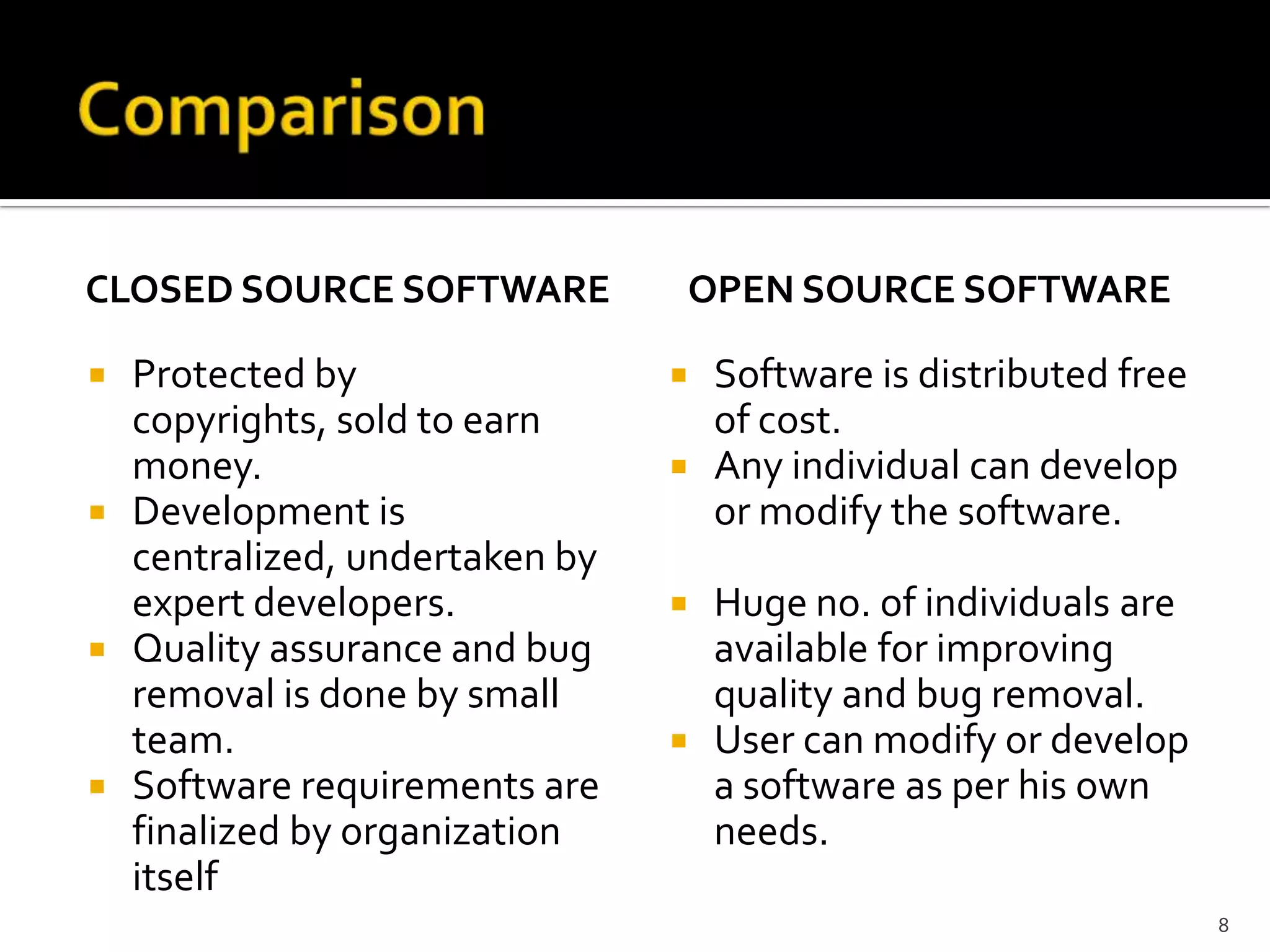
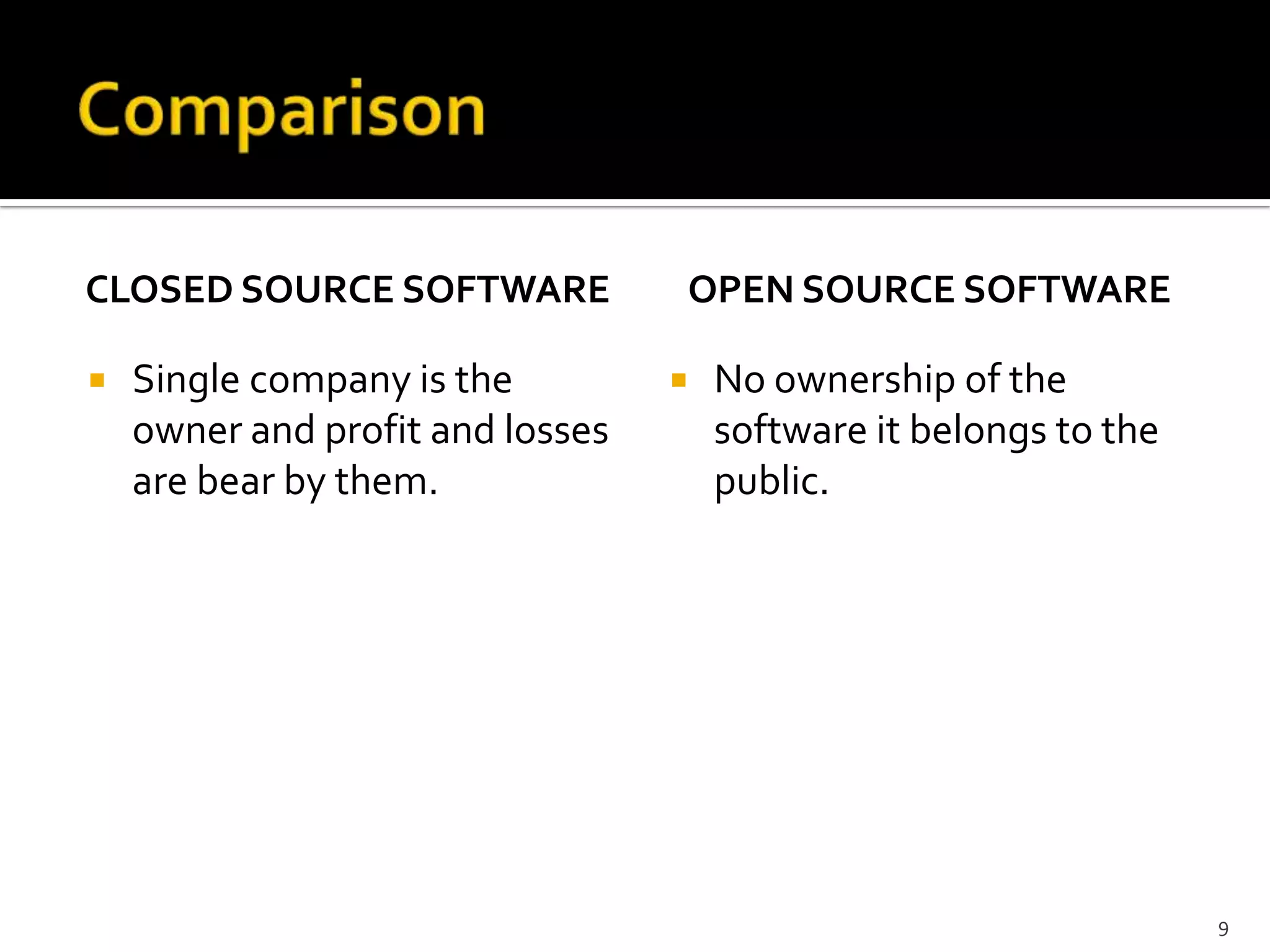
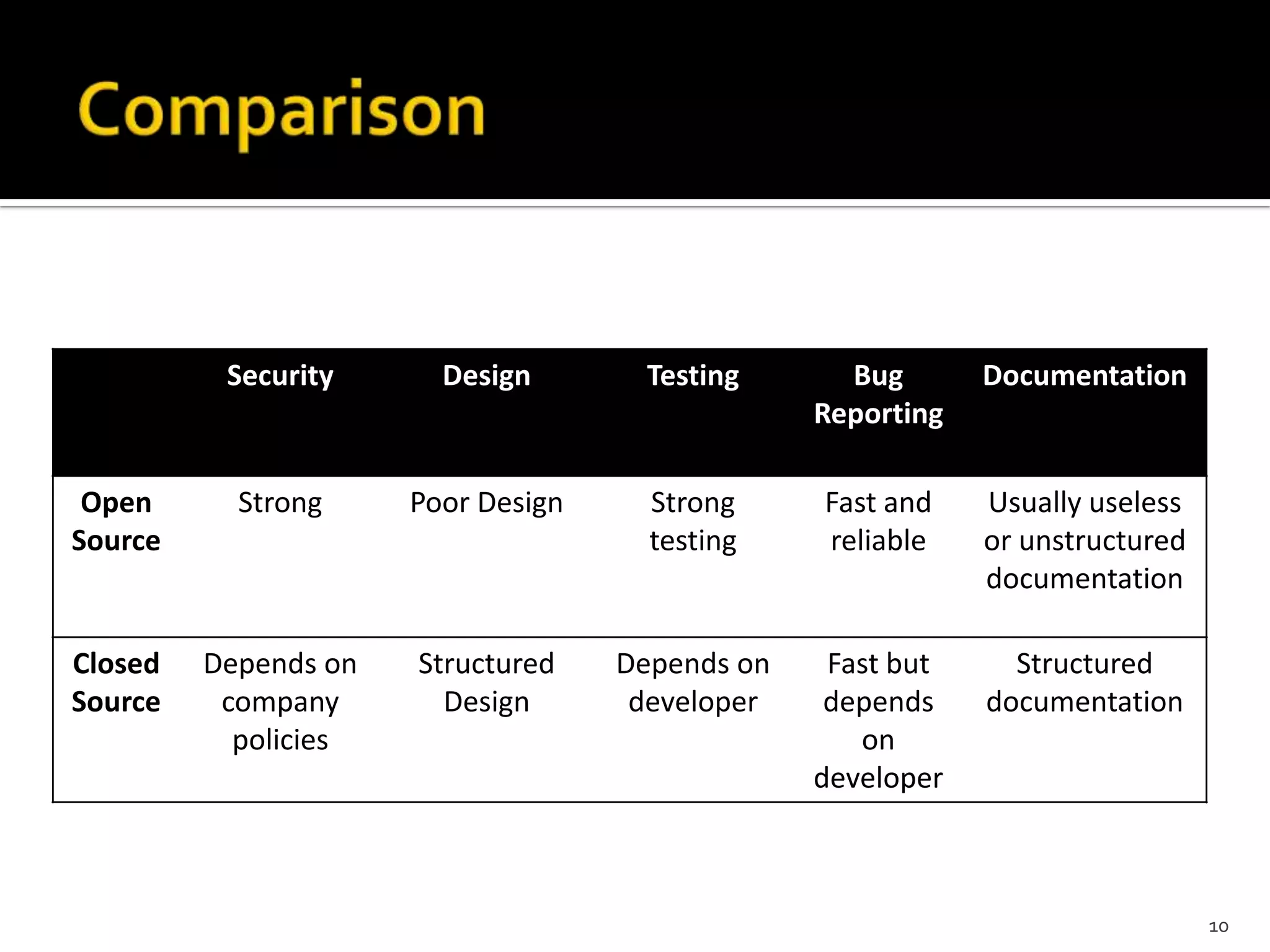
The document discusses open source and closed source software development. Open source software is developed by a distributed network of individuals contributing voluntarily, while closed source refers to proprietary software owned and developed by a single entity. The key advantages of open source include more contributors improving quality and fixing bugs, as well as users having the freedom to modify software for their needs. However, open source also faces challenges of coordination, lack of obligation for developers to remain with a project, and difficulties providing support and updates.









![ [*] Atieh Khanjani, Riza Sulaiman, 2011, The Aspects
of Choosing Open Source Versus Closed Source
A. de Groot, et al., "Call for Quality: Open Source
Software Quality Observation," in Open Source
Systems.
S. Raghunathan, et al., "Open source versus closed
source: software quality in monopoly and
competitive markets,“
blog.ecomsolutions.net/index.php/2007/12/18/disa
dvantages-of-open-source-software
13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osss-130512093223-phpapp02/75/The-Aspects-of-Choosing-Open-Source-Versus-Closed-Source-13-2048.jpg)
