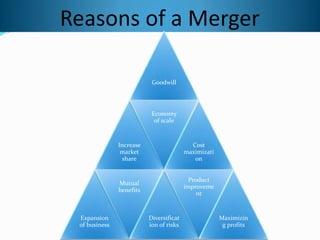
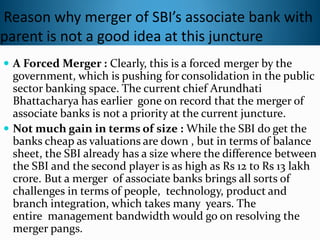
The document discusses the proposed merger of State Bank of India with its five subsidiary banks and Bharatiya Mahila Bank. It provides background on SBI and explains what a merger is. The proposed merger would make SBI one of the top 50 largest banks in the world by assets. However, some analysts believe the merger could initially increase SBI's operating costs and hurt profitability due to having to provide benefits to employees of the subsidiary banks. The merger aims to increase market share and competitiveness but may also be challenging to integrate different banks and their people, technology, products and branches.