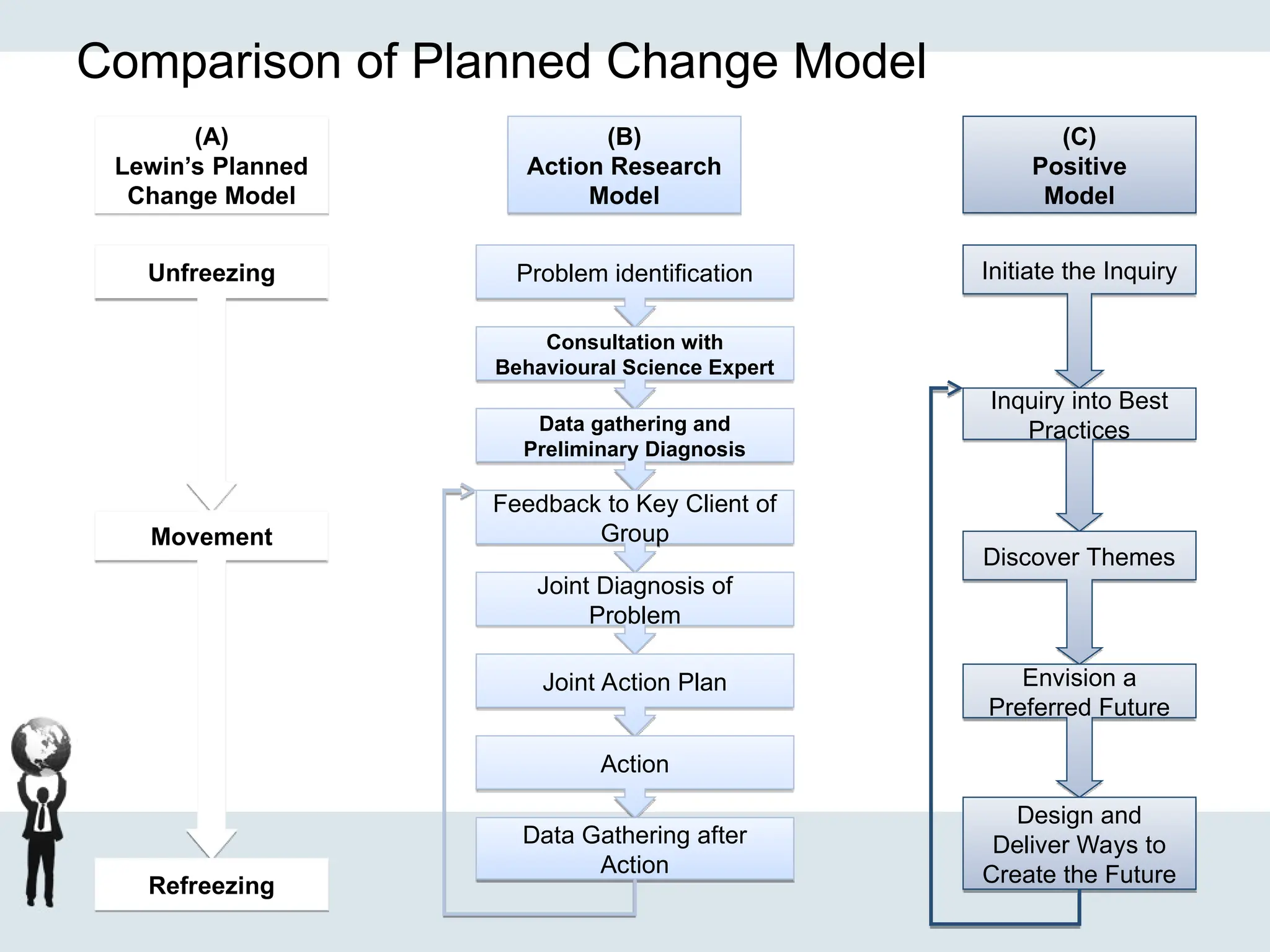
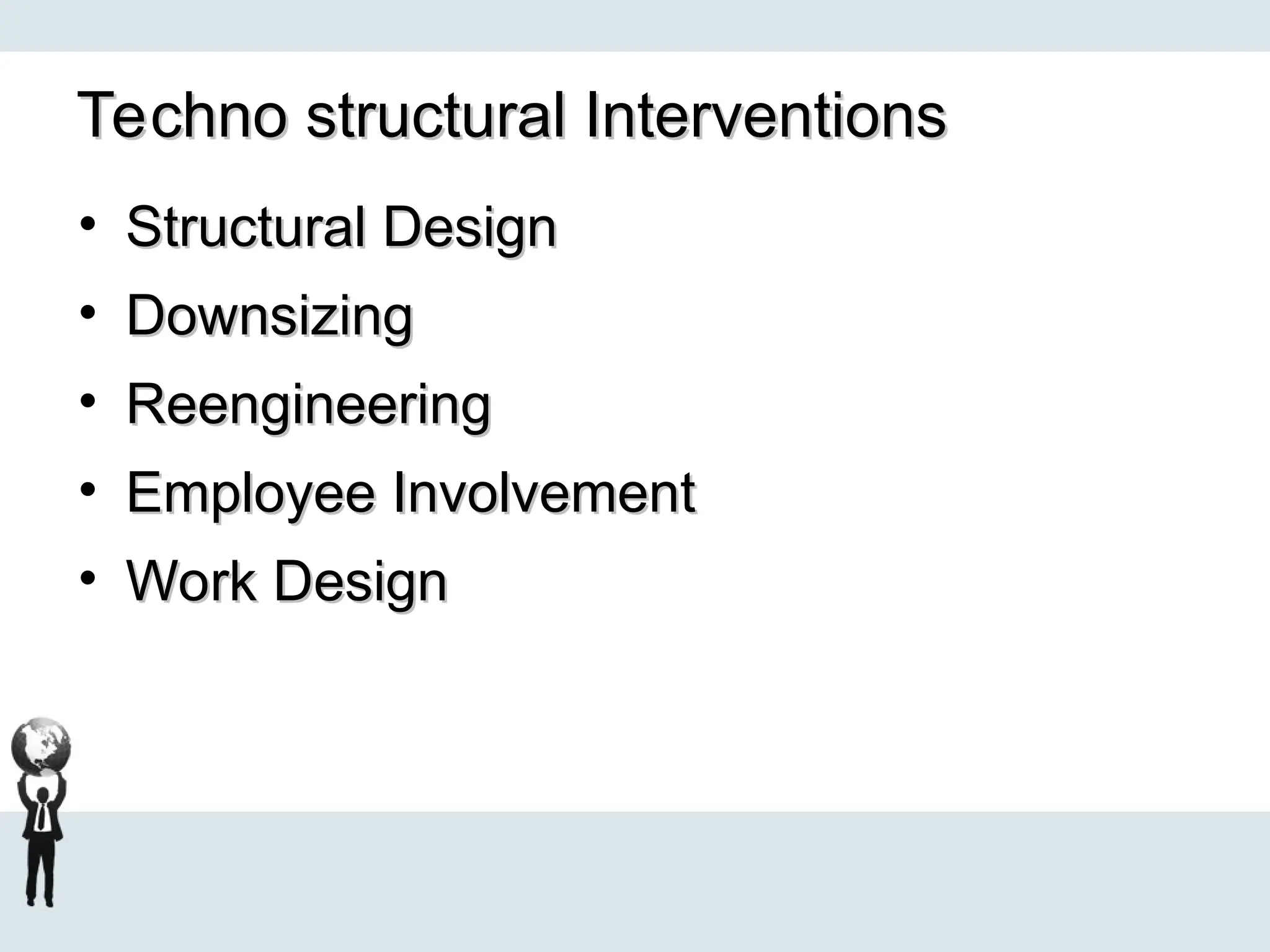
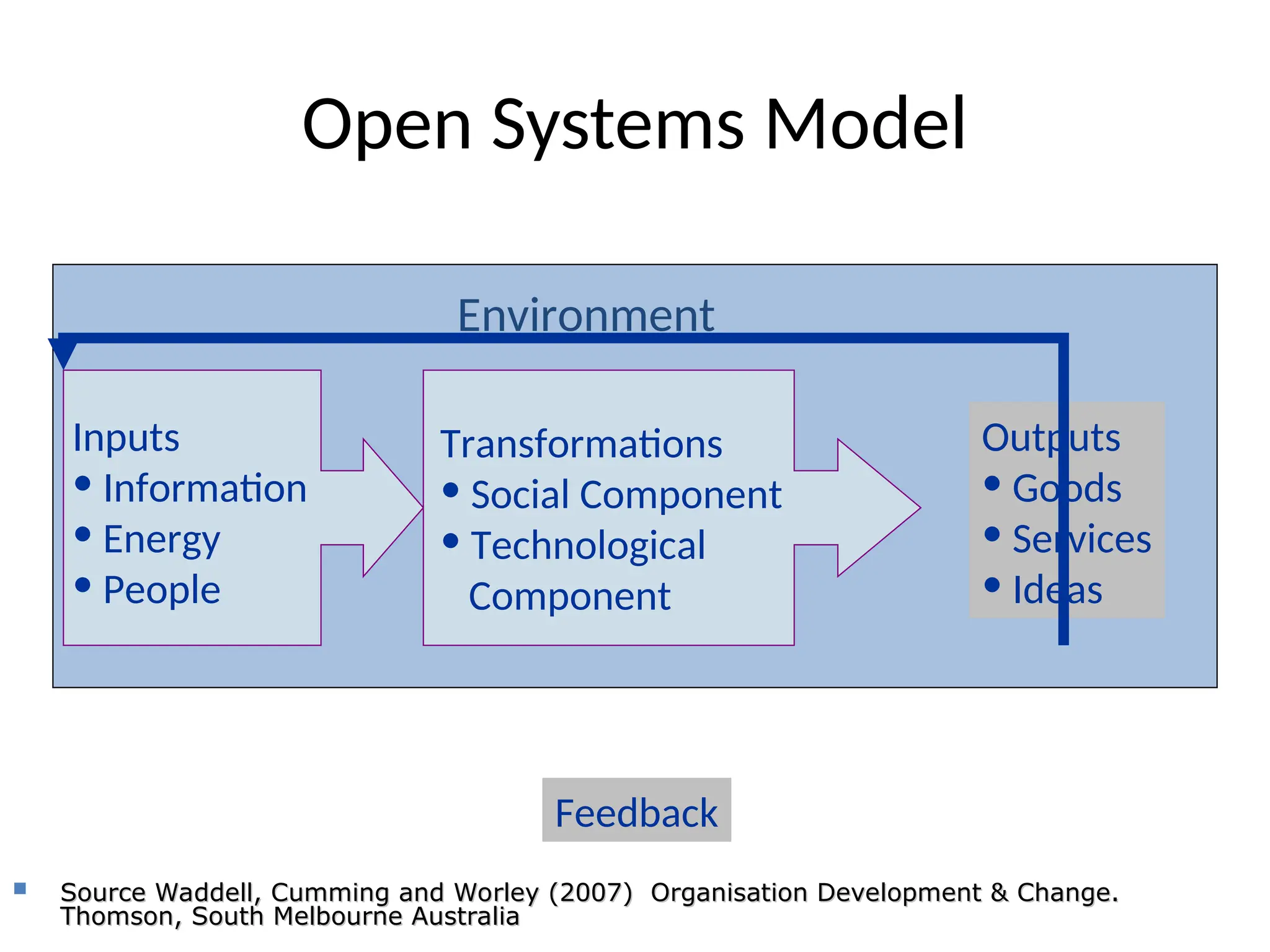
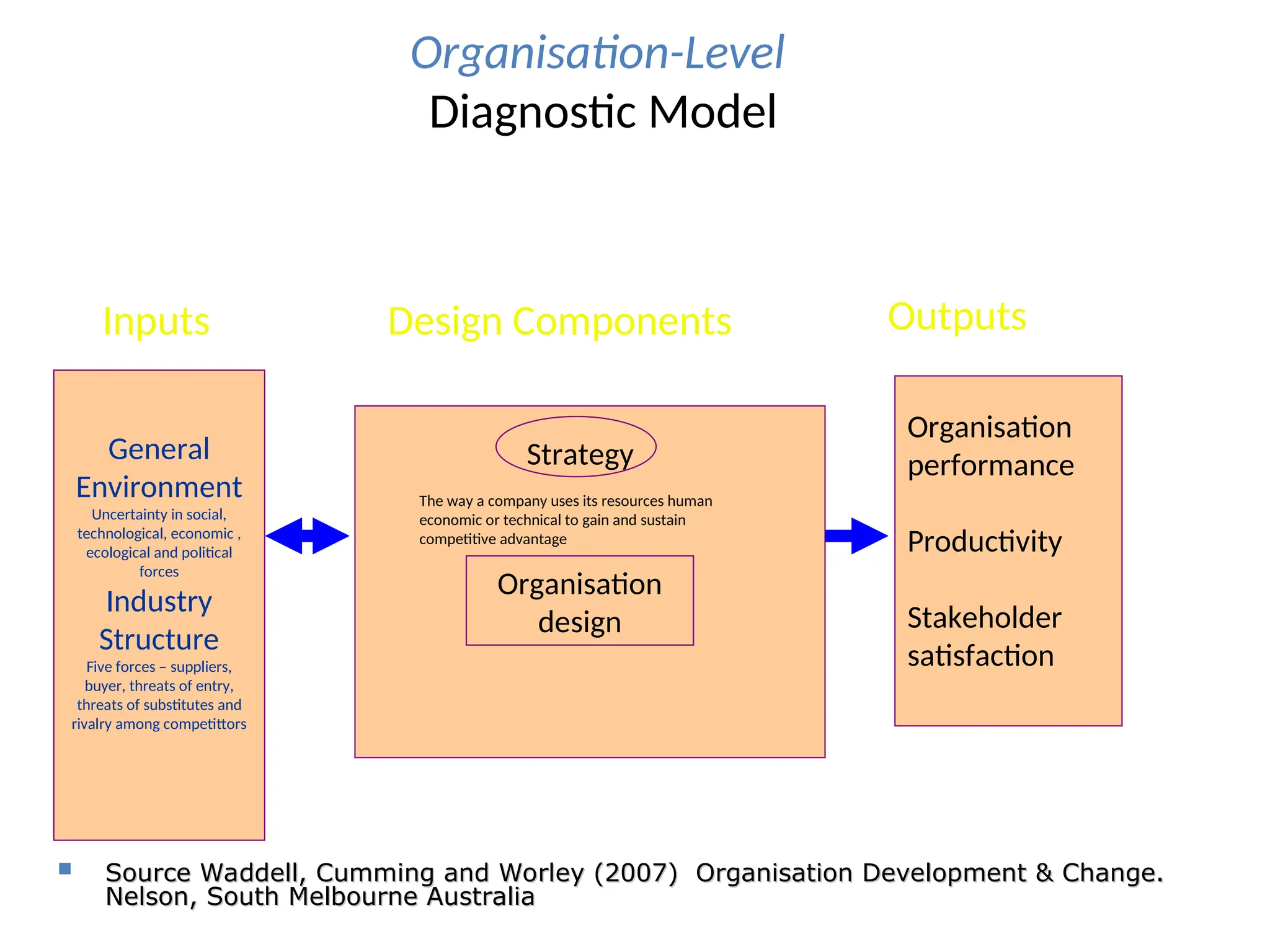
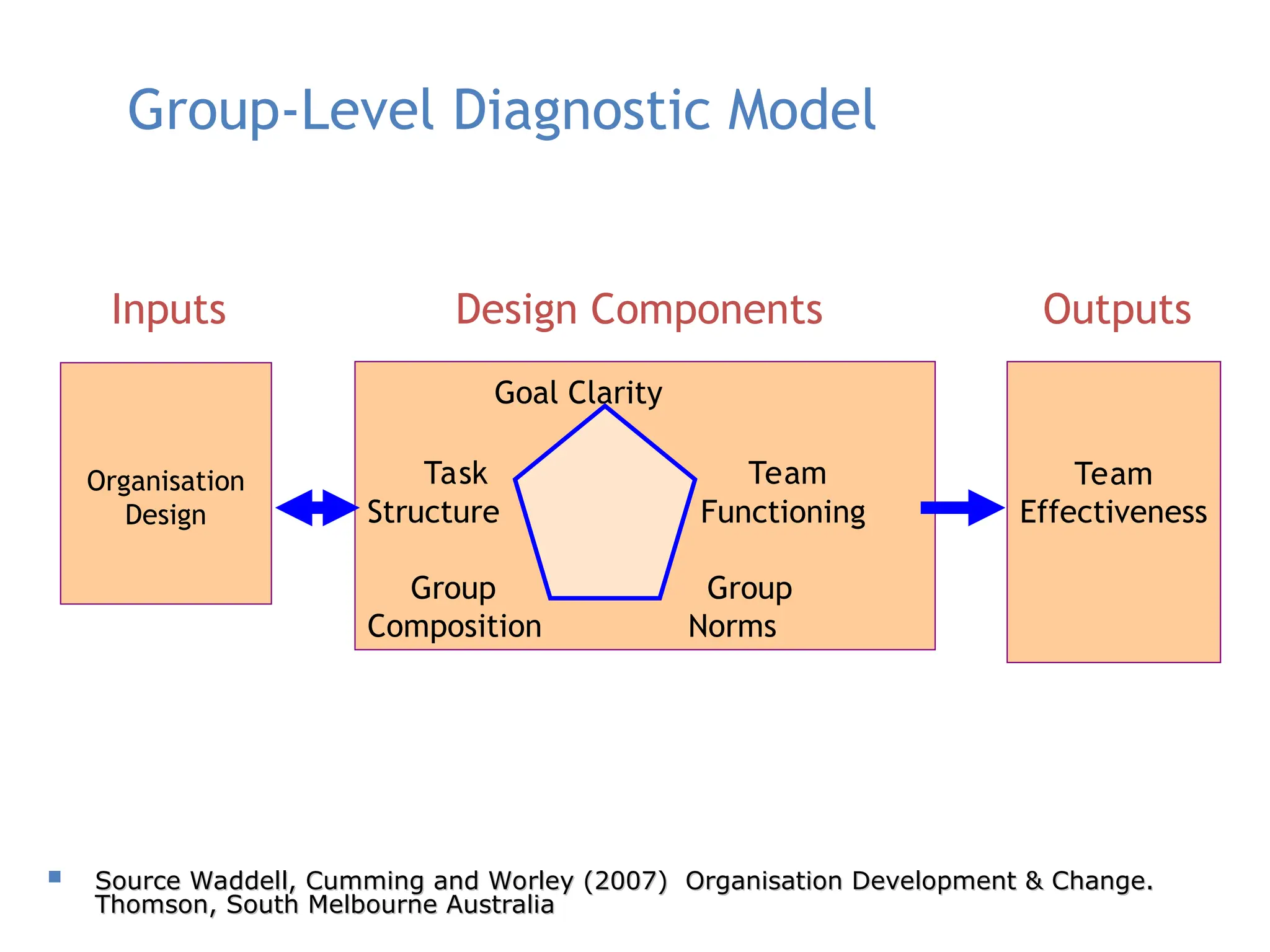
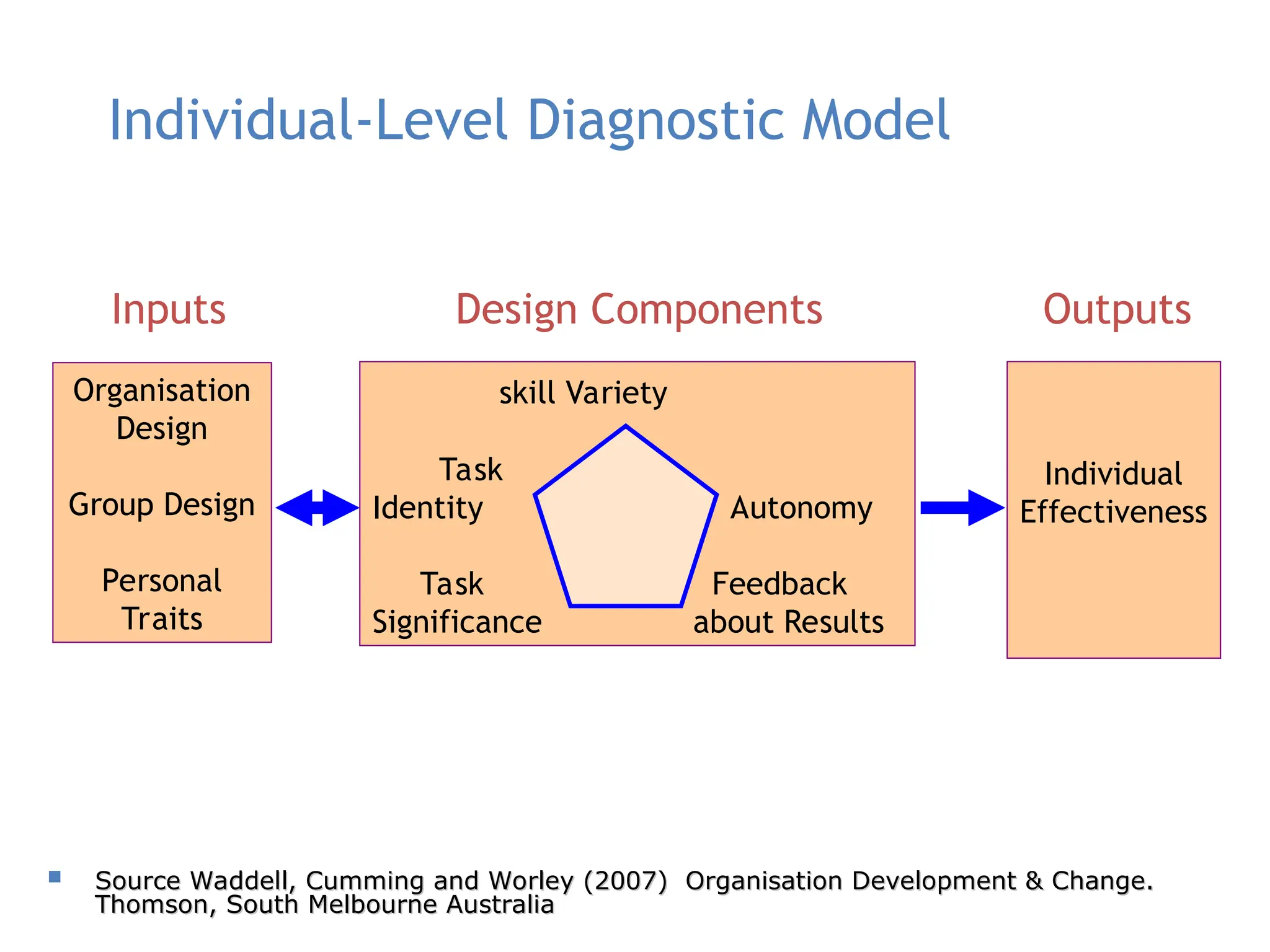
Examples of organizational development include leadership development, employee engagement, change management, and performance management.
Leadership development Improving employee skills, Promoting a positive work culture, and Aligning leadership with organizational goals.
Employee engagement Involving employees in decision-making, Seeking their input, and Valuing their contributions.
Change management
Guiding organizations through transitions
Mastering change management frameworks, tools, and techniques
Employee development Enhancing employee skills through work process improvements, Competency enhancement, Training, and Learning programs.
Feedback
Returning information to the learning management system
Using surveys to gather data
Using the data to better understand the situation and possible solutions
Improved organizational culture
Supporting experimentation
Rewarding creative problem-solving
Setting the tone for a culture that sees change as a pathway to growth
Performance management Setting expectations, Providing feedback, and Supporting employee development.
Encourage collaboration
Promoting teamwork and collaboration among employees, managers, and stakeholders