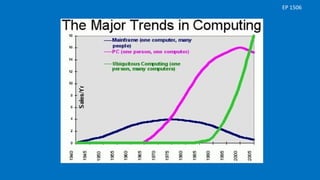
The document discusses ubiquitous computing, characterized by embedding microprocessors in everyday objects to facilitate communication and connectivity. It outlines the goals, characteristics, examples, advantages, and challenges associated with this technology, emphasizing user-friendly operating systems and the impact of the Internet of Things (IoT). Key devices highlighted include smartphones, smart home appliances, and wearable technology.