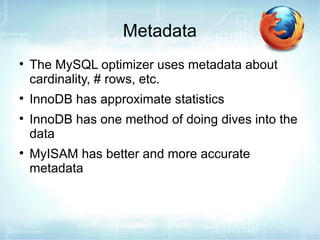
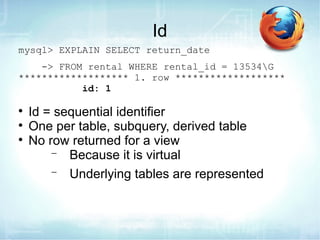
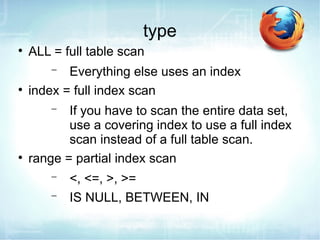
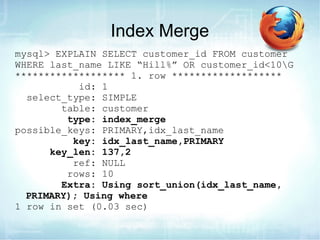
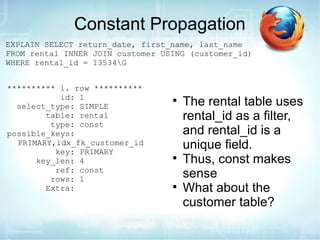
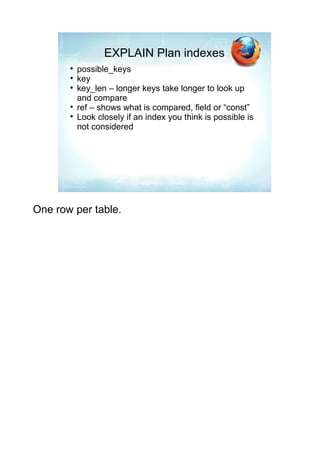
The document discusses how to use EXPLAIN to optimize SQL queries. EXPLAIN shows how tables are joined, indexes used, and records examined. It returns information like the number of tables, join types, and data access methods. The fastest strategies are const, which uses a primary or unique key to lookup at most one value, and eq_ref, which joins on a unique index. EXPLAIN helps identify inefficient queries to improve performance.