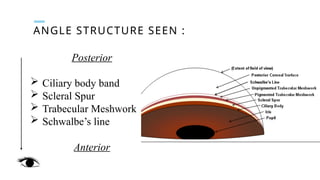
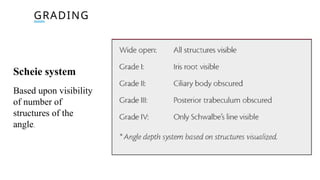
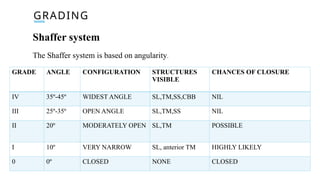
Gonioscopy is a biomicroscopic examination of the anterior chamber angle using a goniolens, essential due to the lack of transparency at the corneoscleral junction. There are two types: direct (for bedside use) and indirect (using a slit lamp), each allowing visualization of the angle structures via various gonioscopes. It aids in glaucoma classification, locating foreign bodies, and identifying tumors, but is contraindicated in cases of hyphaema or compromised cornea.