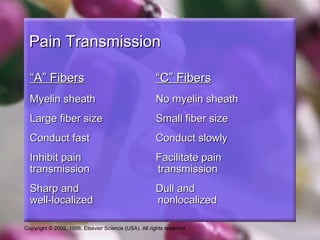
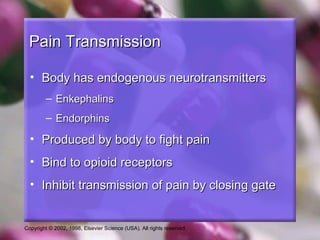
This document discusses pain and opioid analgesics. It defines analgesics as medications that relieve pain without causing loss of consciousness. It describes different classifications of pain including by onset, duration, source, and transmission pathways. The gate control theory of pain is explained, where large "A" fibers close the spinal gate and inhibit pain transmission while small "C" fibers open the gate. Opioid analgesics work by binding to opioid receptors in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and brain to prevent opening of the spinal gate and transmission of pain impulses. Common opioid analgesics and their mechanisms and side effects are outlined.