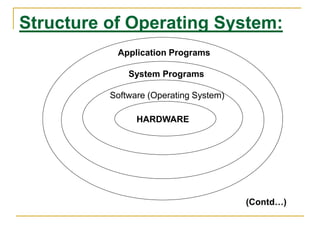
This document provides an introduction to operating systems. It defines an operating system as software that enables all computer programs to function and acts as an interface between programs and hardware. The document then lists and describes the main functions of operating systems, including controlling memory allocation, prioritizing requests, managing input/output devices, and more. Finally, it distinguishes between single-user systems that support one user at a time and multi-user systems that enable regulated access for multiple simultaneous users through user accounts and databases.