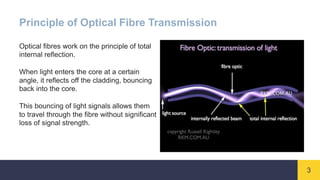
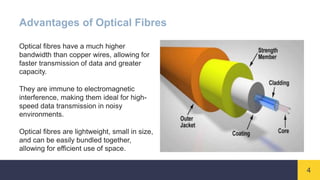
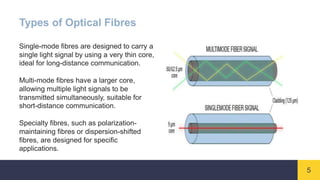
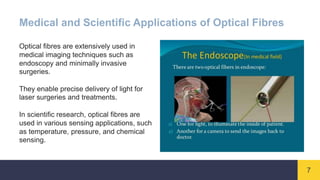
Optical fibres are thin, flexible strands of glass or plastic that transmit light signals over long distances. They consist of a core for transmitting light, a cladding layer surrounding the core with a lower refractive index, and an outer buffer coating. Optical fibres work on the principle of total internal reflection, where light entering the core at a certain angle reflects off the cladding, bouncing back into the core and allowing signals to travel through the fibre with minimal loss. Optical fibres are widely used in telecommunications and provide higher bandwidth and data transmission rates compared to traditional copper wires.