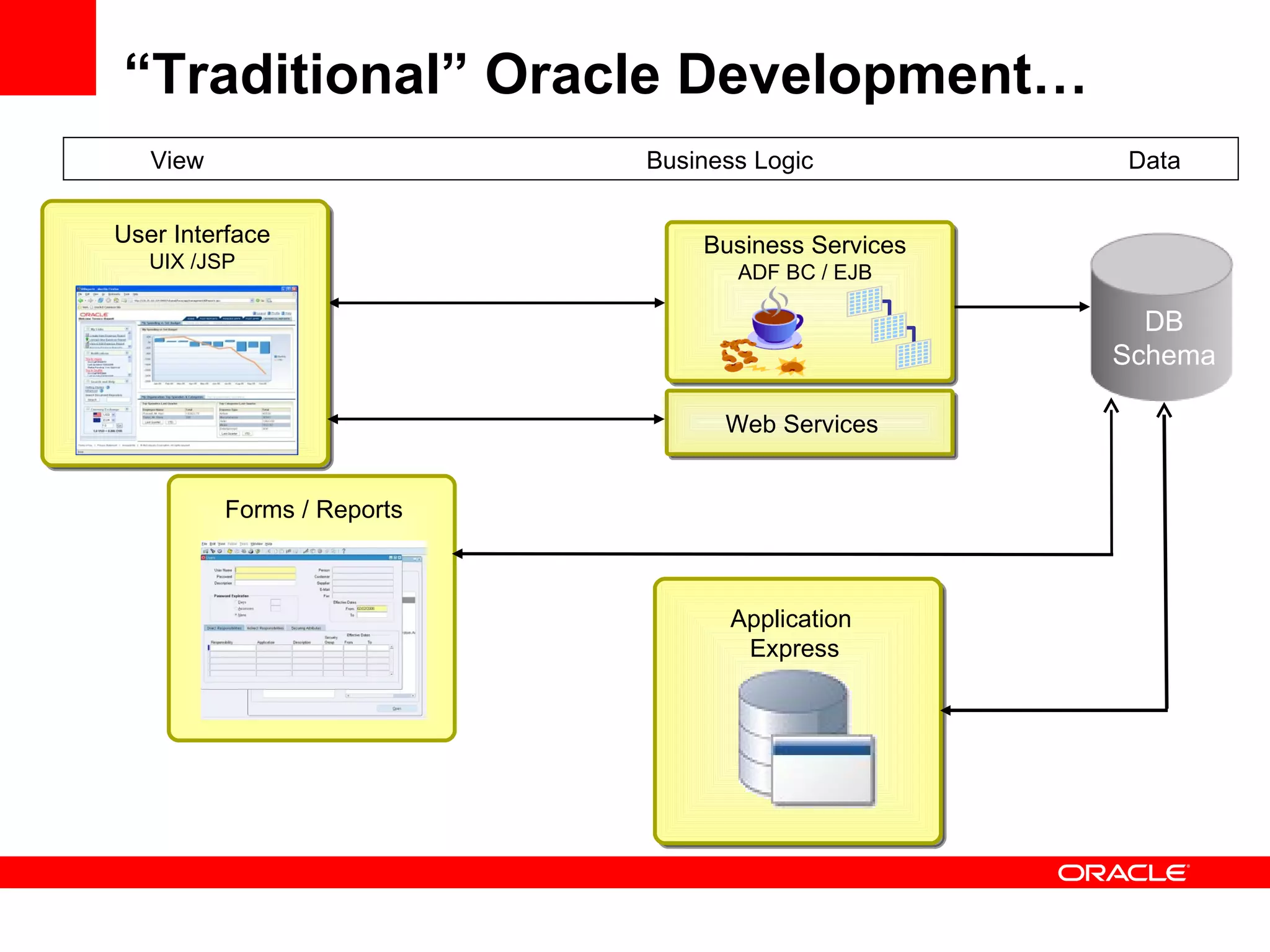
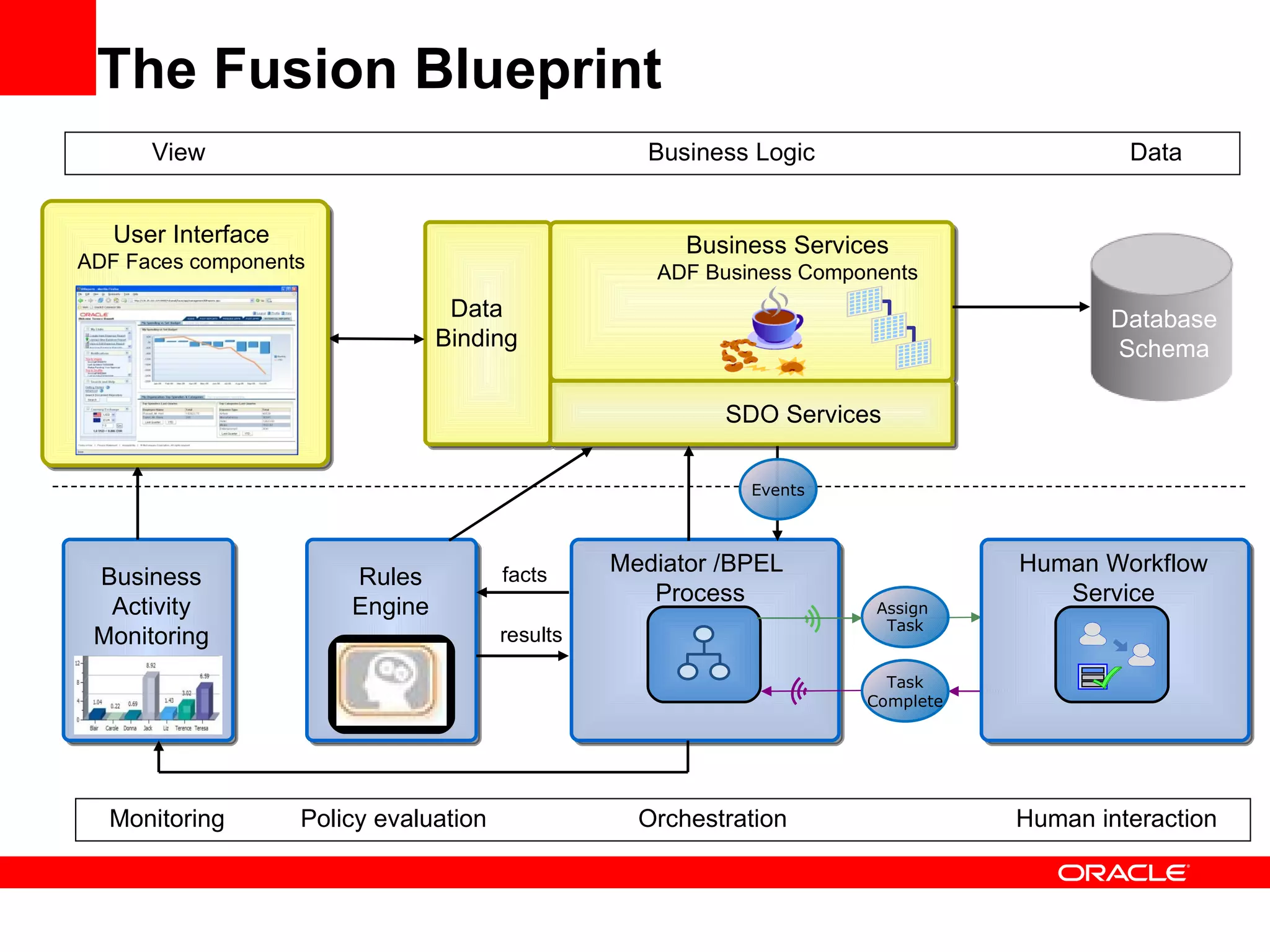
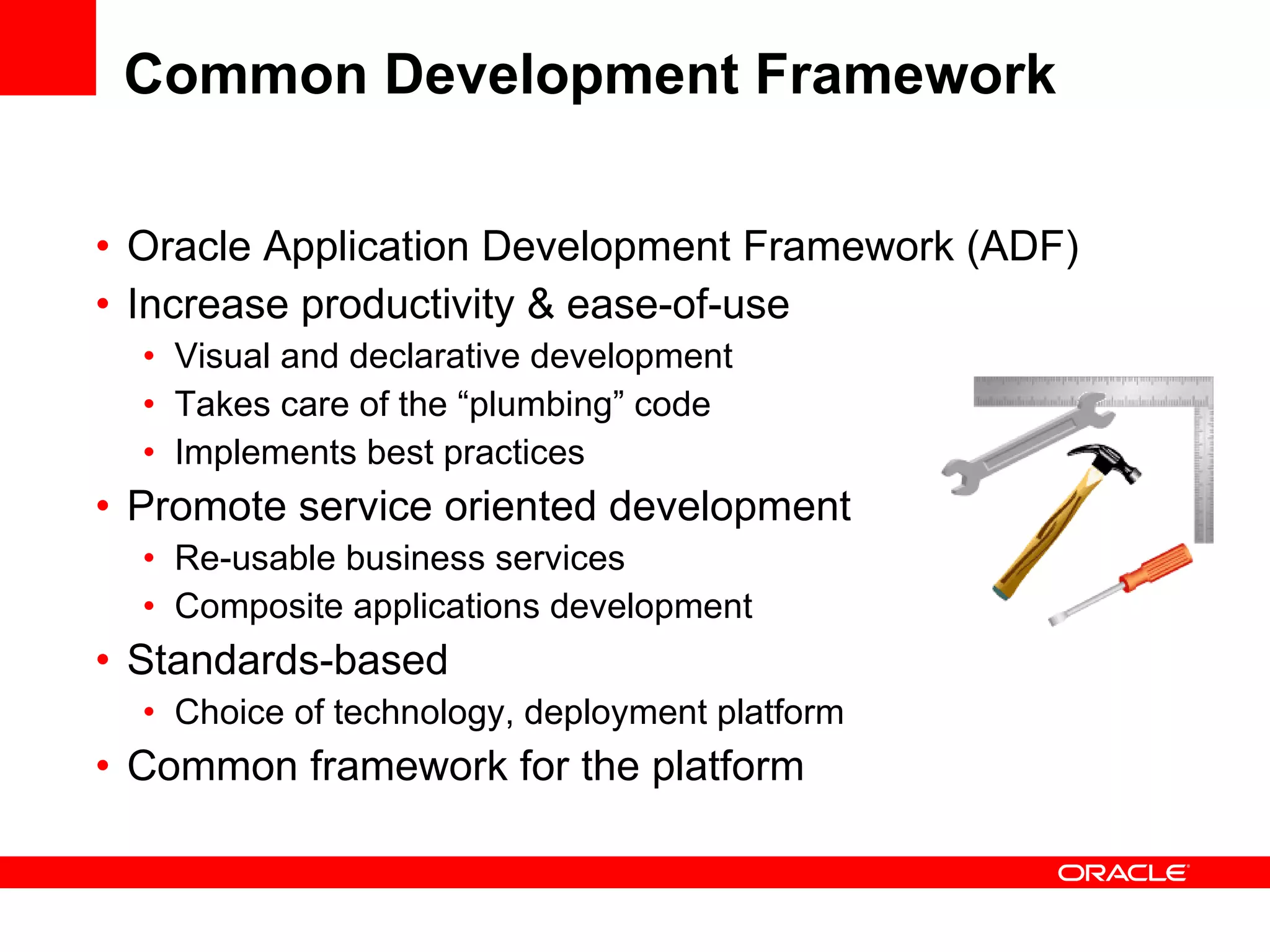
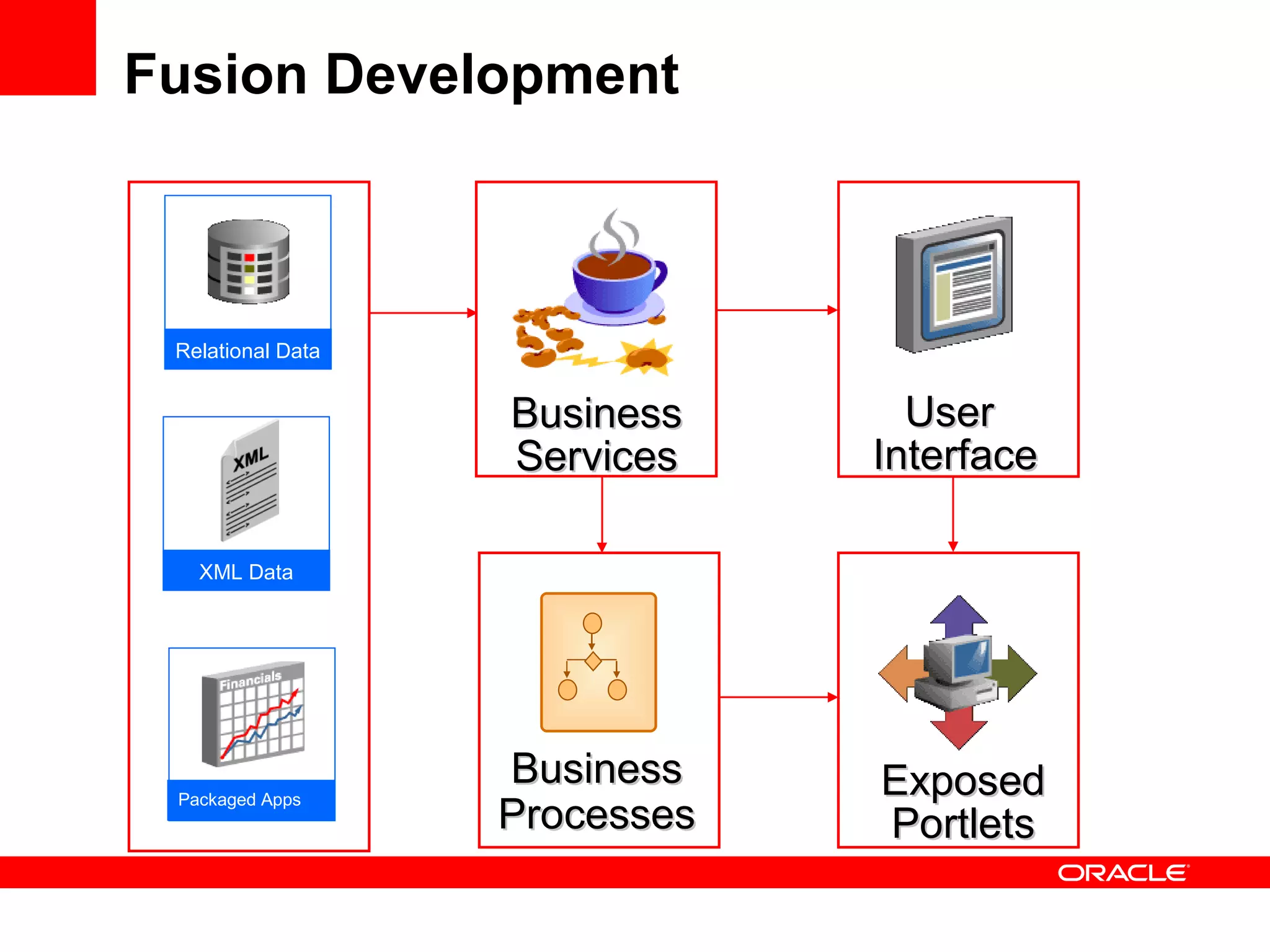
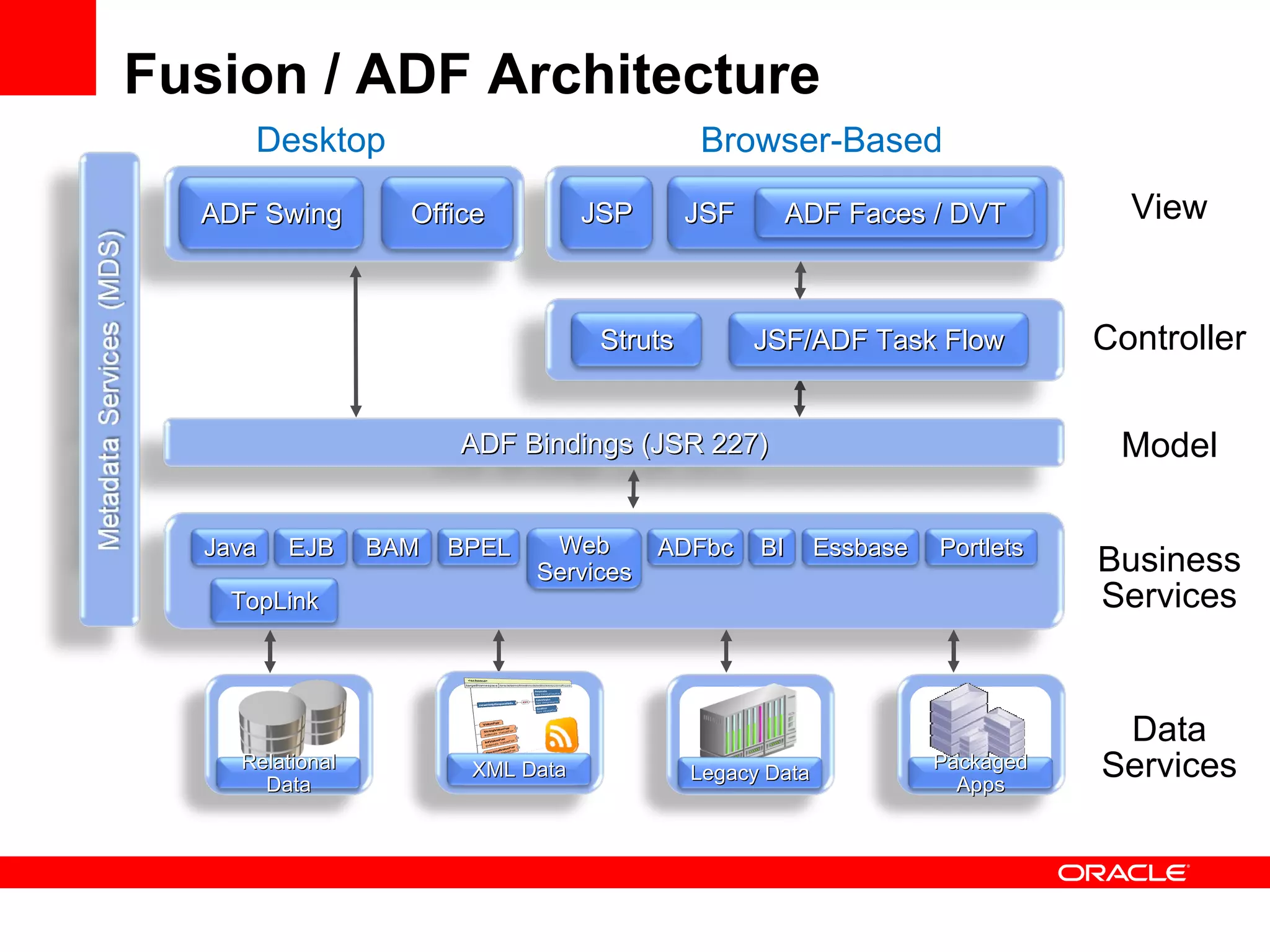
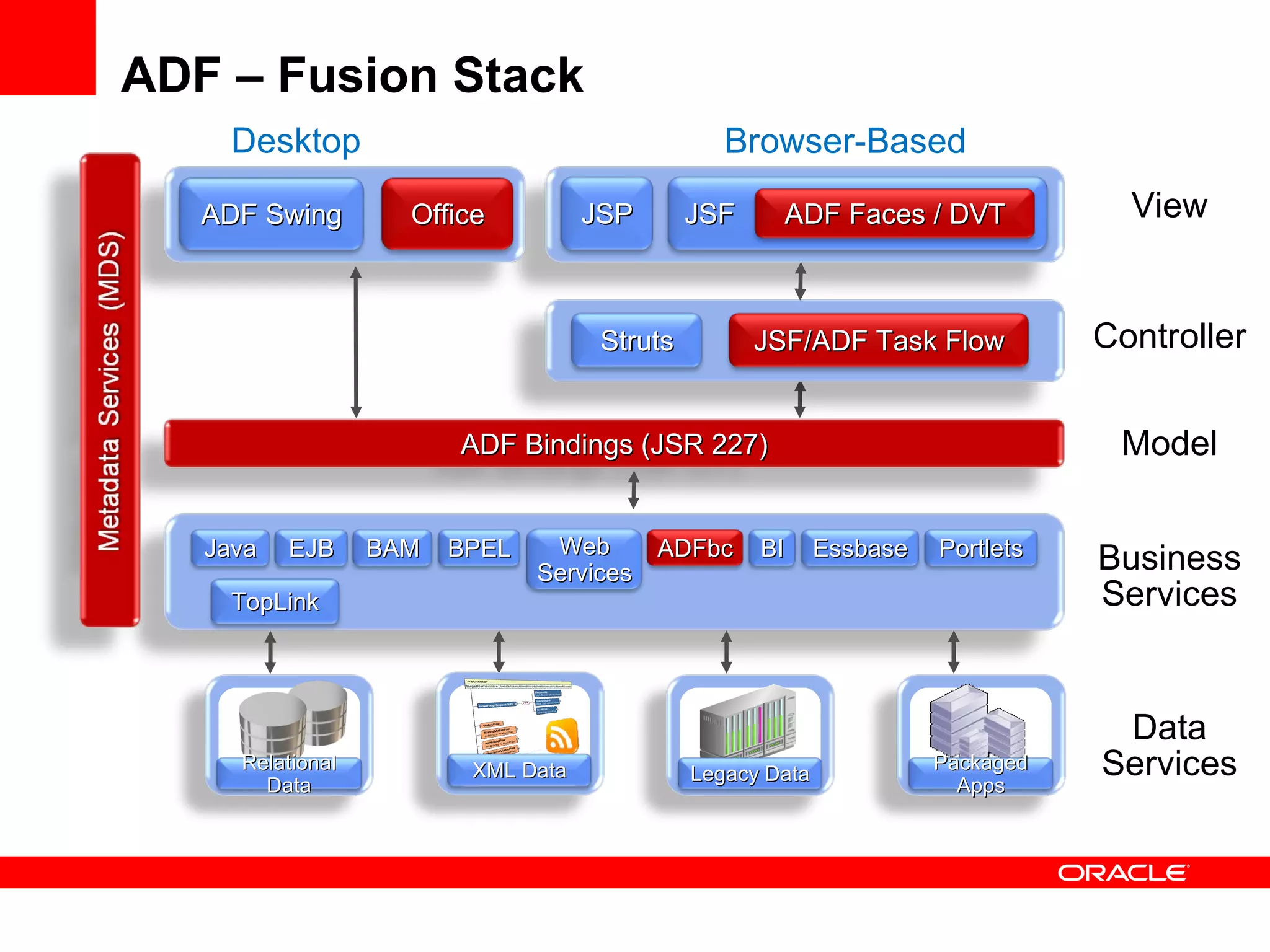
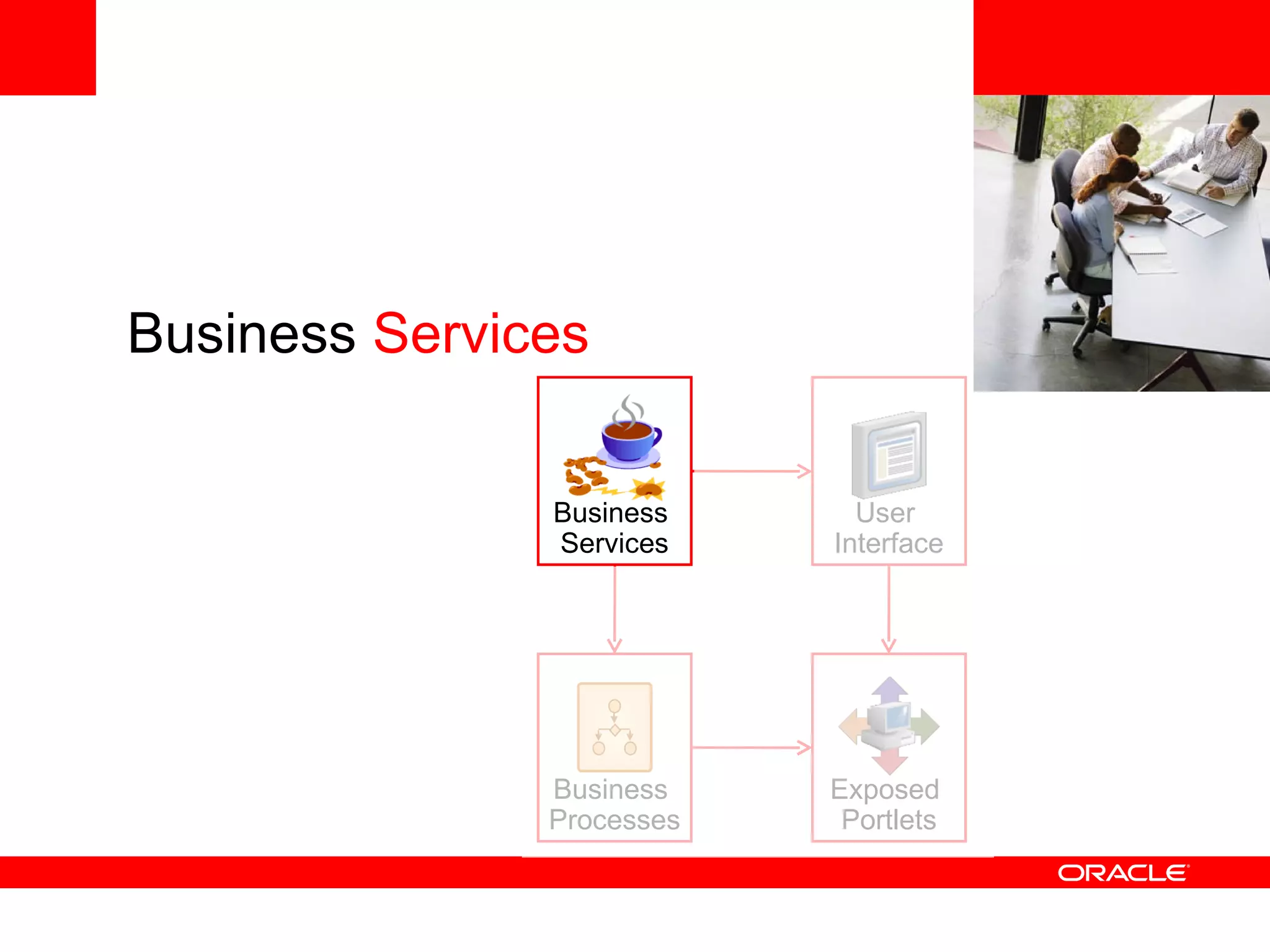
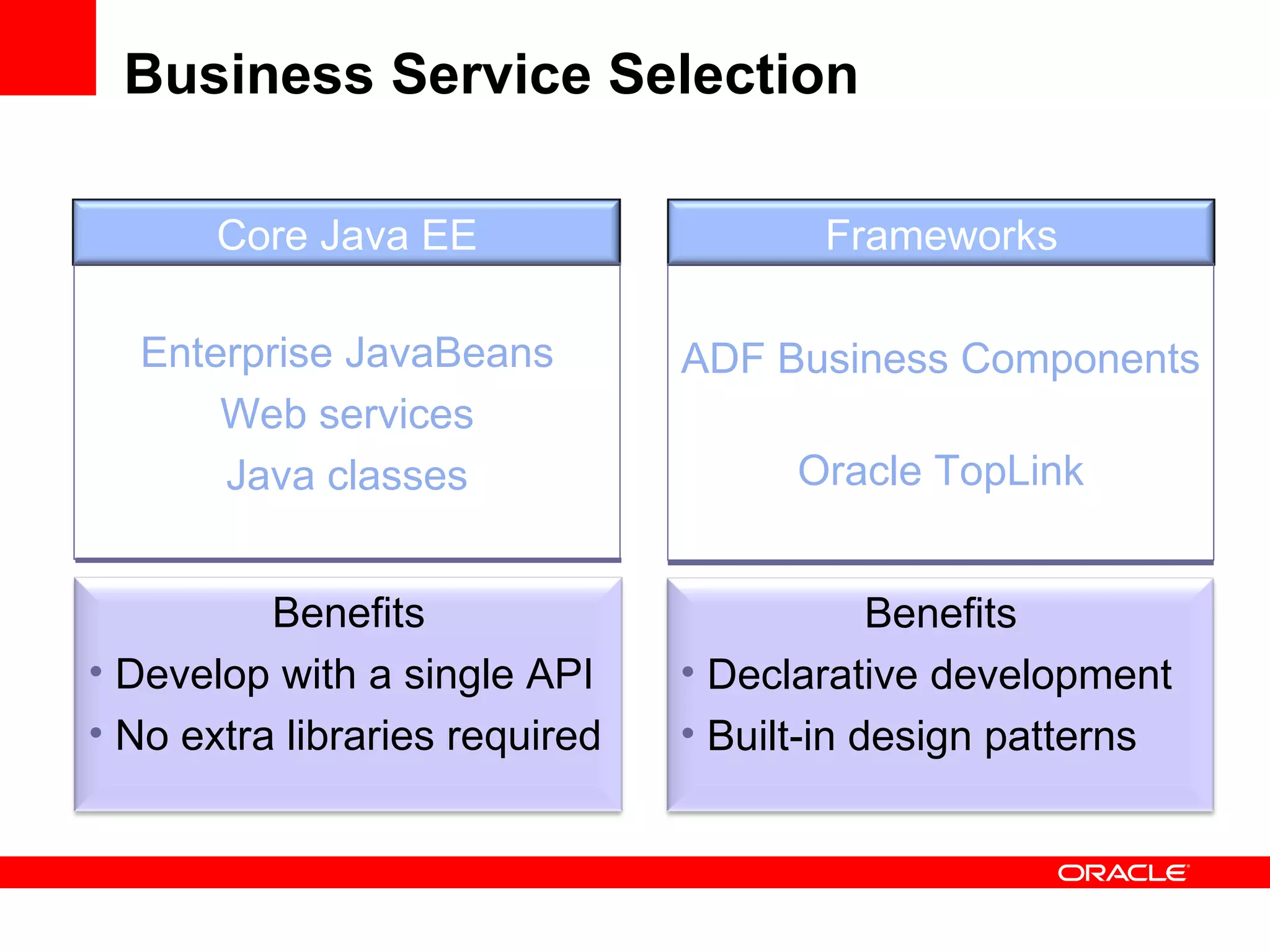
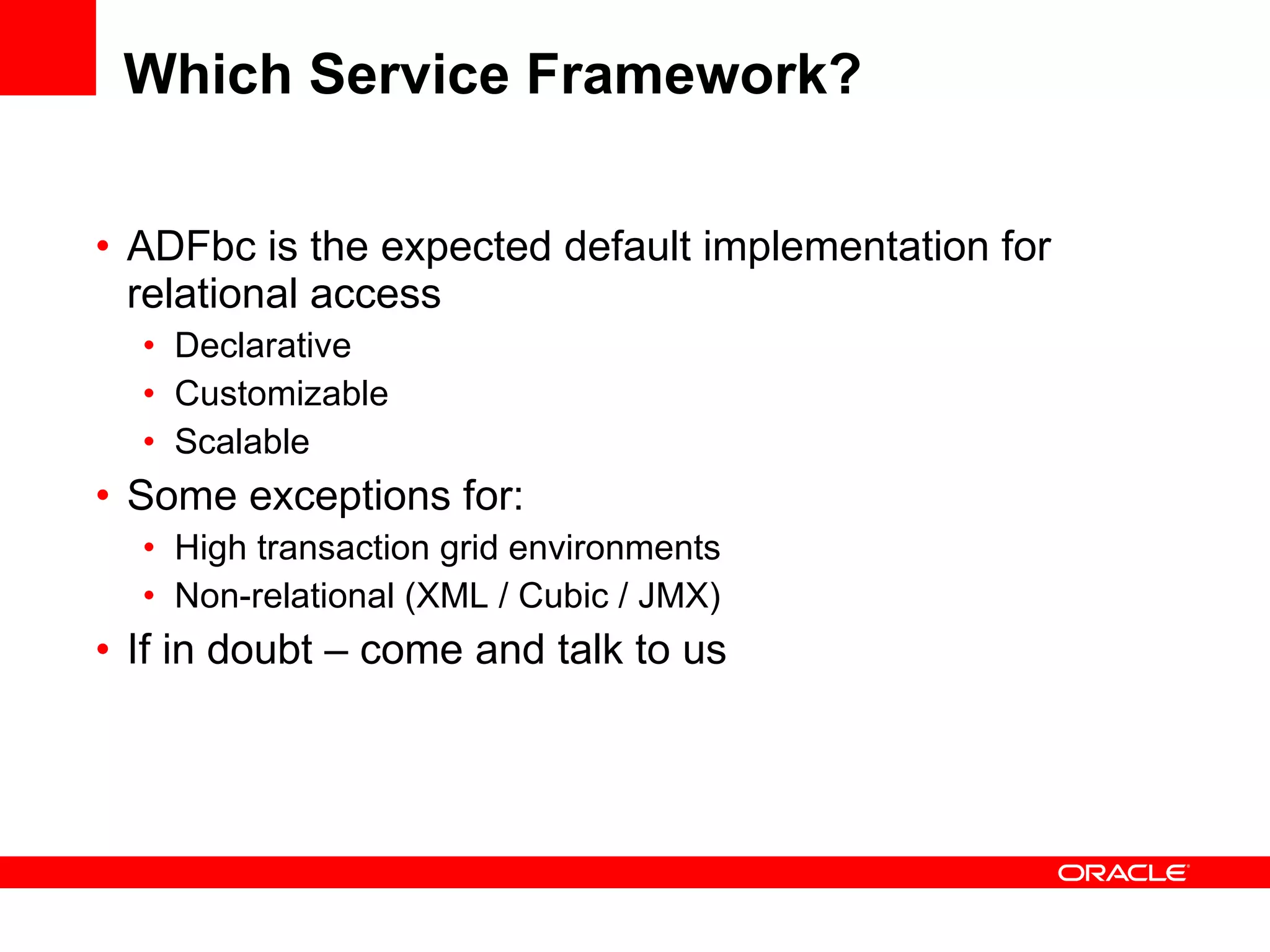
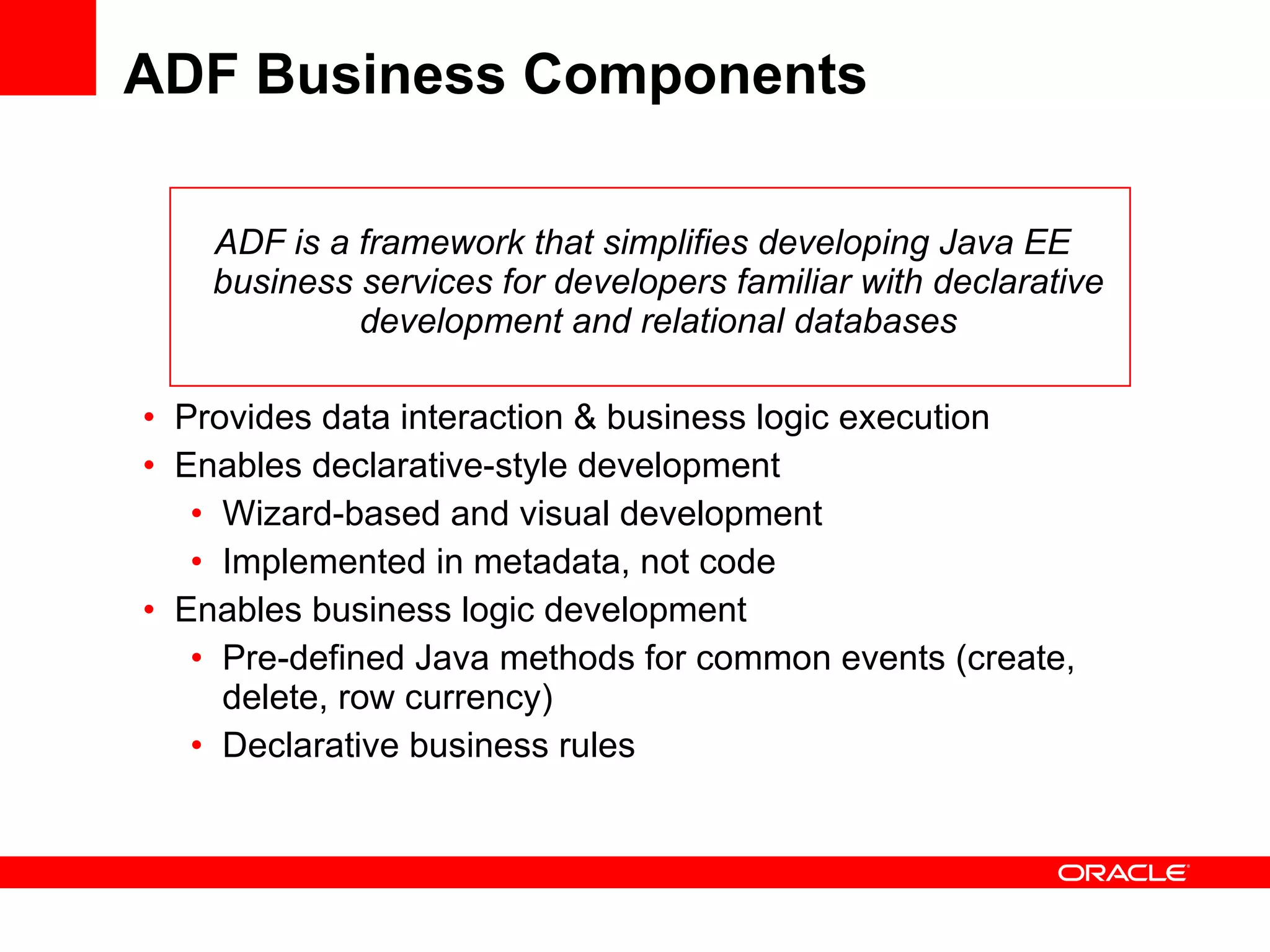
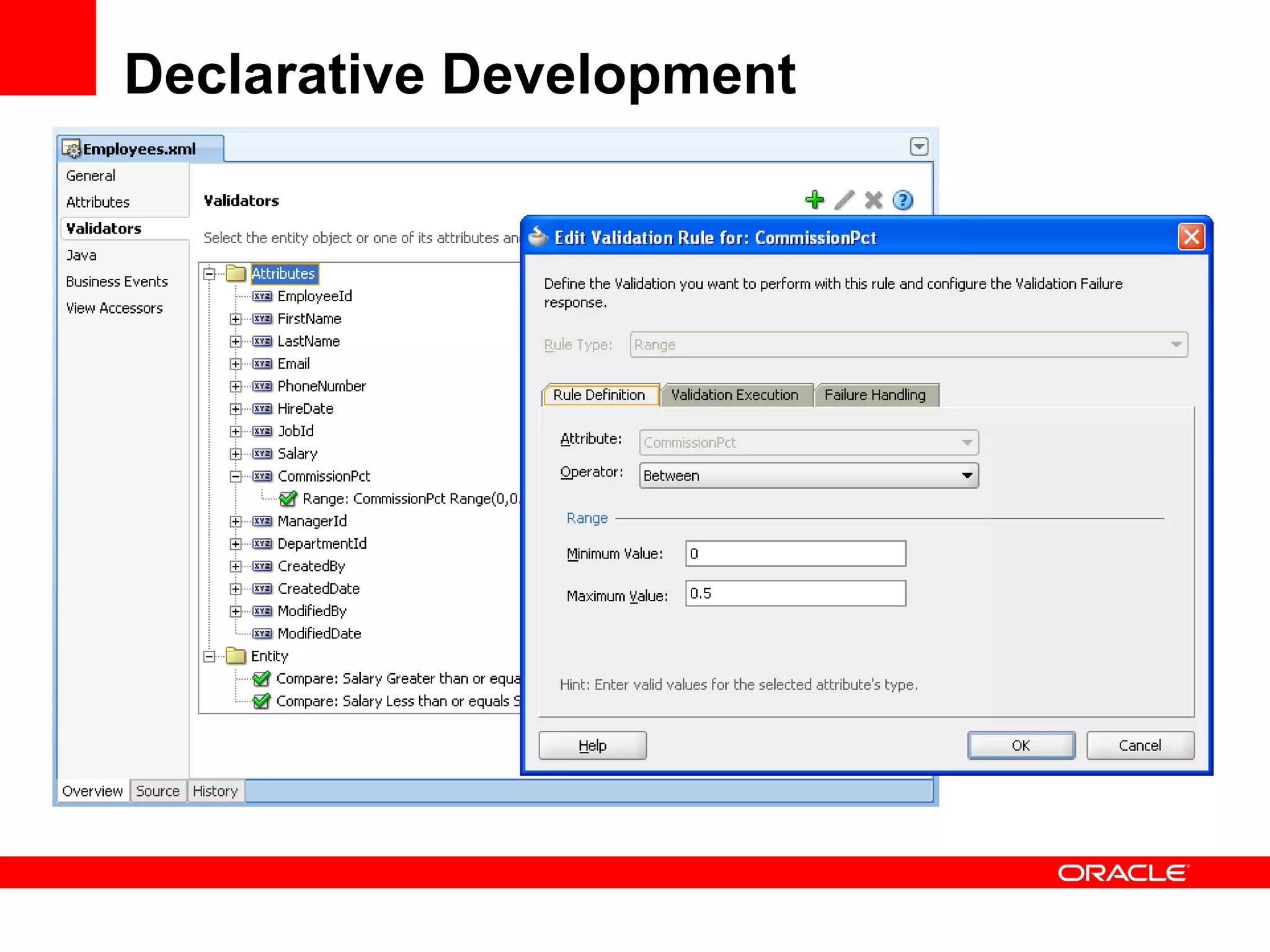
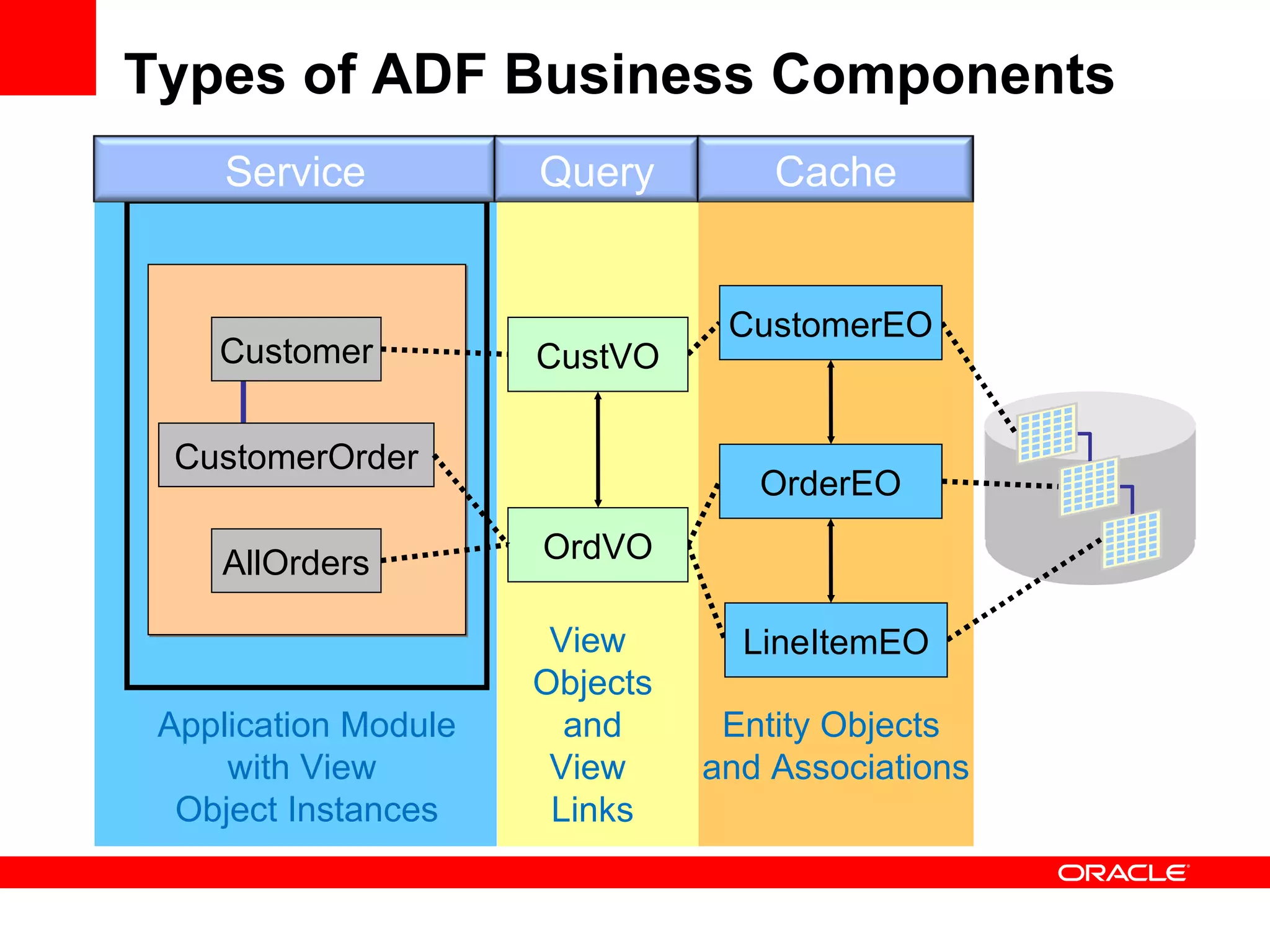
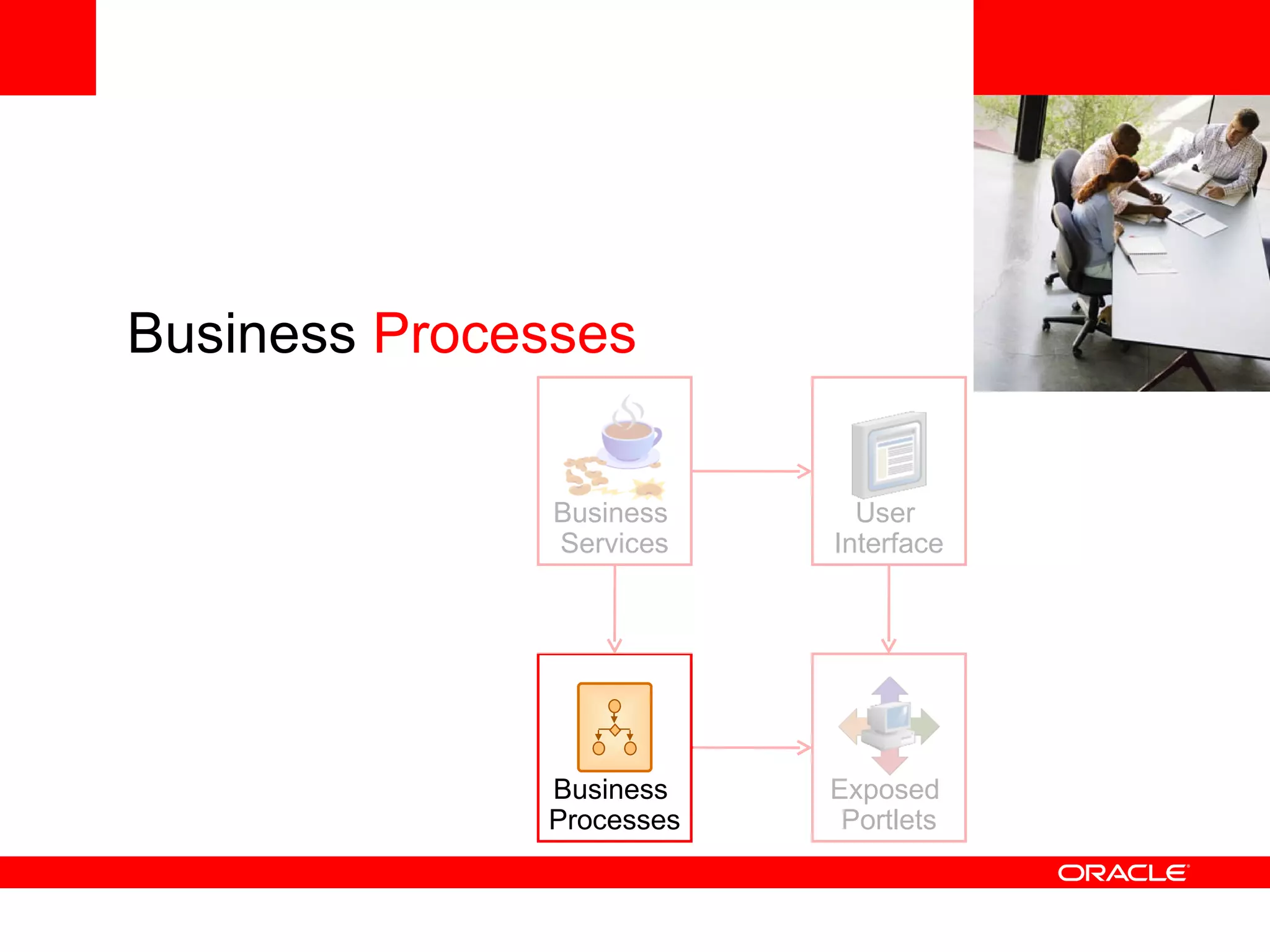
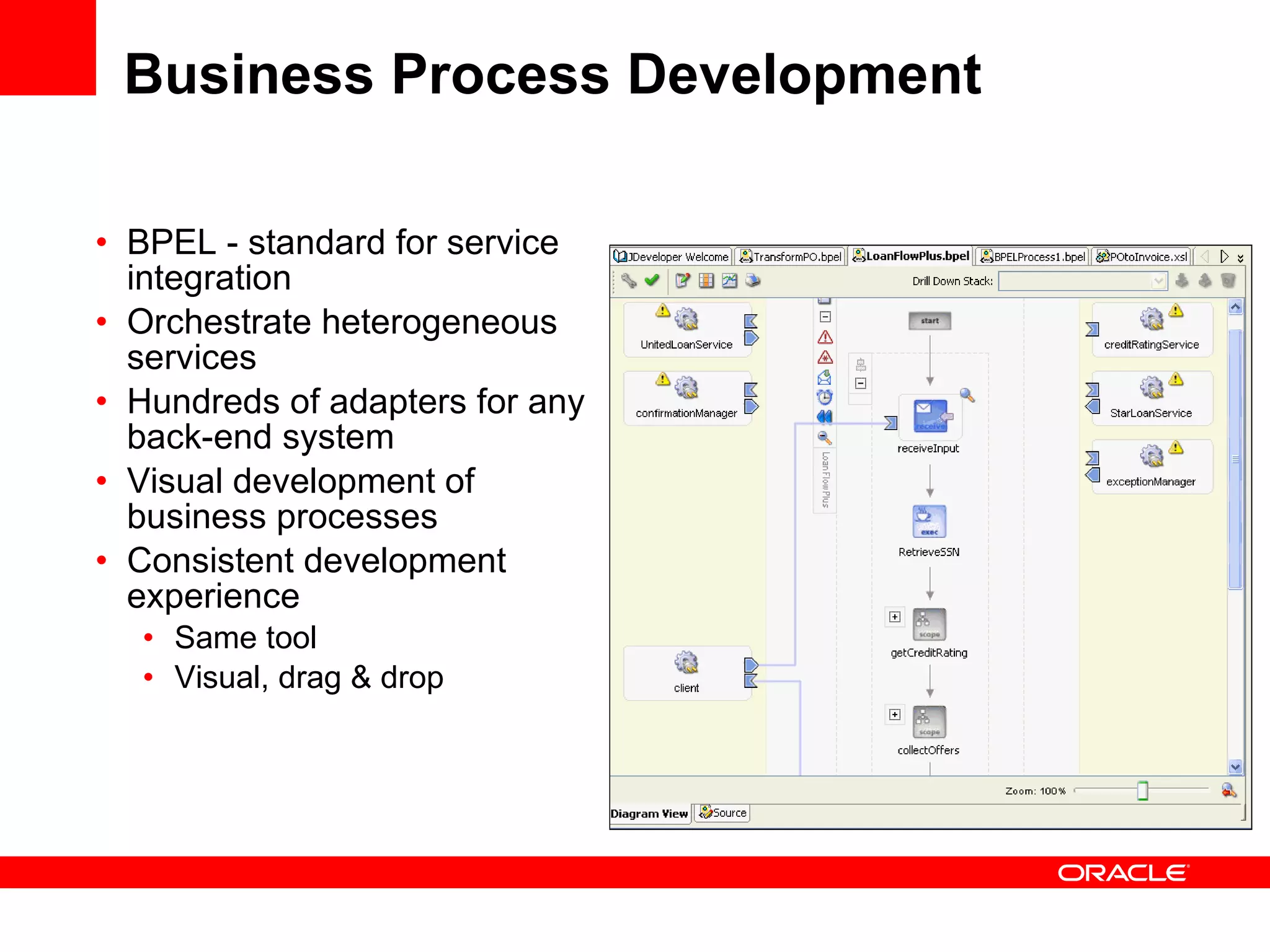
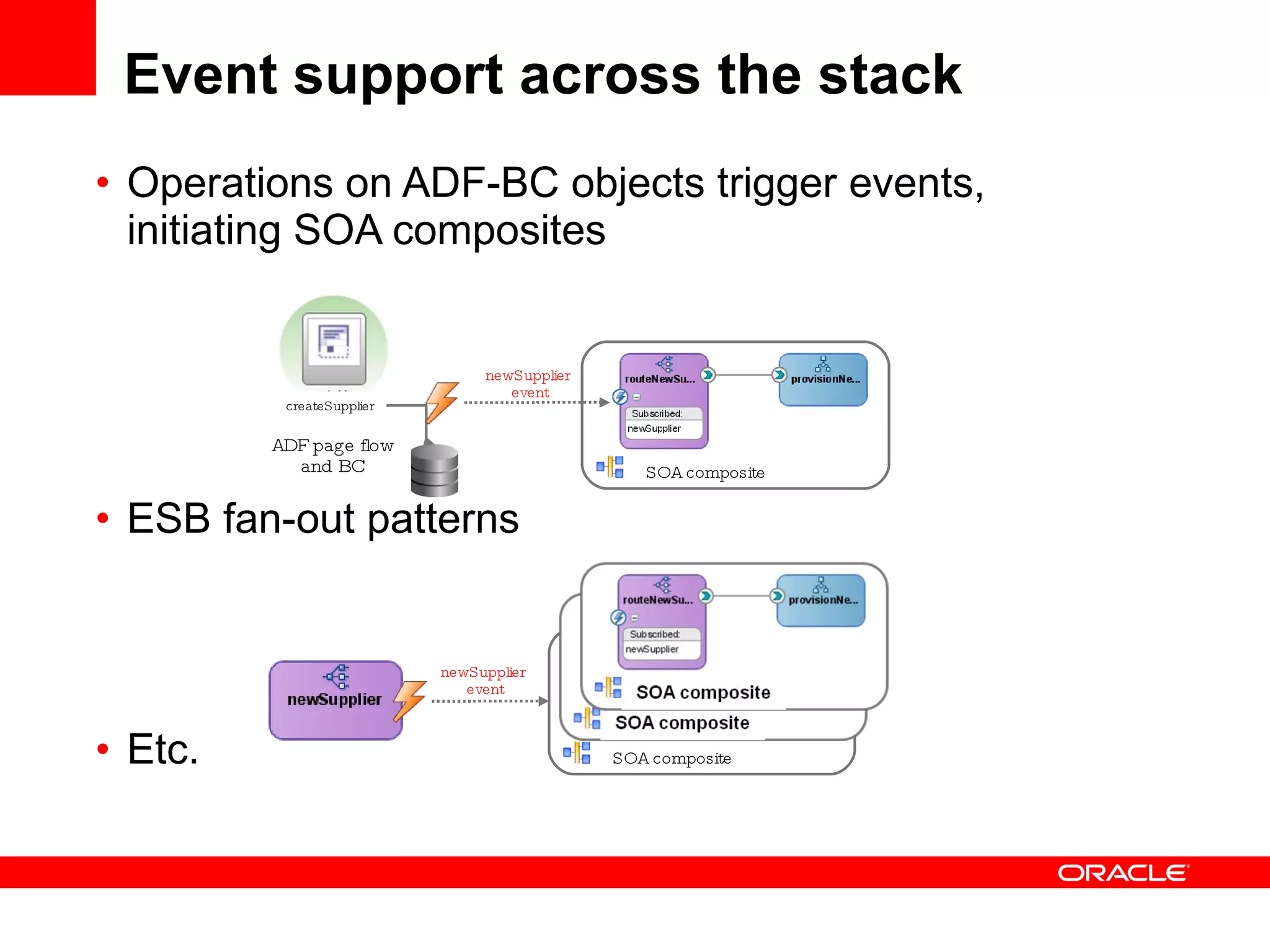
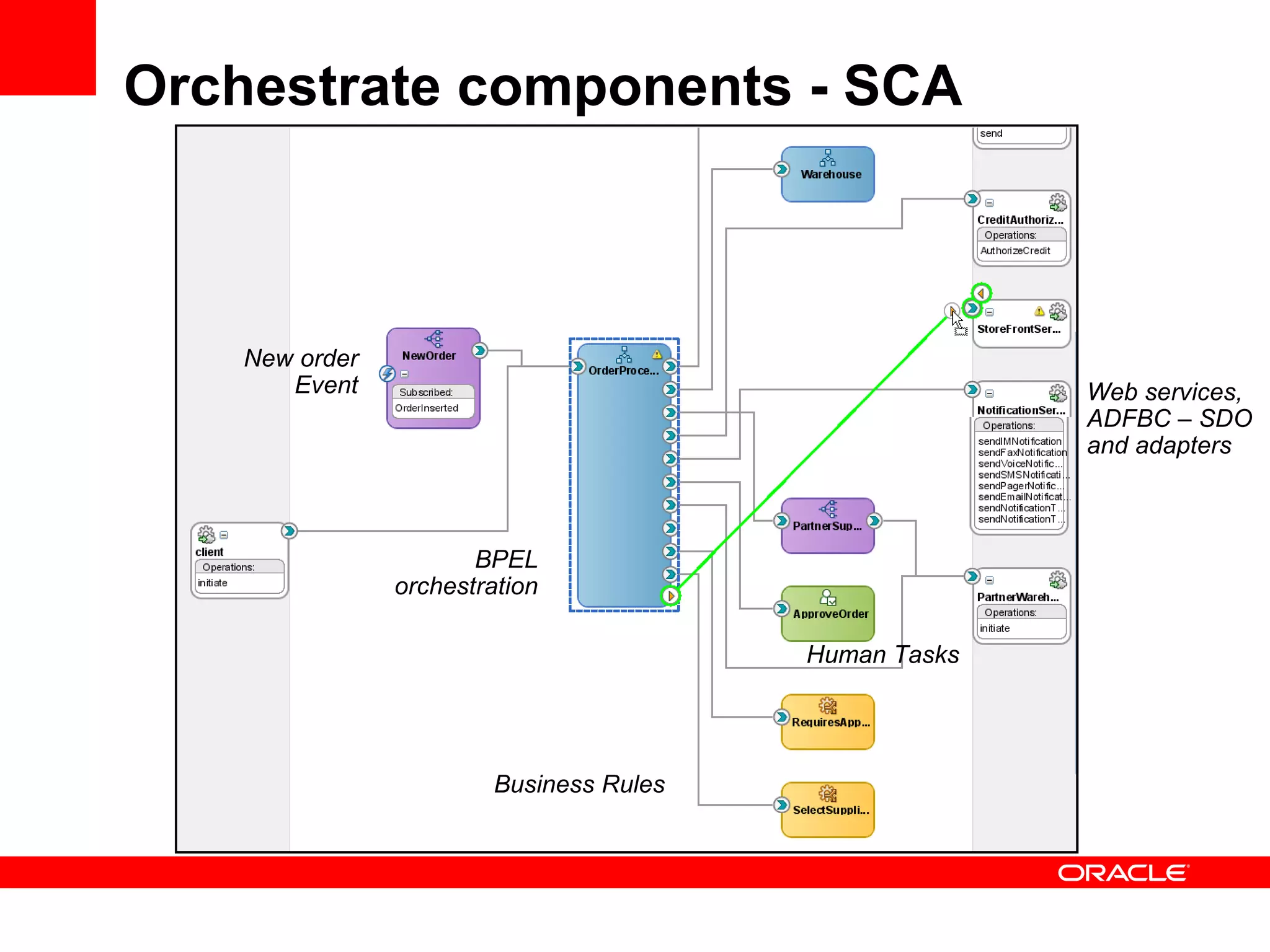
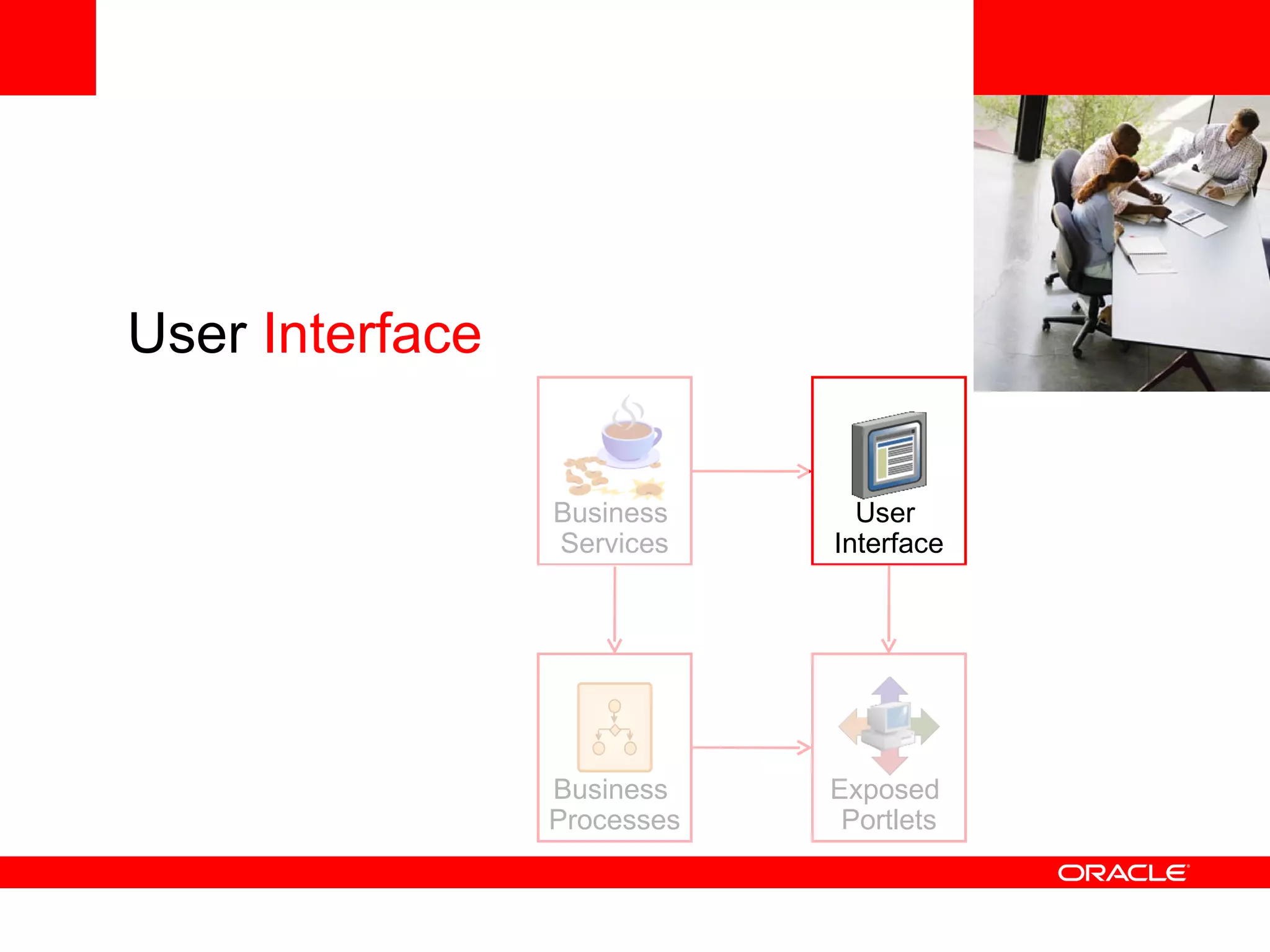
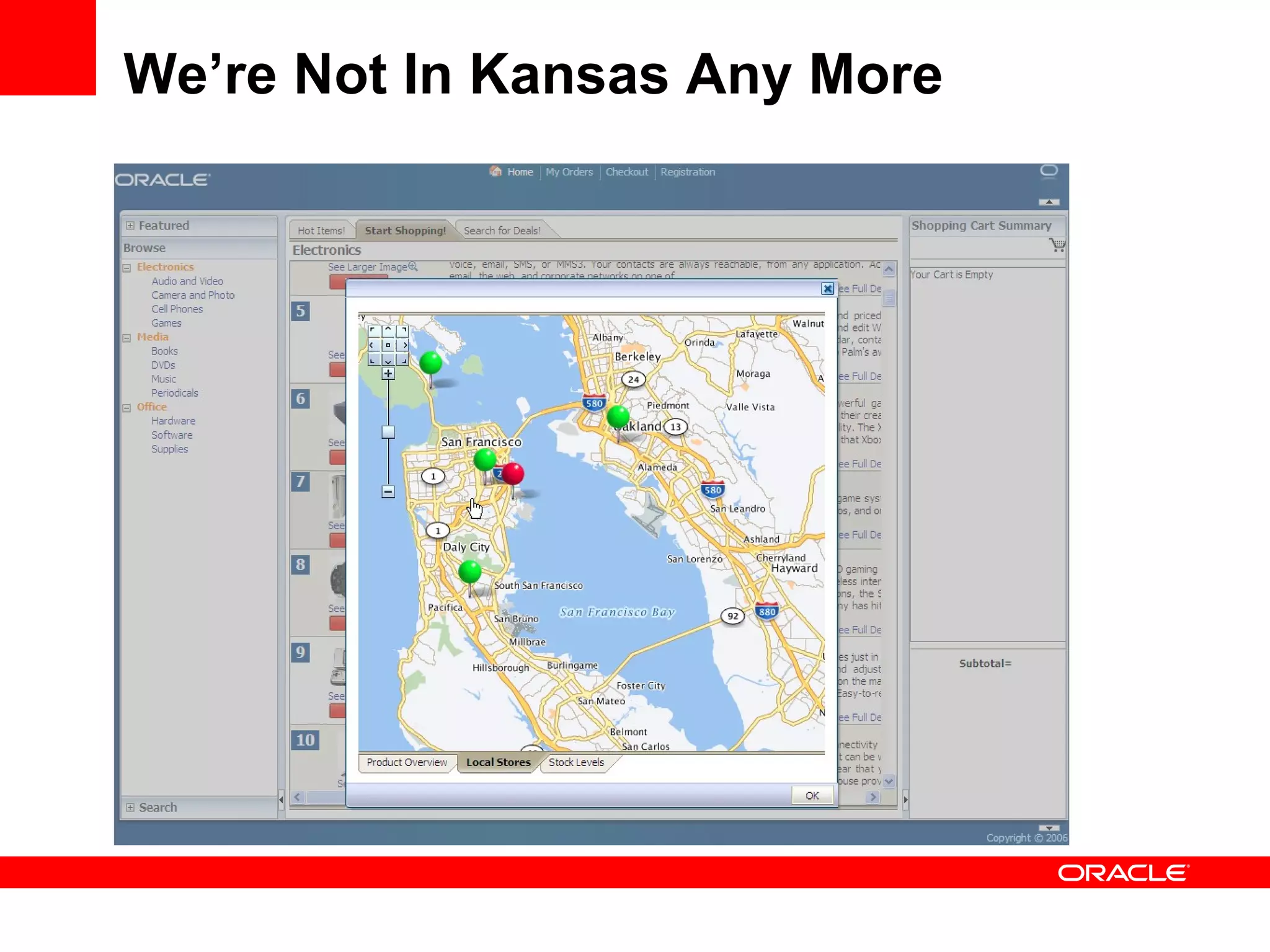
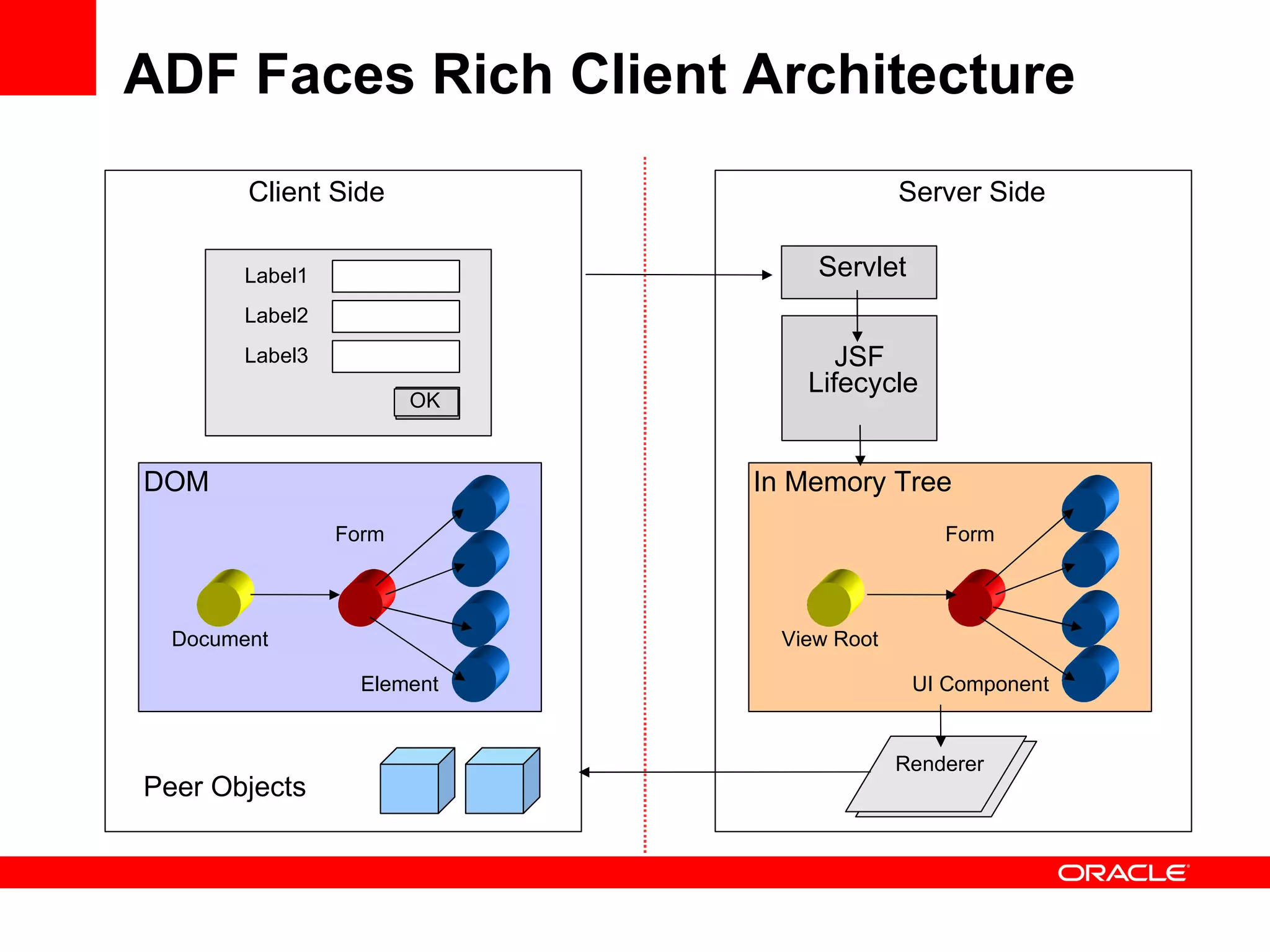
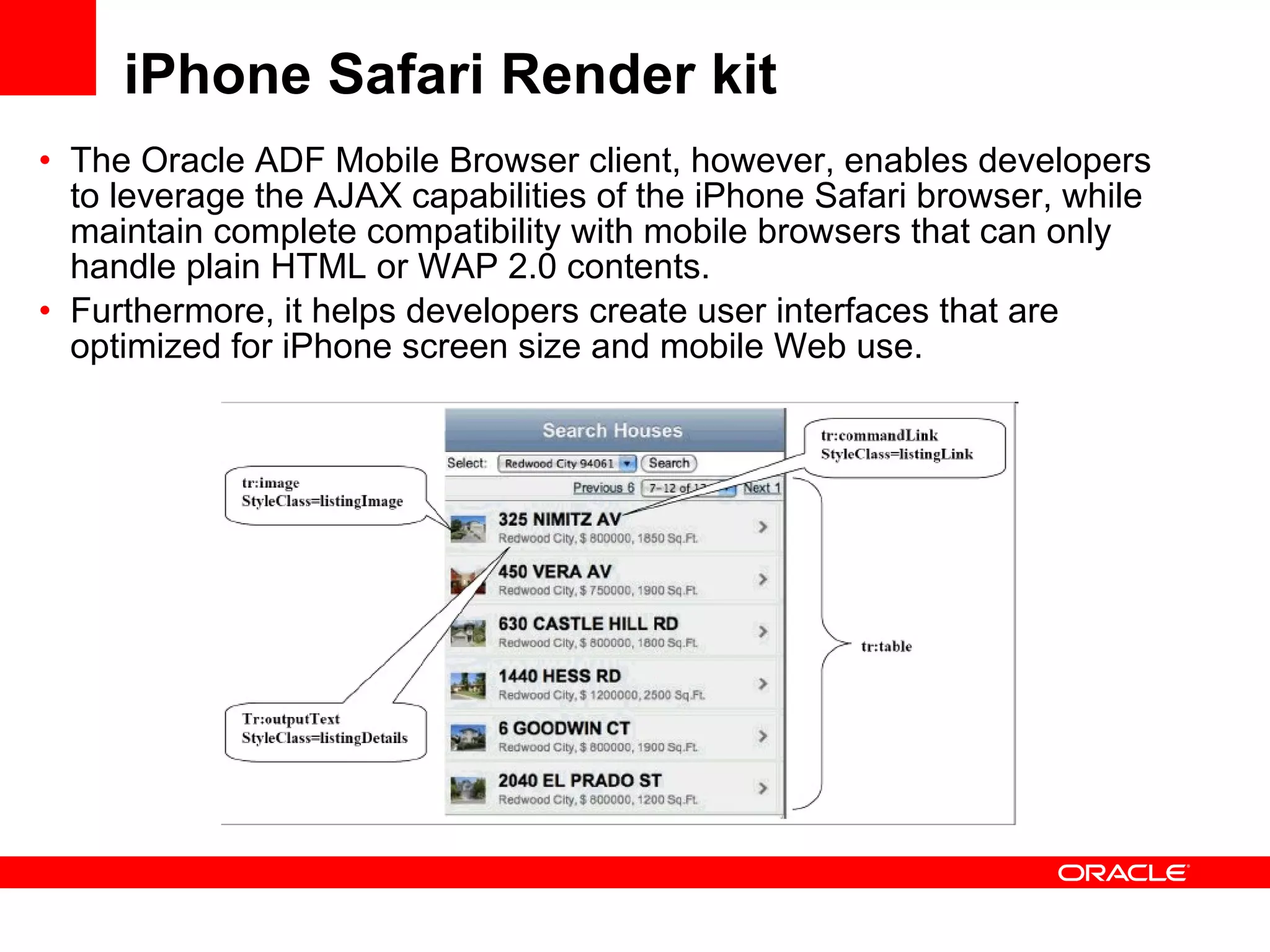
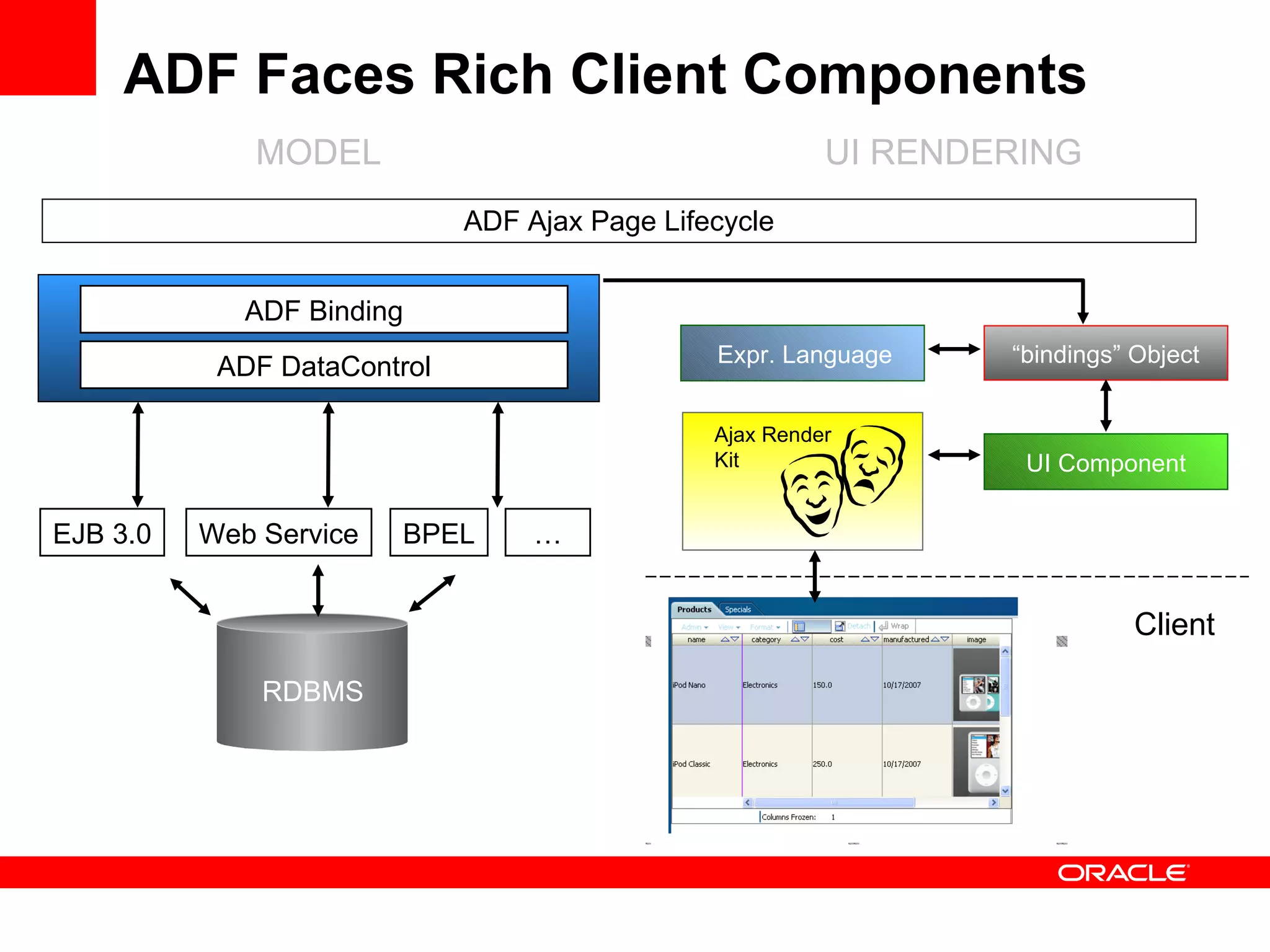
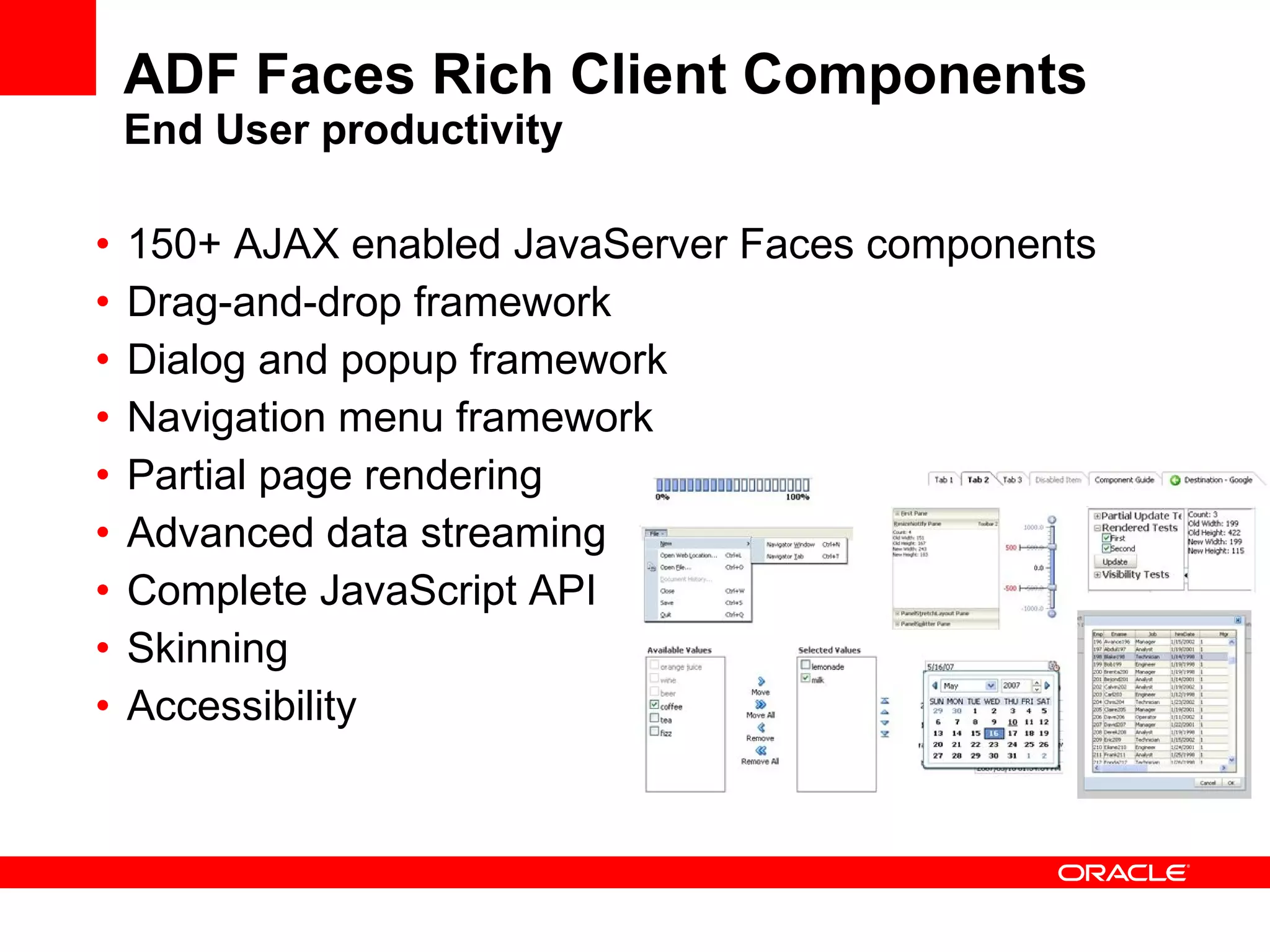
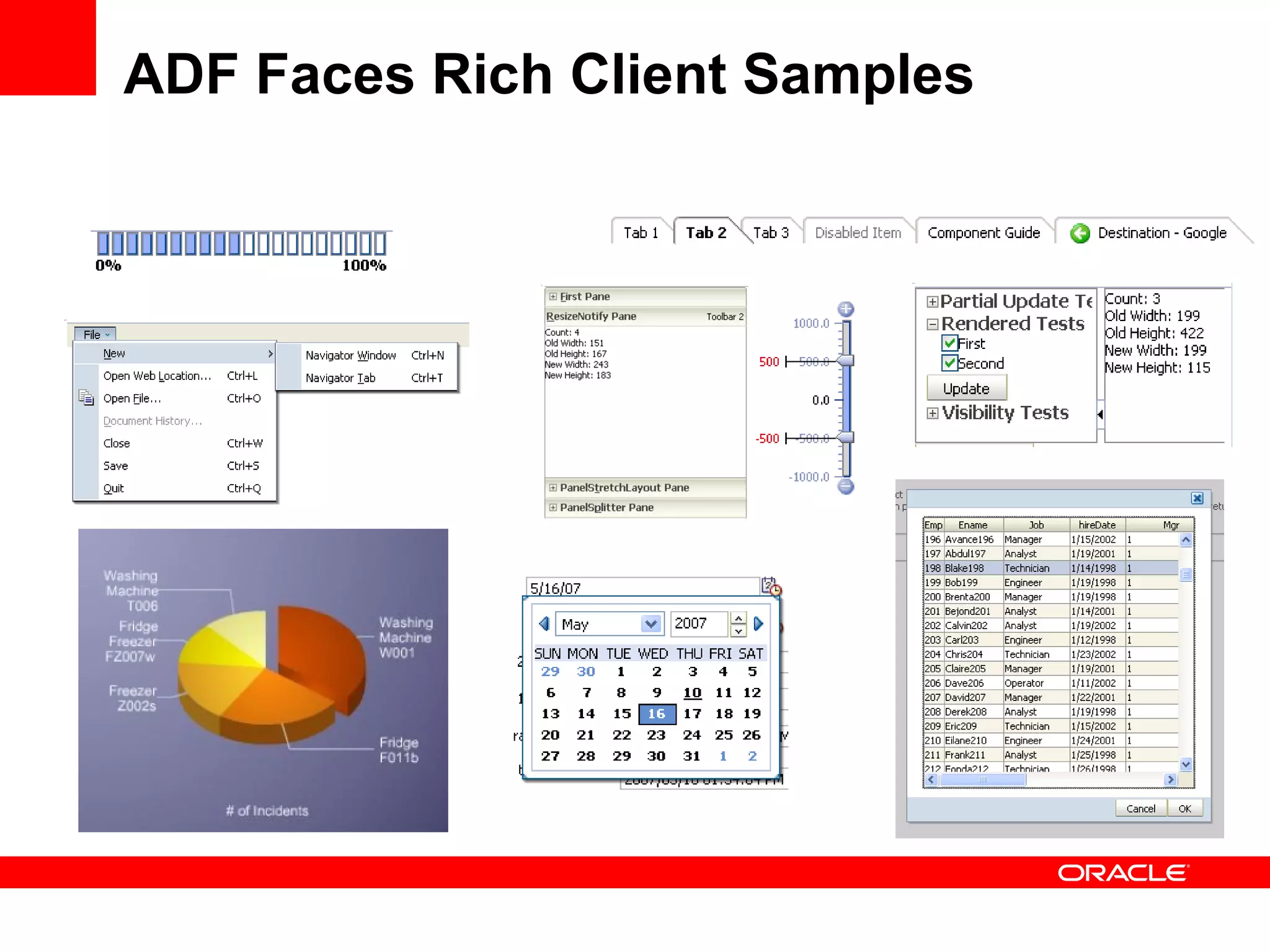
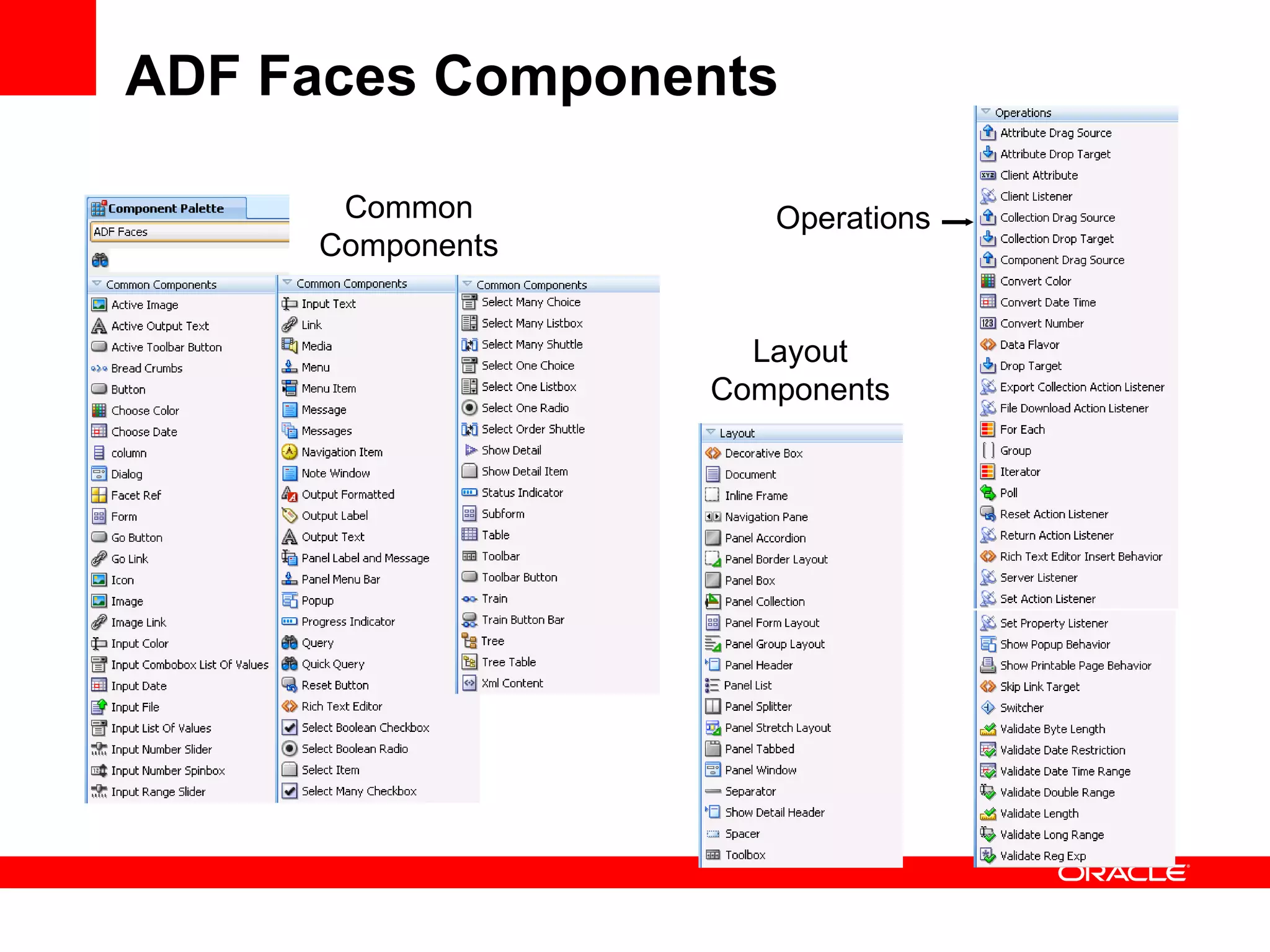
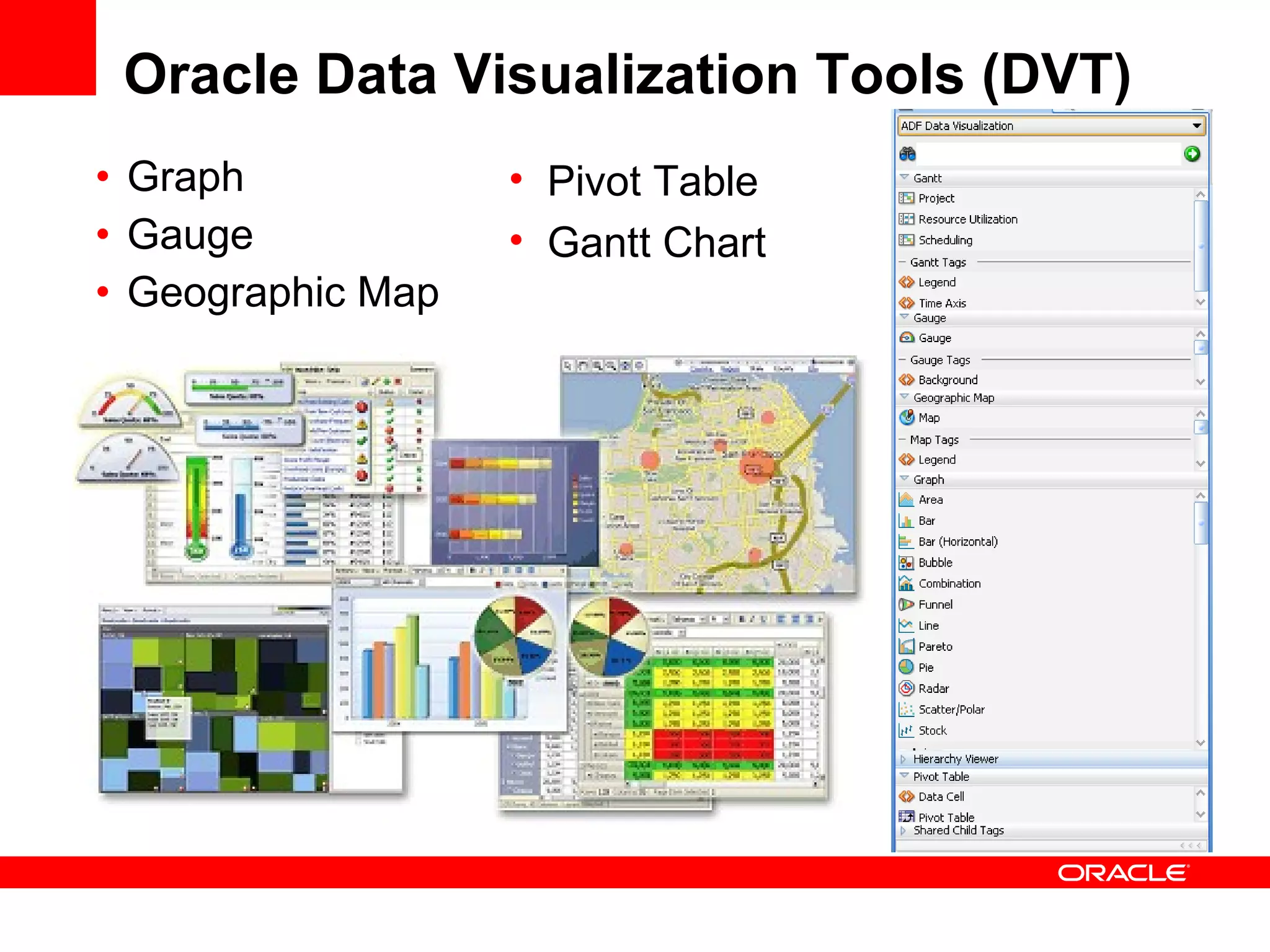
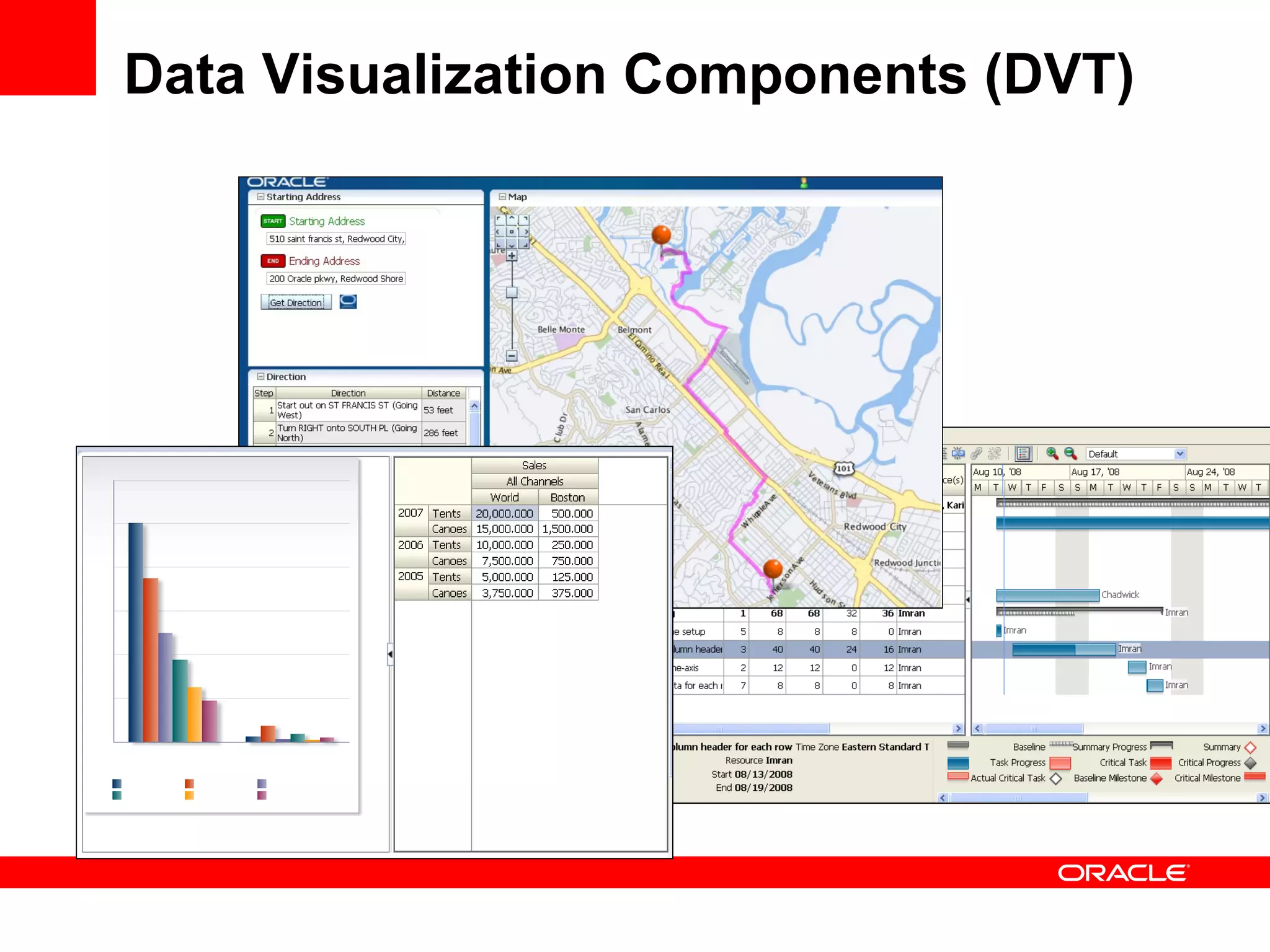
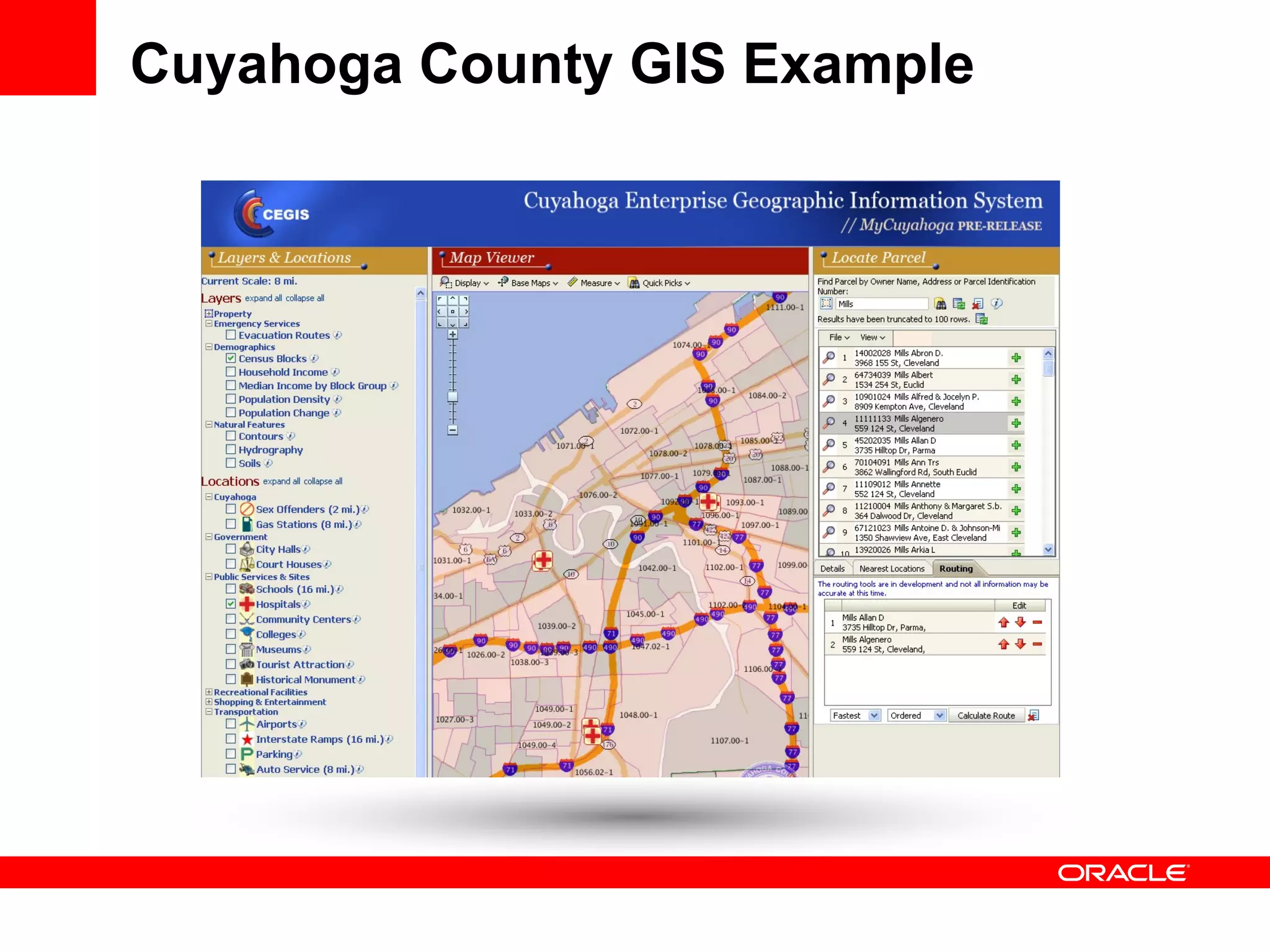
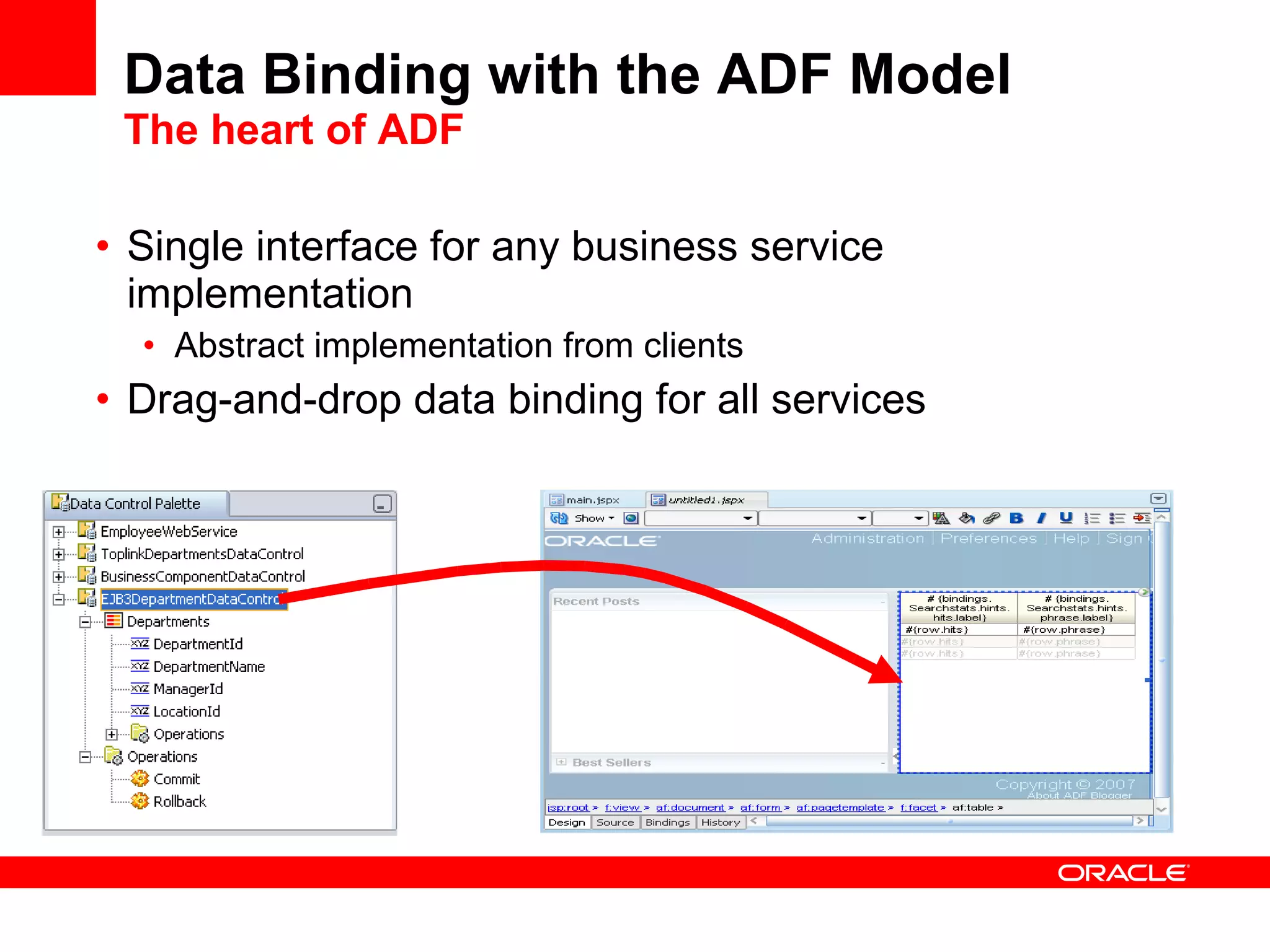
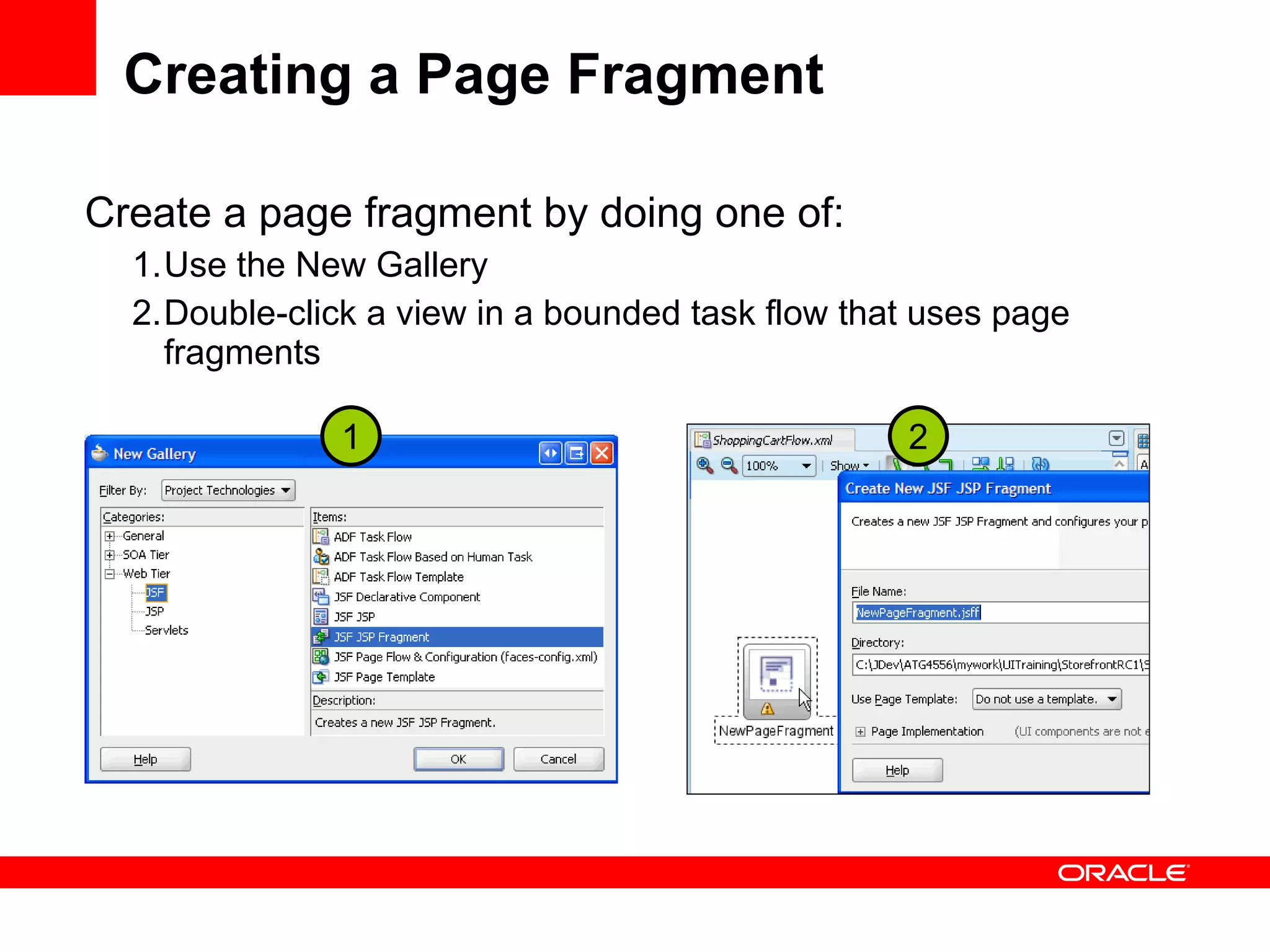
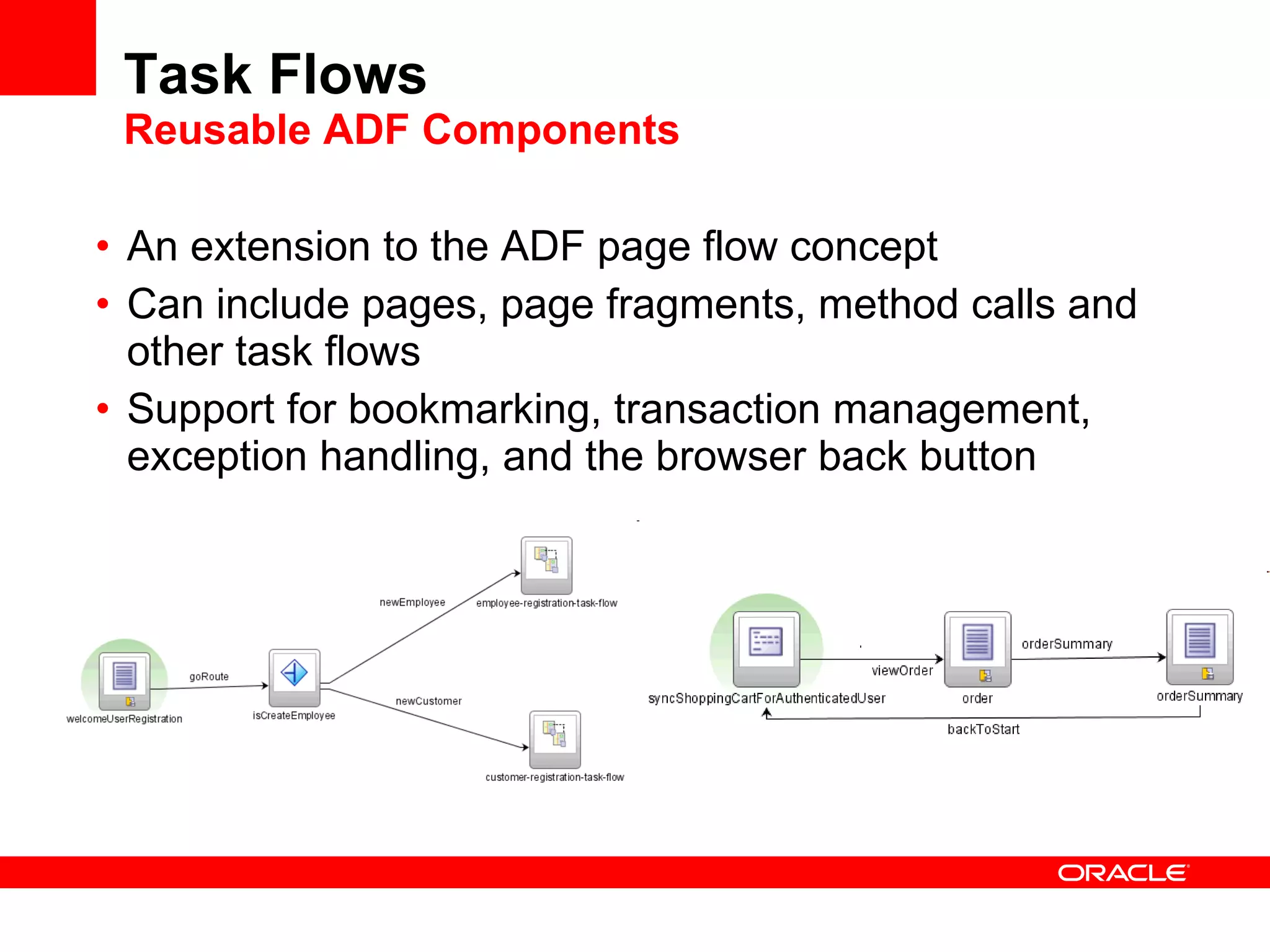
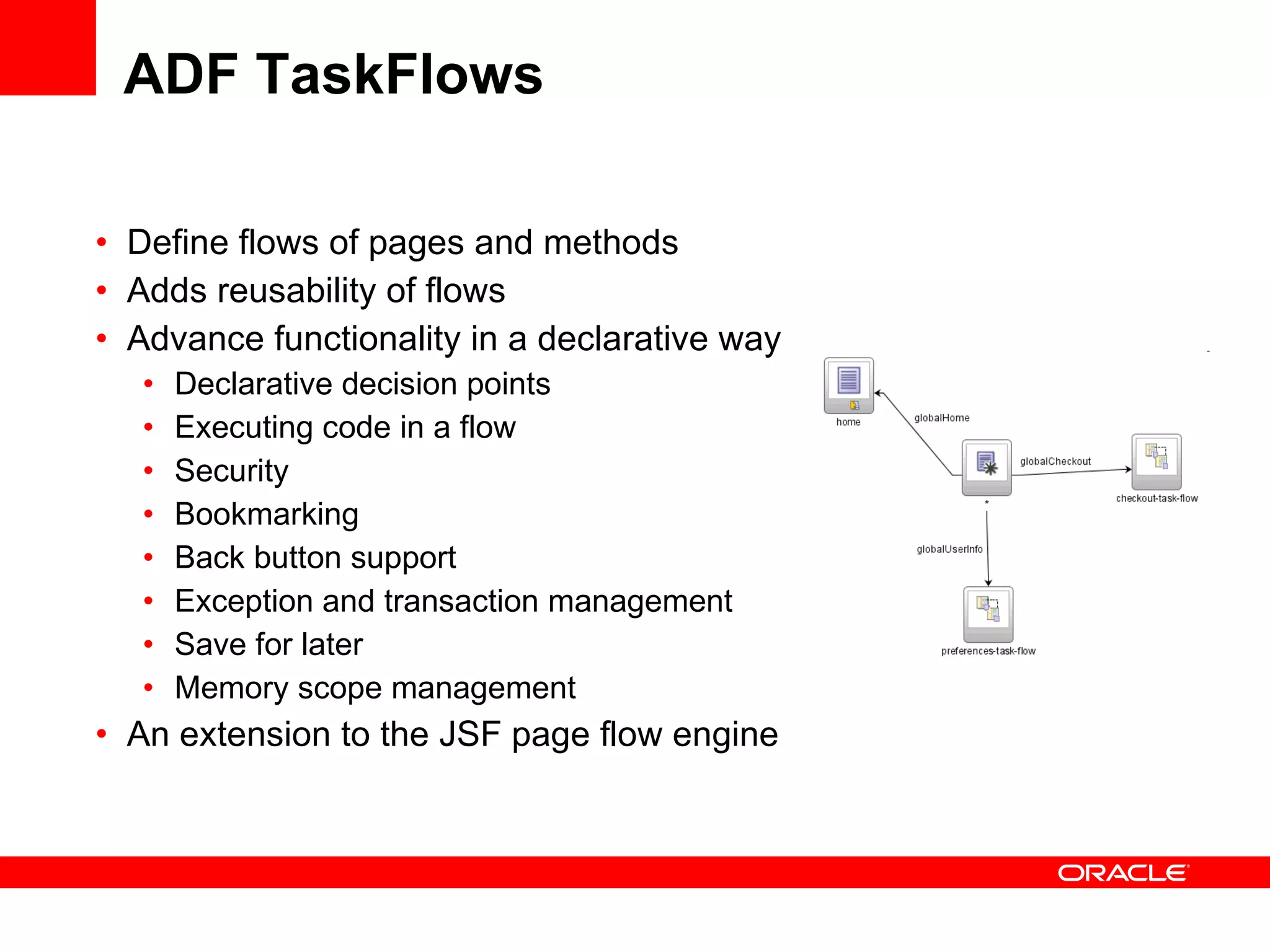
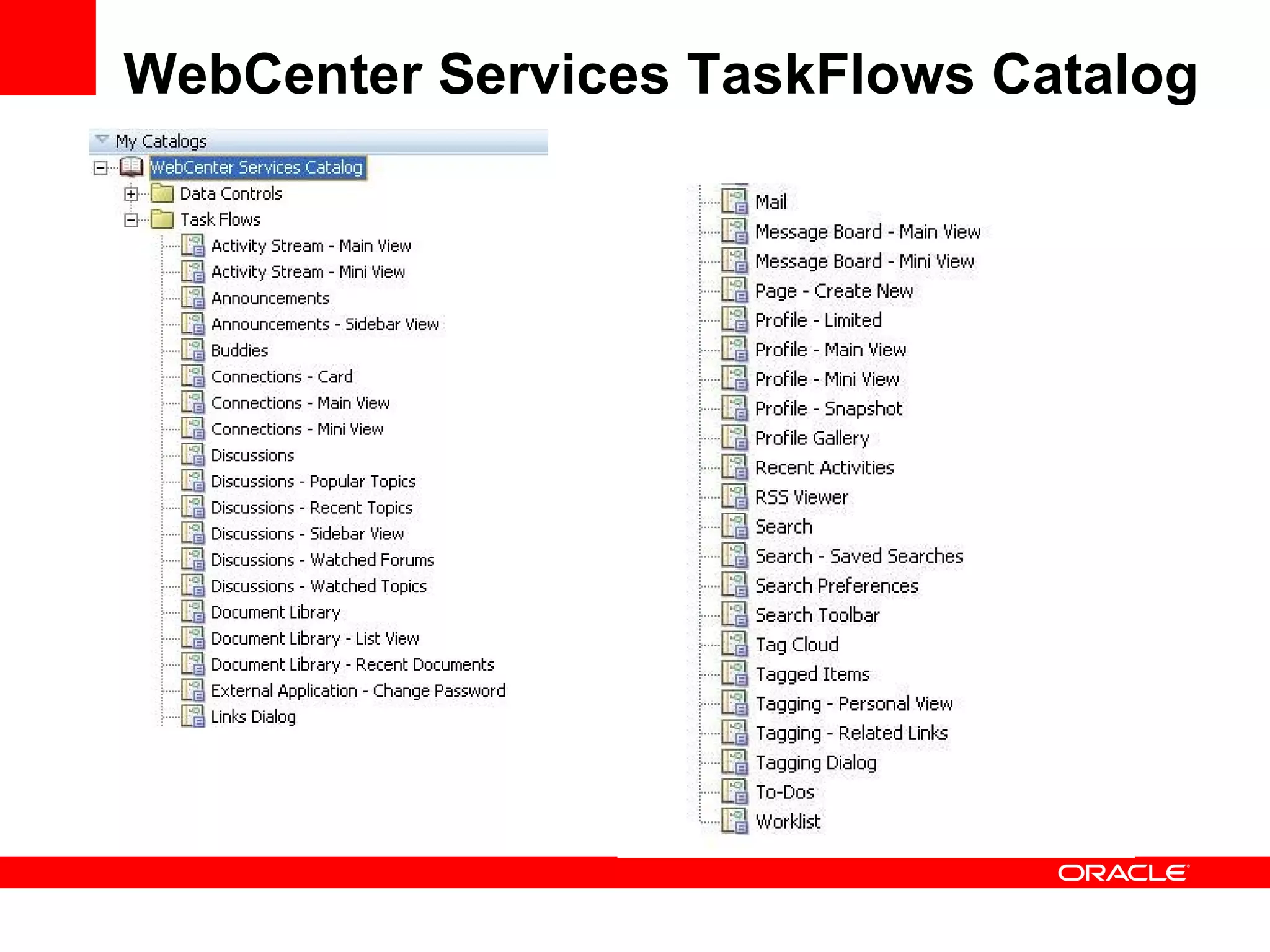
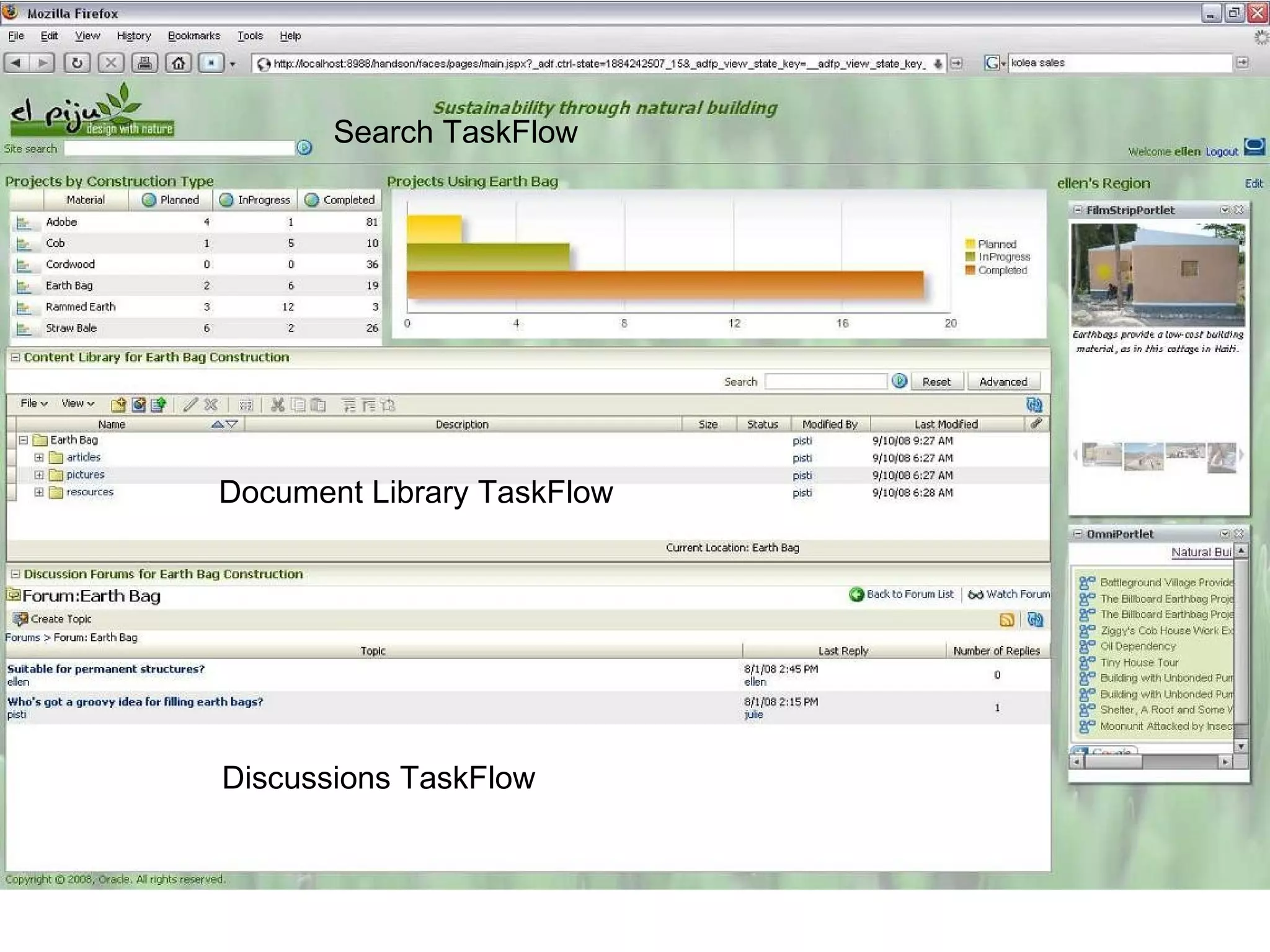
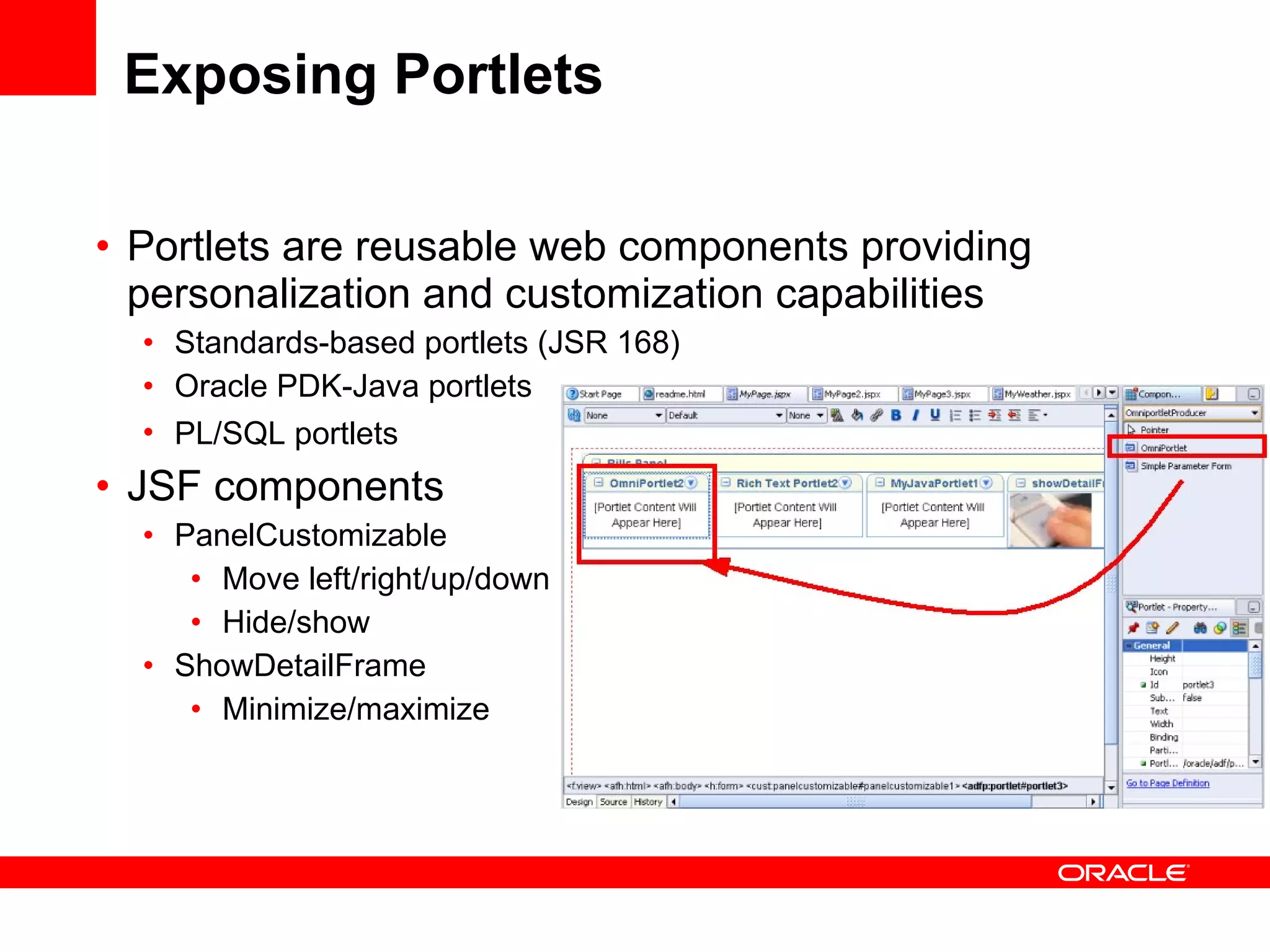
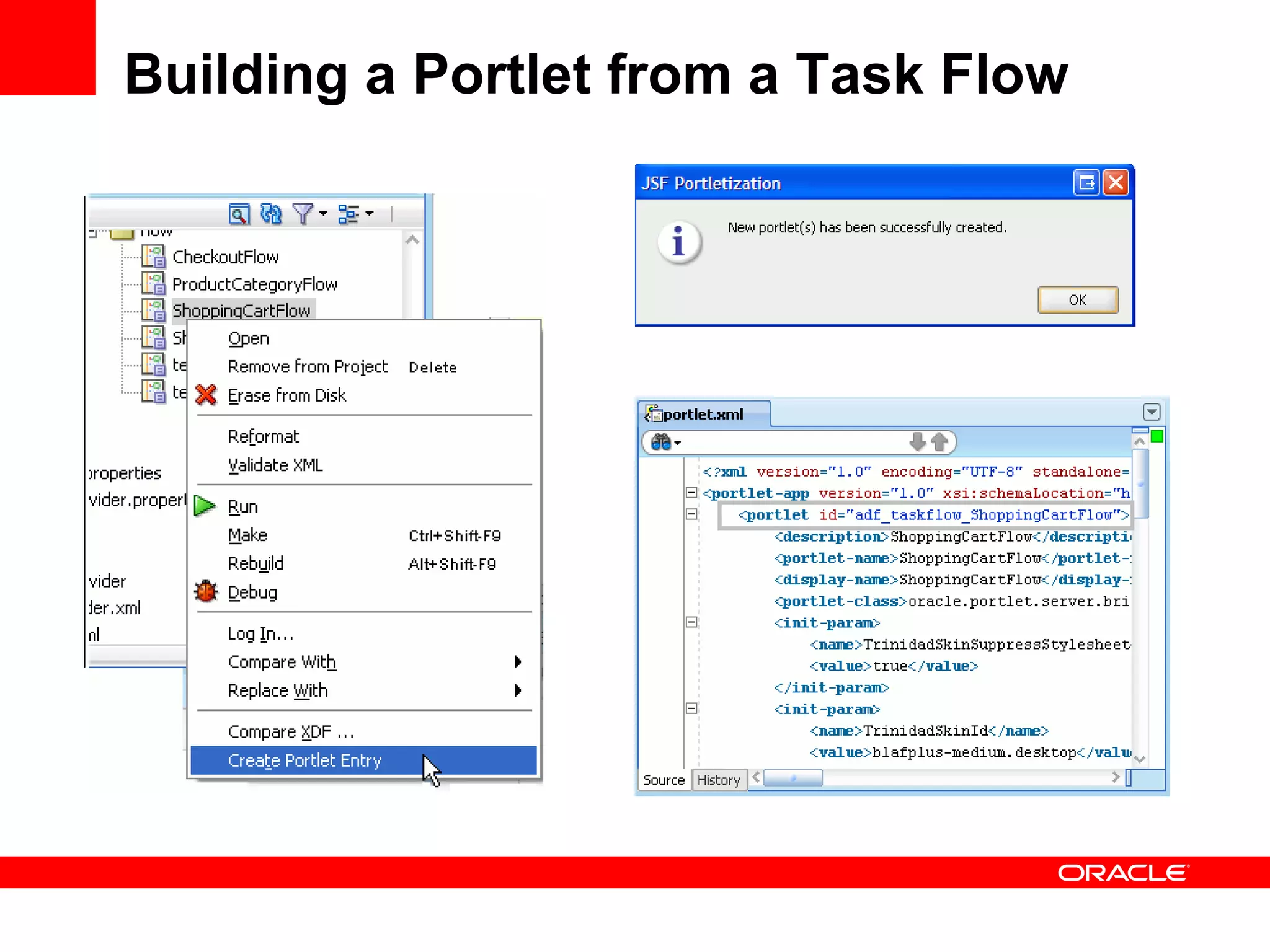
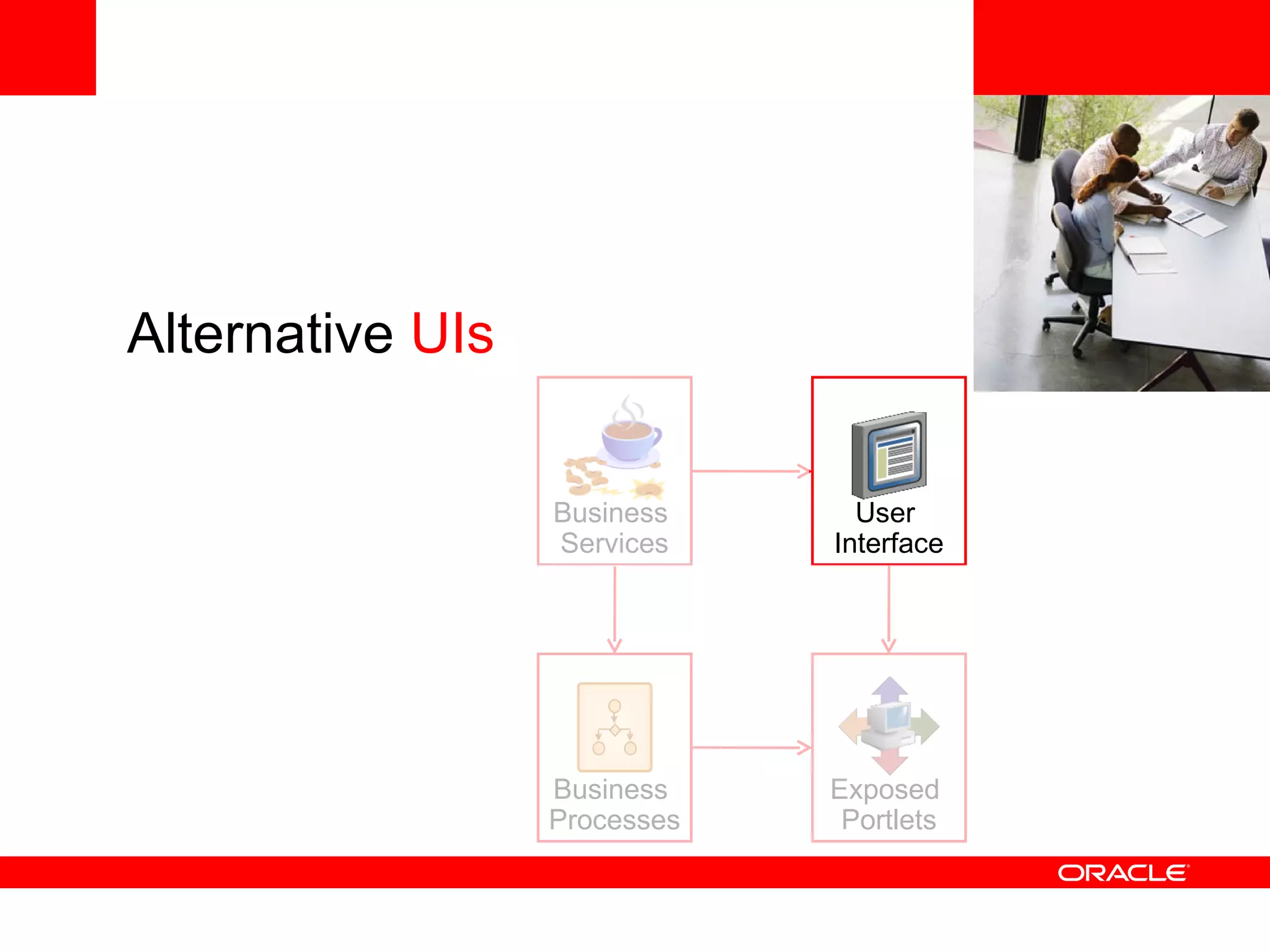
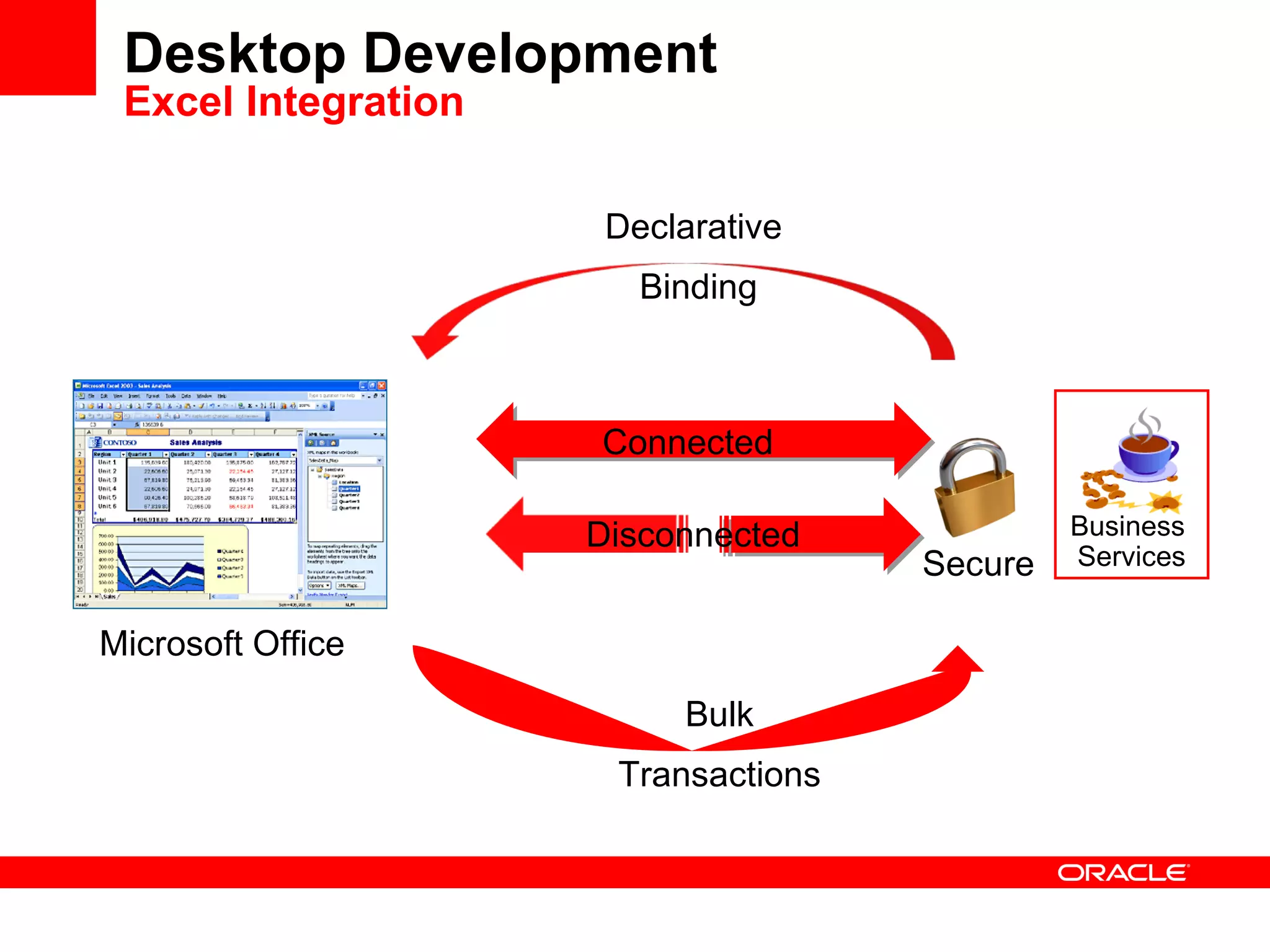
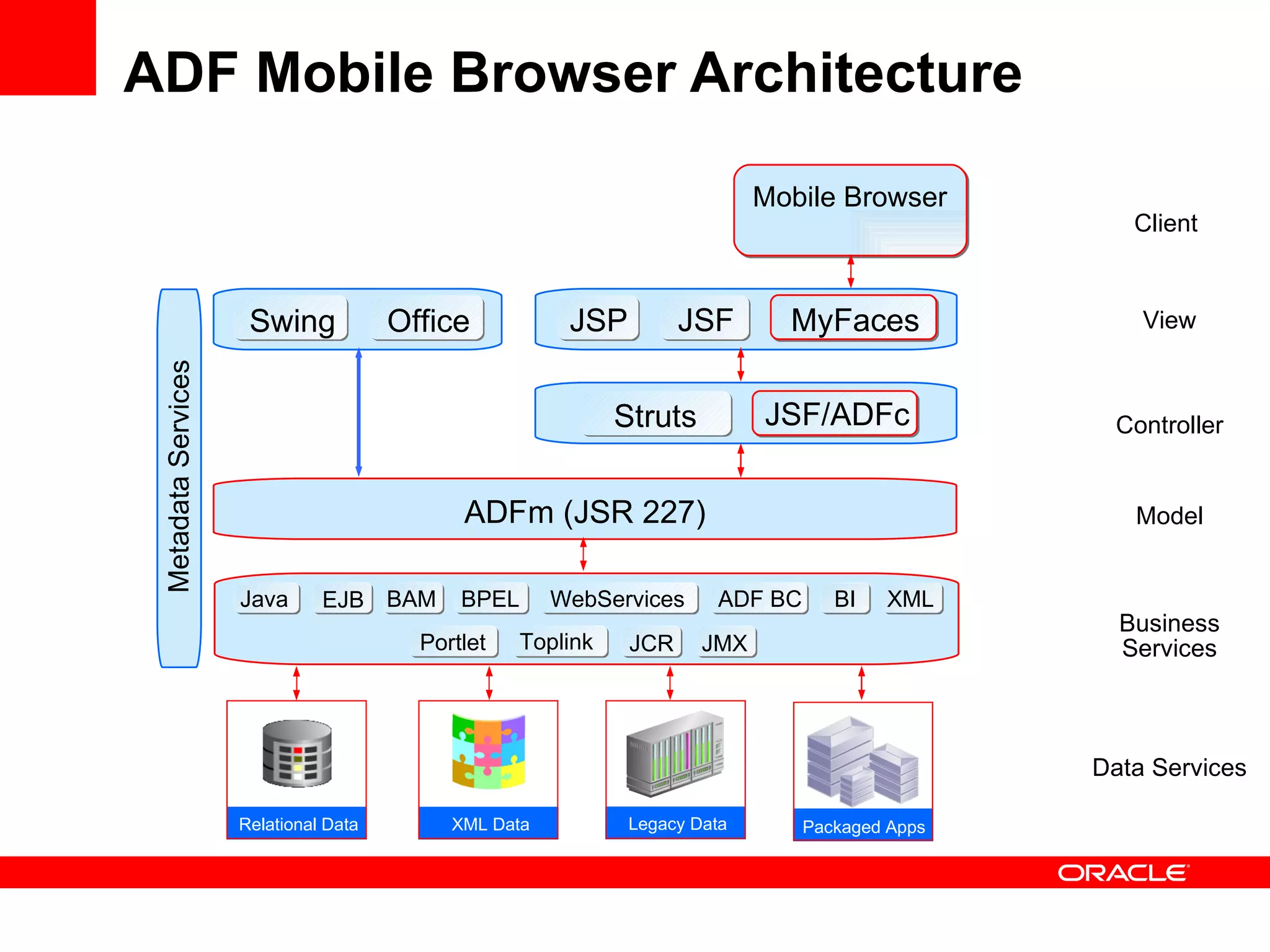
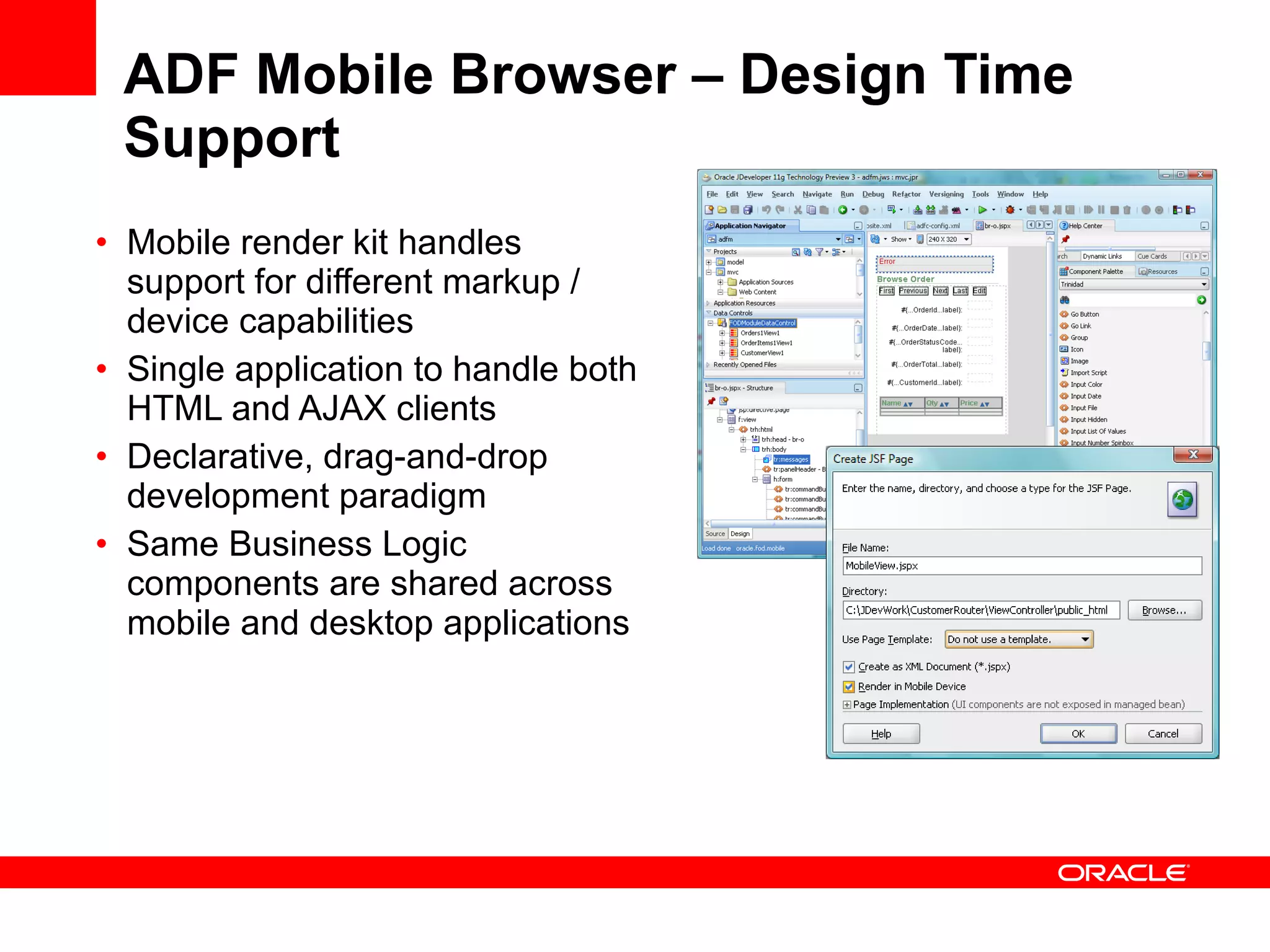
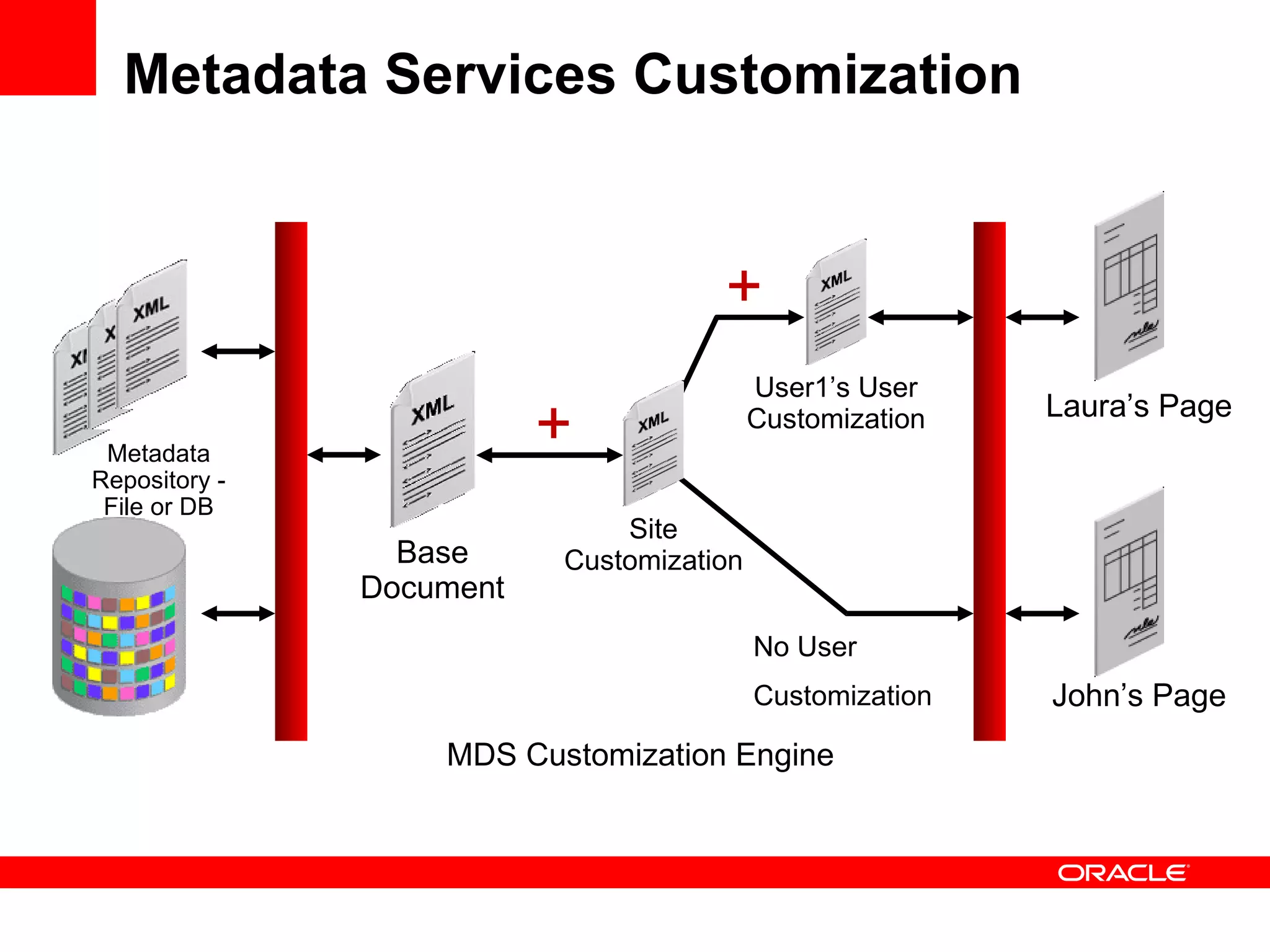
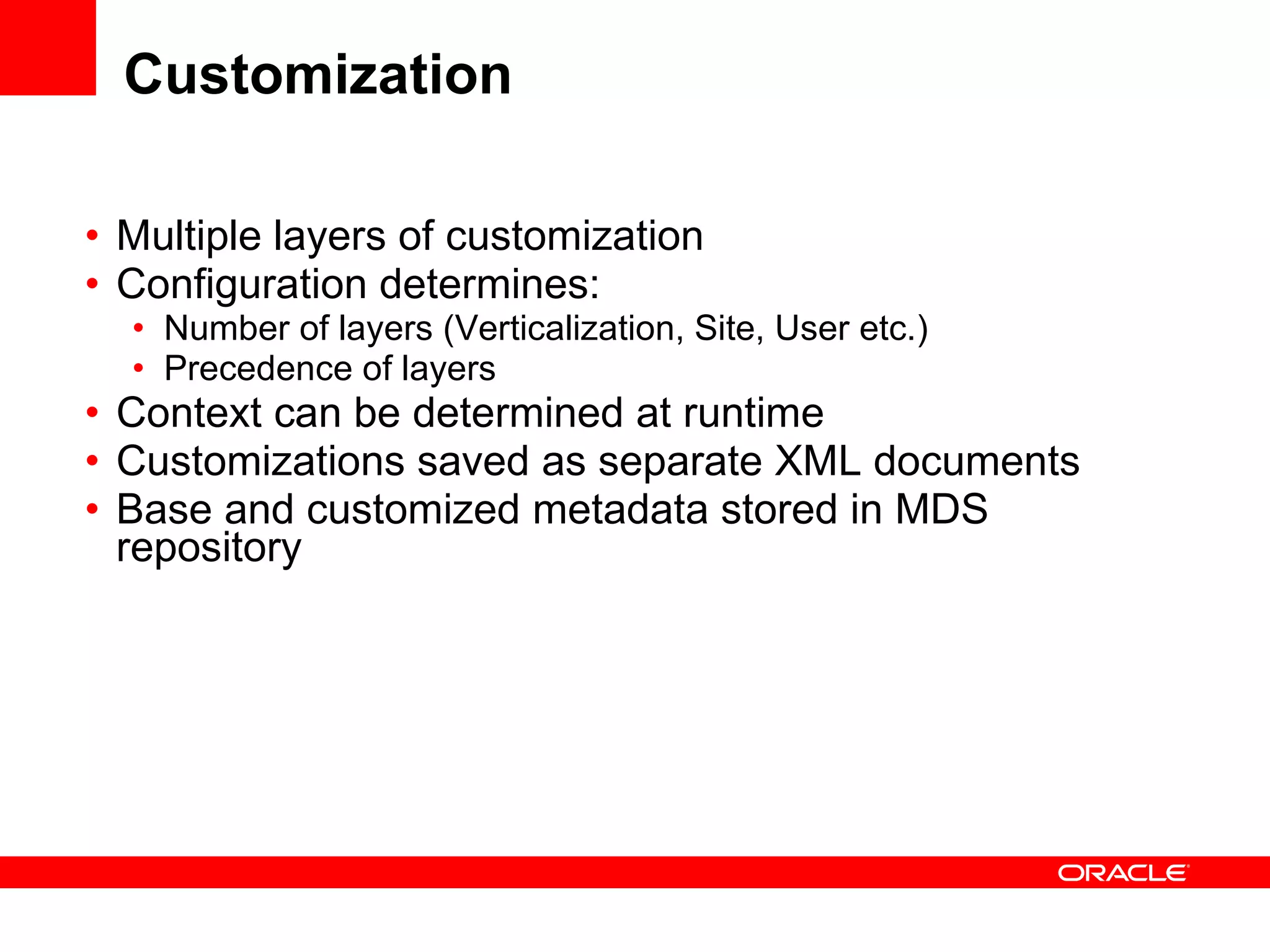
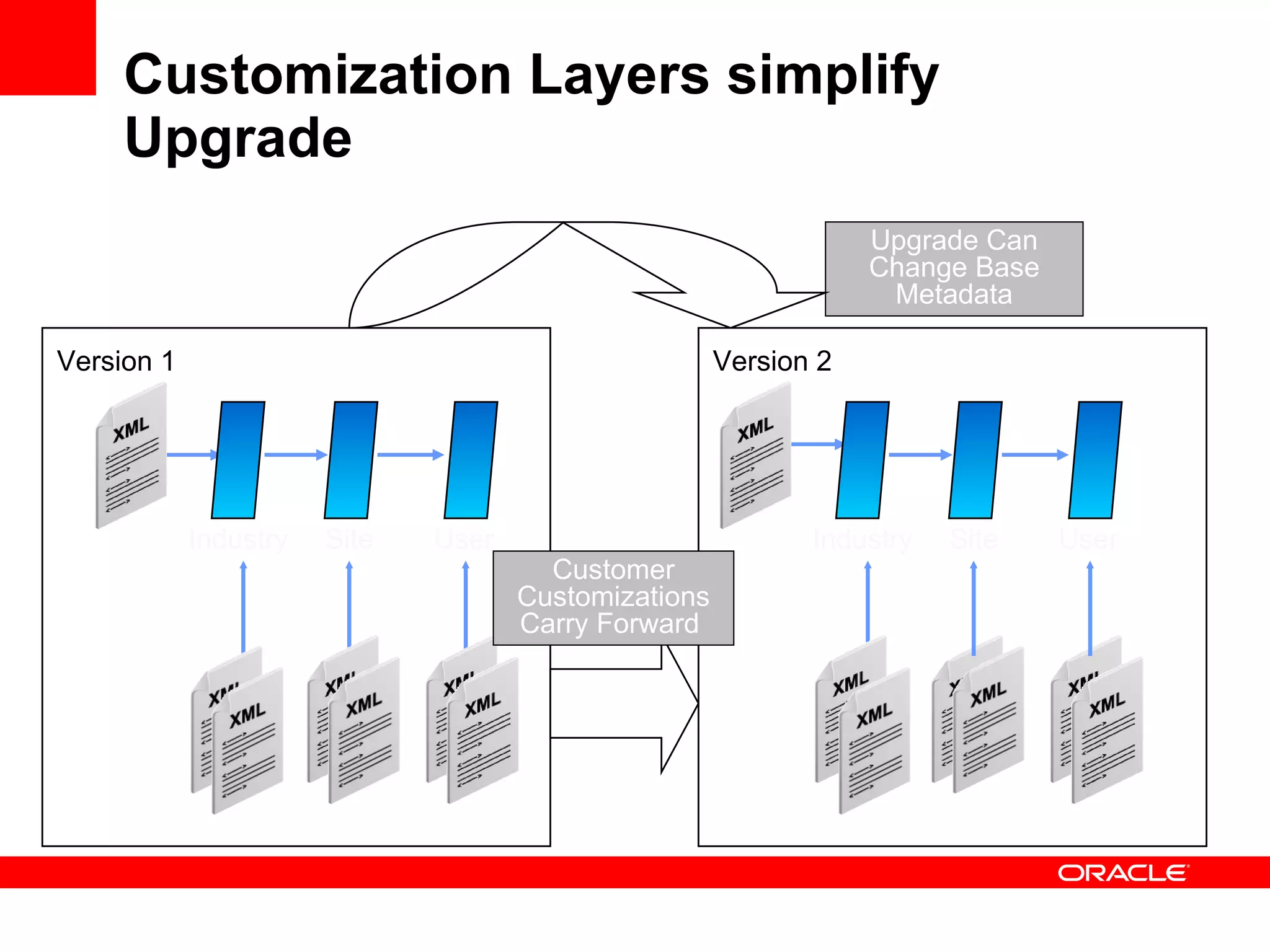
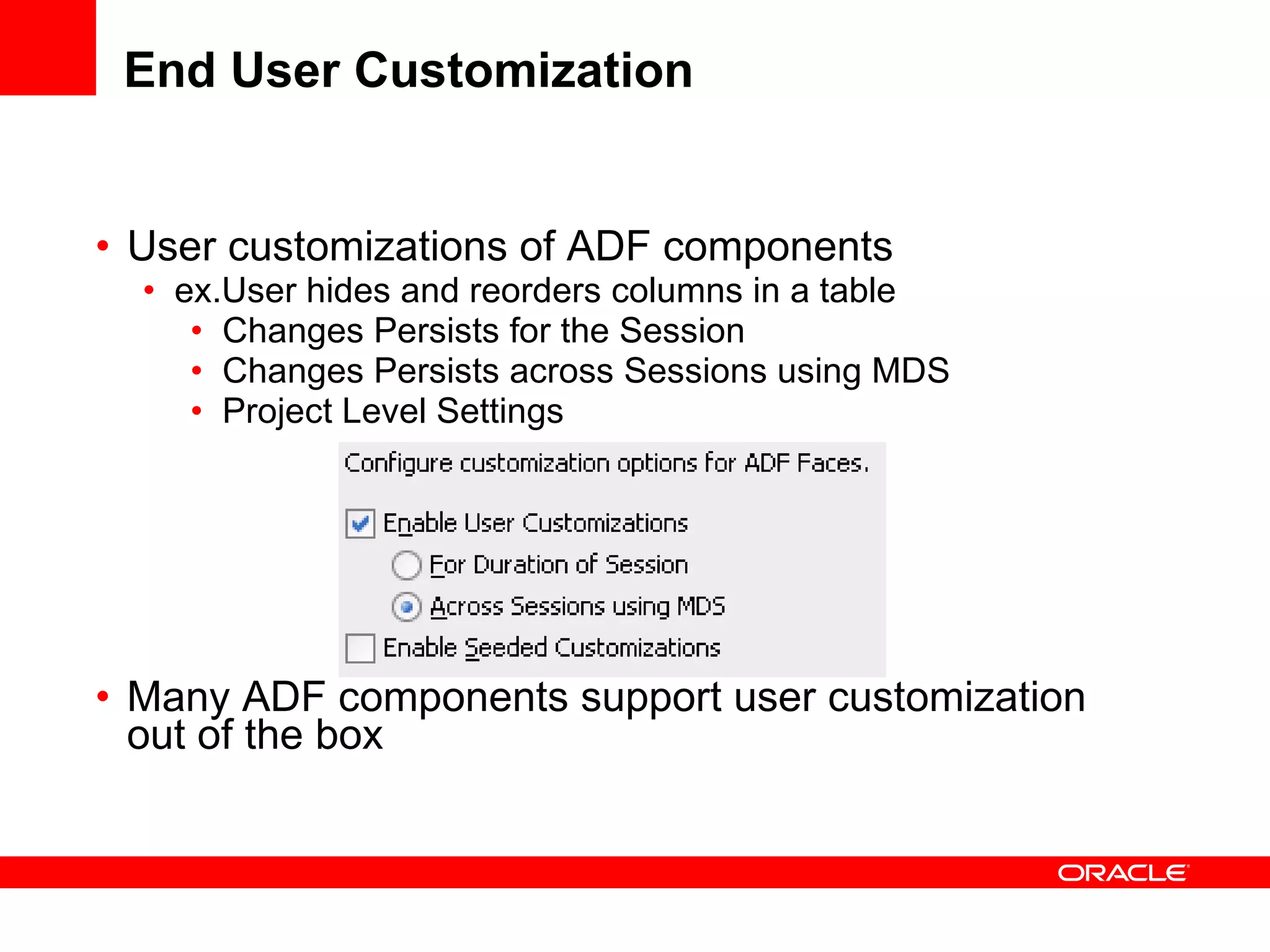
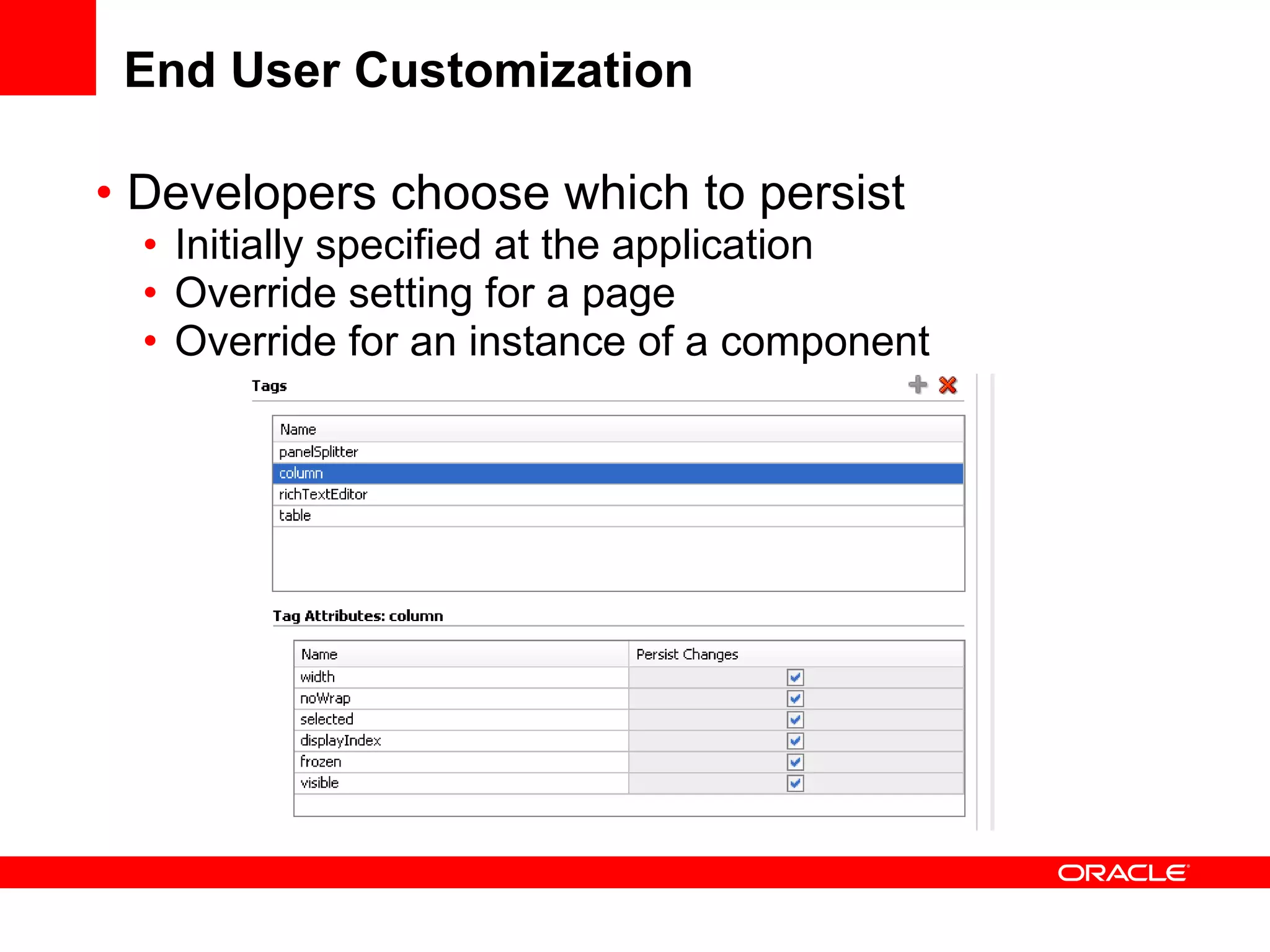
The document discusses Oracle's Fusion Development Platform. It provides an overview of Oracle as a company and its various software products. It then discusses Oracle Fusion Middleware and Applications, which aim to merge Oracle's acquired software like E-Business Suite, PeopleSoft, and Siebel into a single offering. The development of Fusion Applications involved thousands of developers over several years. The document outlines Oracle's vision and technologies behind Fusion, including the Java EE 5 stack, SOA, Web 2.0, and Oracle Fusion Middleware as the platform. It discusses features and components of the Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) for developing user interfaces, business services, and business processes on Fusion.