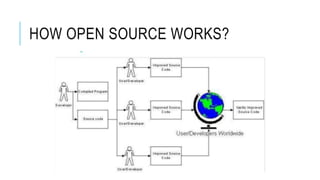
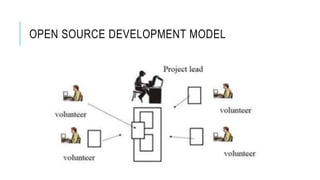
Open source refers to a philosophy of free access to software design and implementation details. It promotes sharing and modifying source code. Some key advantages of open source include availability of the source code, contributions from a large development community, lower costs, and greater customizability compared to proprietary software. However, open source software may require more learning and have issues with incompatibility or quality assurance. Popular examples of open source include Android, Linux, and open source digital content. Licenses like GPL determine how open source code can be used and distributed.