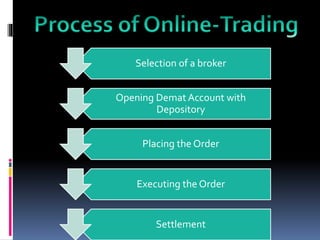
This document discusses online trading in securities in India. It begins by defining online trading as placing orders through internet trading platforms offered by broker members. It then outlines some key advantages like lower fees, more flexibility and control, avoiding brokerage bias, and access to online tools. Potential disadvantages discussed include risk of over-trading too quickly, lack of personal broker relationships, addictive nature, and internet dependency. The document also covers the process of online trading including selecting a broker, opening a demat account, order placement, order execution, and settlement.