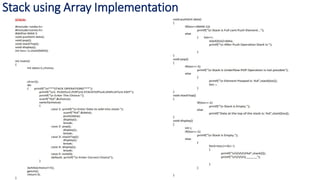
A stack is a linear abstract data type that allows insertion and removal of elements at one end, known as the top. It can be implemented using arrays or linked lists, providing basic operations such as push, pop, display, and stack top examination. The document includes example code for stack operations using static memory allocation with arrays.




![Implementation of Stack using Array(Static Memory
Allocation)
Step 1: initialization of Stack
#define MAX 5 //to define constant size of stack
//set of operations to be perform on stack(Function
Prototype)
void push(int data); // to insert data
void pop(); // to remove data or fetch data
void stackTop(); // to examine data on top of the stack
void display(); // to display all elements from stack
int tos=-1,stack[MAX];
5
4
3
2
1
0
MAX
tos -1
stack[MAX]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackdsa-240718045737-42ce5451/85/Operations-on-Stack-Stack-using-Array-and-Linked-List-6-320.jpg)
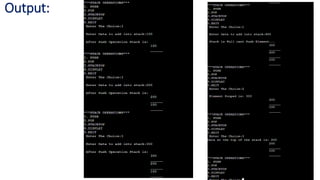
![STACK Operations: push() and pop()
void push(int data)
{
if(tos==(MAX-1))
printf("n Stack is Full cant Push Element...");
else
{
tos++;
stack[tos]=data;
printf("n After Push Operation Stack is:");
}
}
void pop()
{
if(tos==-1)
printf("n Stack is Underflow POP Operation is not
possible");
else
{
printf("n Element Pooped is: %d",stack[tos]);
tos--;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackdsa-240718045737-42ce5451/85/Operations-on-Stack-Stack-using-Array-and-Linked-List-7-320.jpg)
![STACK Operations: stackTop() and display()
void display()
{
int i;
if(tos==-1)
printf("n Stack is Empty.");
else
{
for(i=tos;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("n%d",stack[i]);
}
}
}
void stackTop()
{
if(tos==-1)
printf("n Stack is Empty.");
else
printf(“Top of the stack is: %d",stack[tos]);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stackdsa-240718045737-42ce5451/85/Operations-on-Stack-Stack-using-Array-and-Linked-List-8-320.jpg)