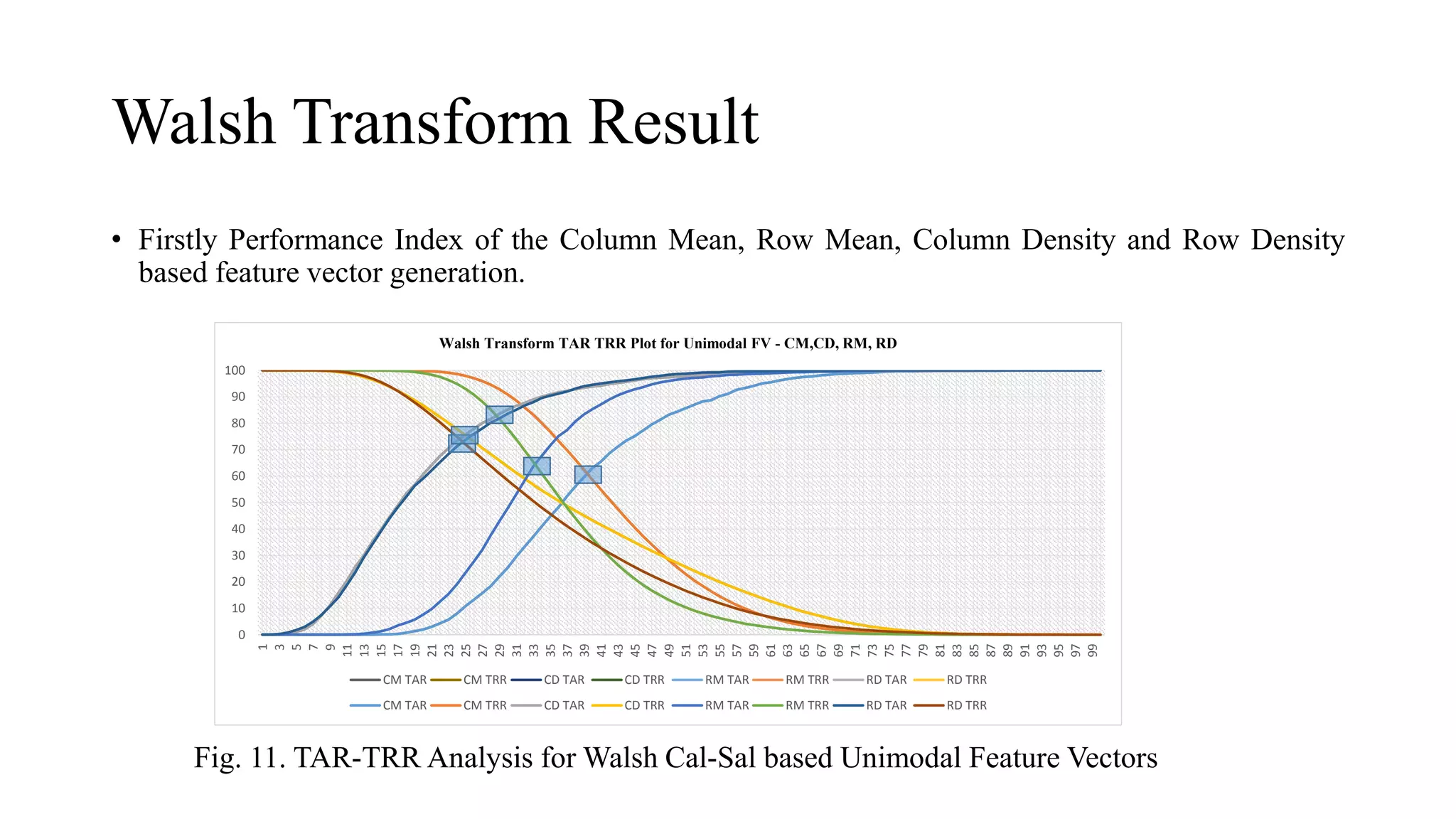
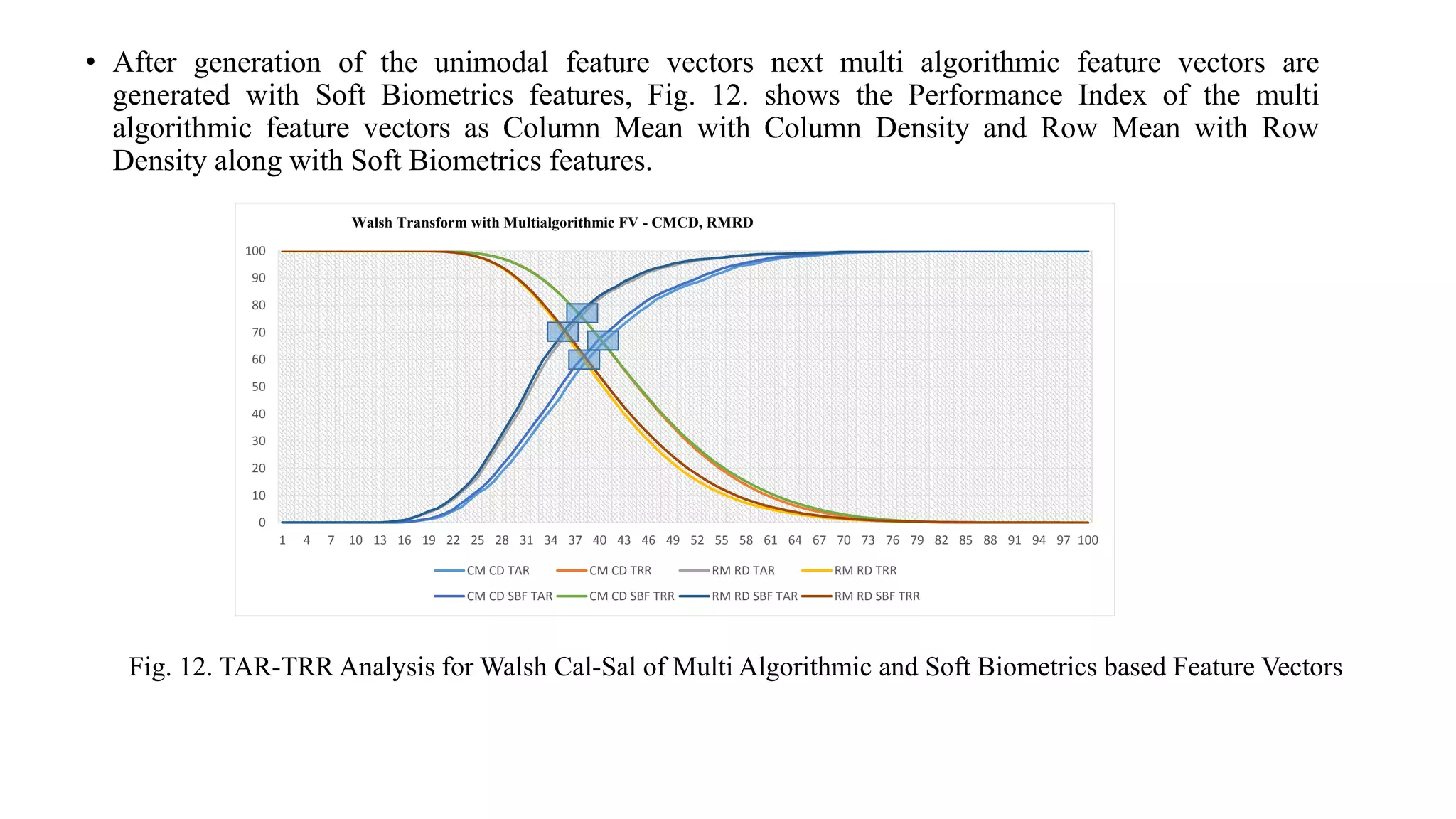
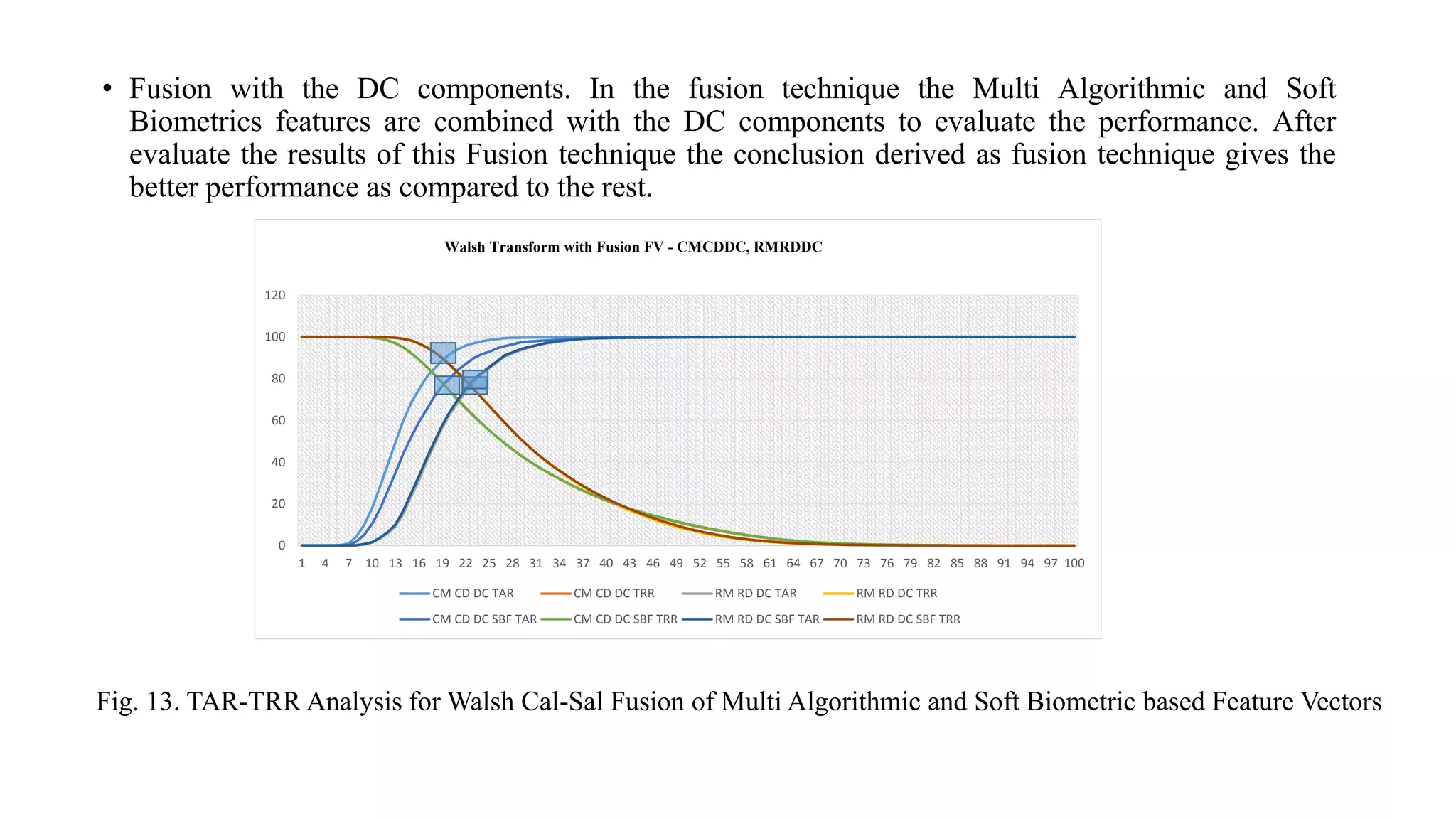
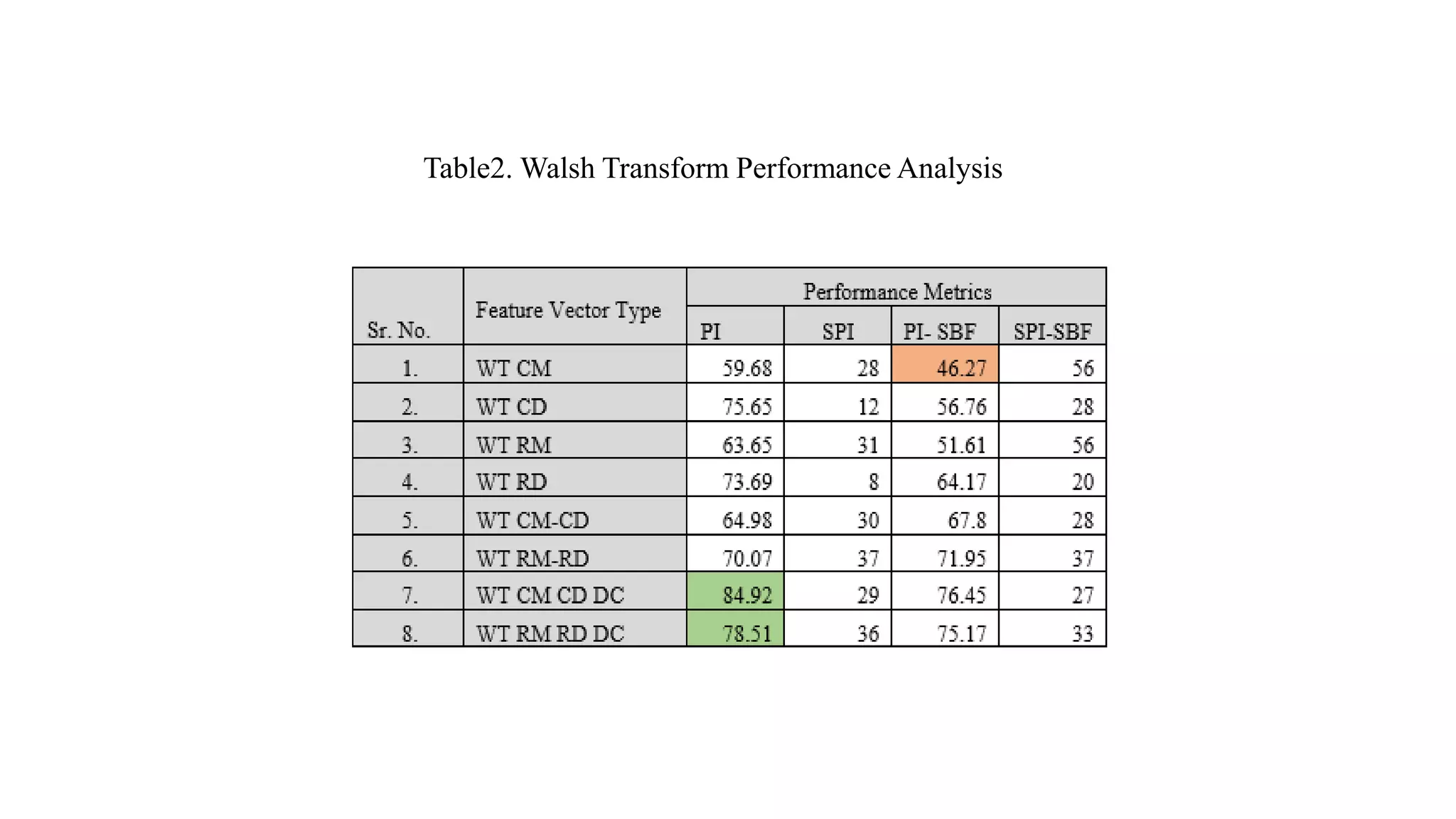
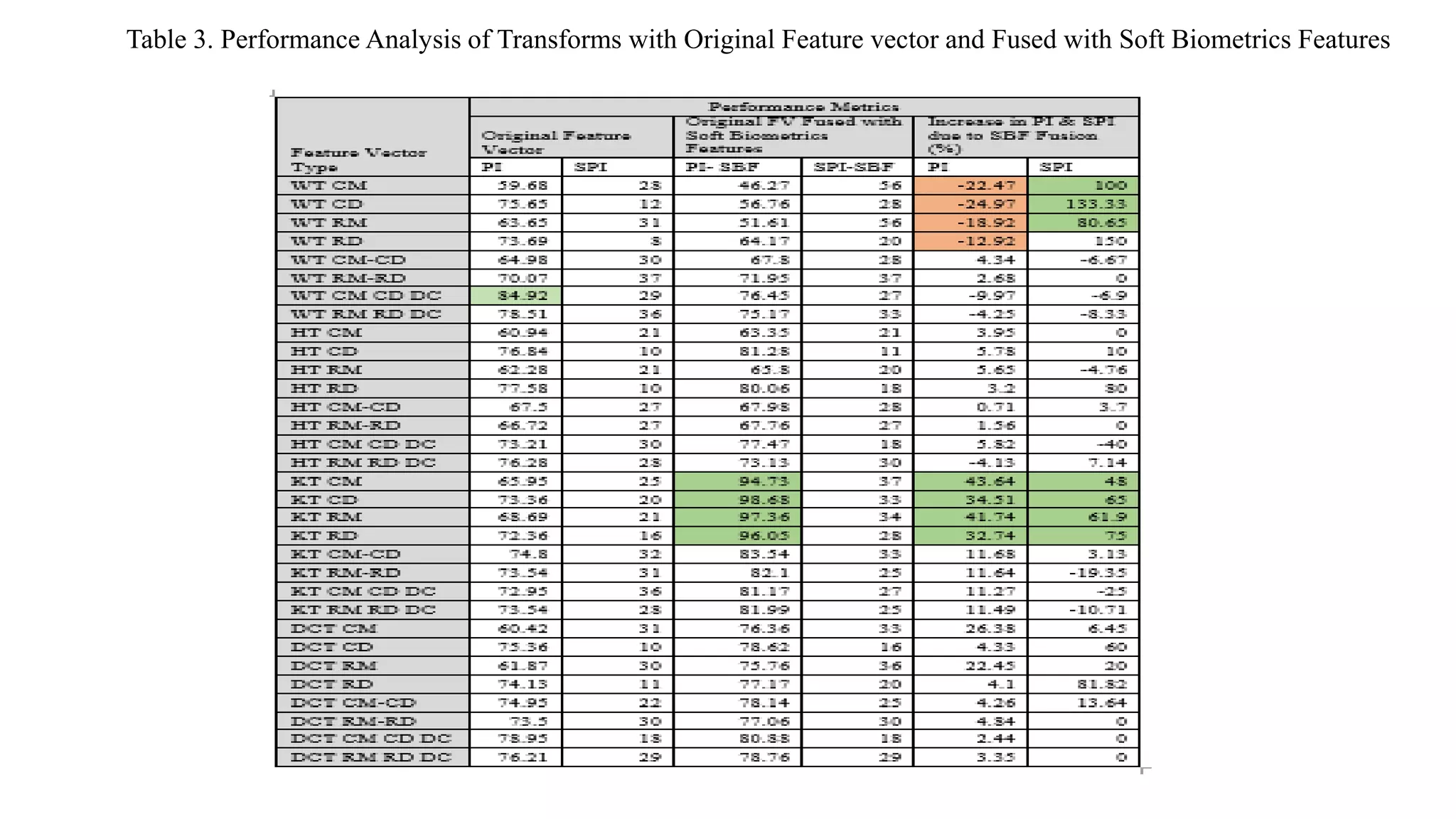
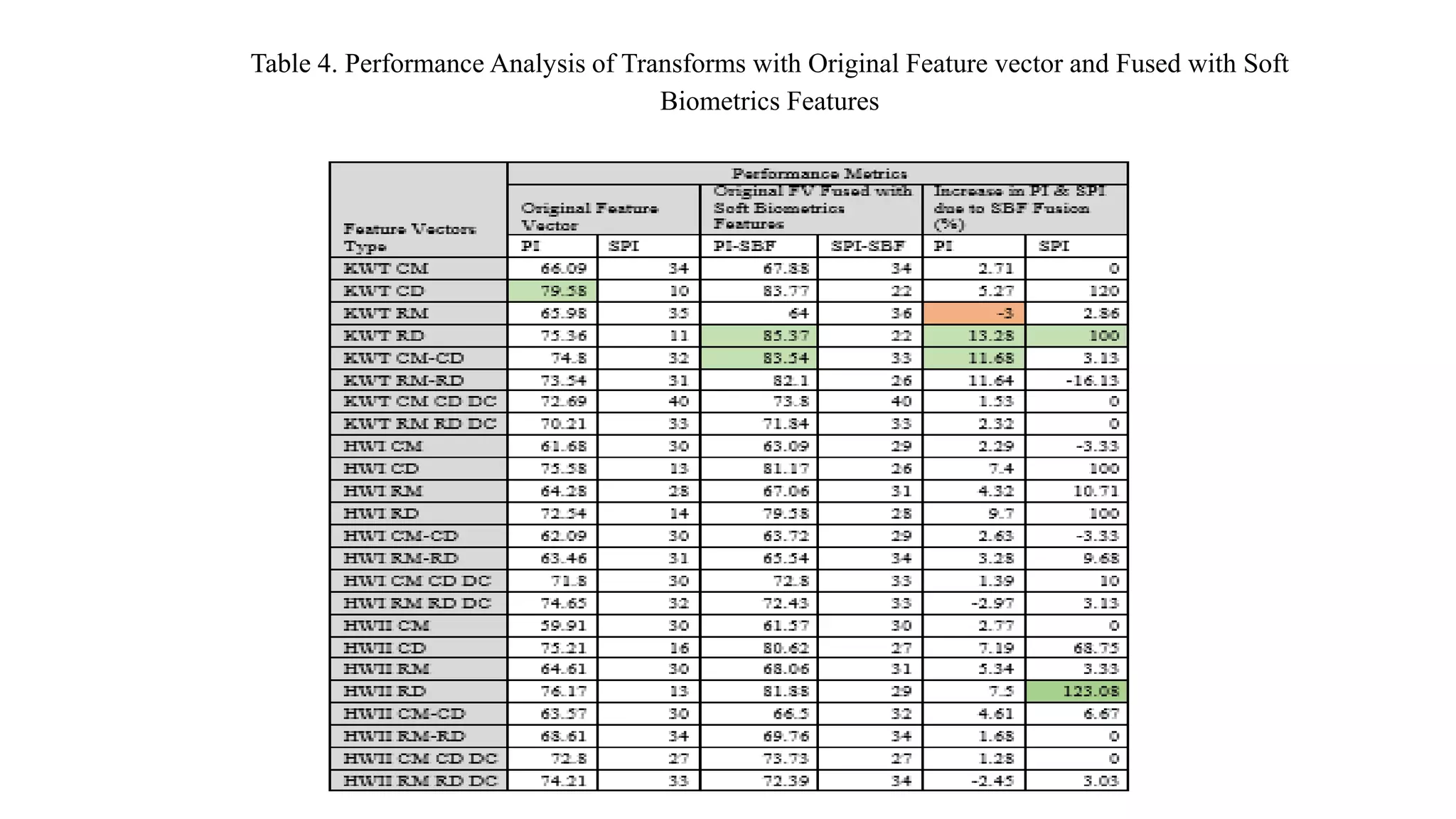
This document discusses online signature recognition using sectorization of the complex Walsh plane. It proposes extracting features from the intermediate transforms of signatures by plotting CAL and SAL functions on the complex Walsh plane. The plane is divided into blocks and mean values in each block are calculated to form feature vectors. Both unimodal and multi-algorithmic techniques are explored. Soft biometric features are also added. The Kekre transform is found to perform best, achieving 98.68% performance index for column density-based vectors. Future work could involve designing better classifiers and generating new hybrid wavelets from different transforms.






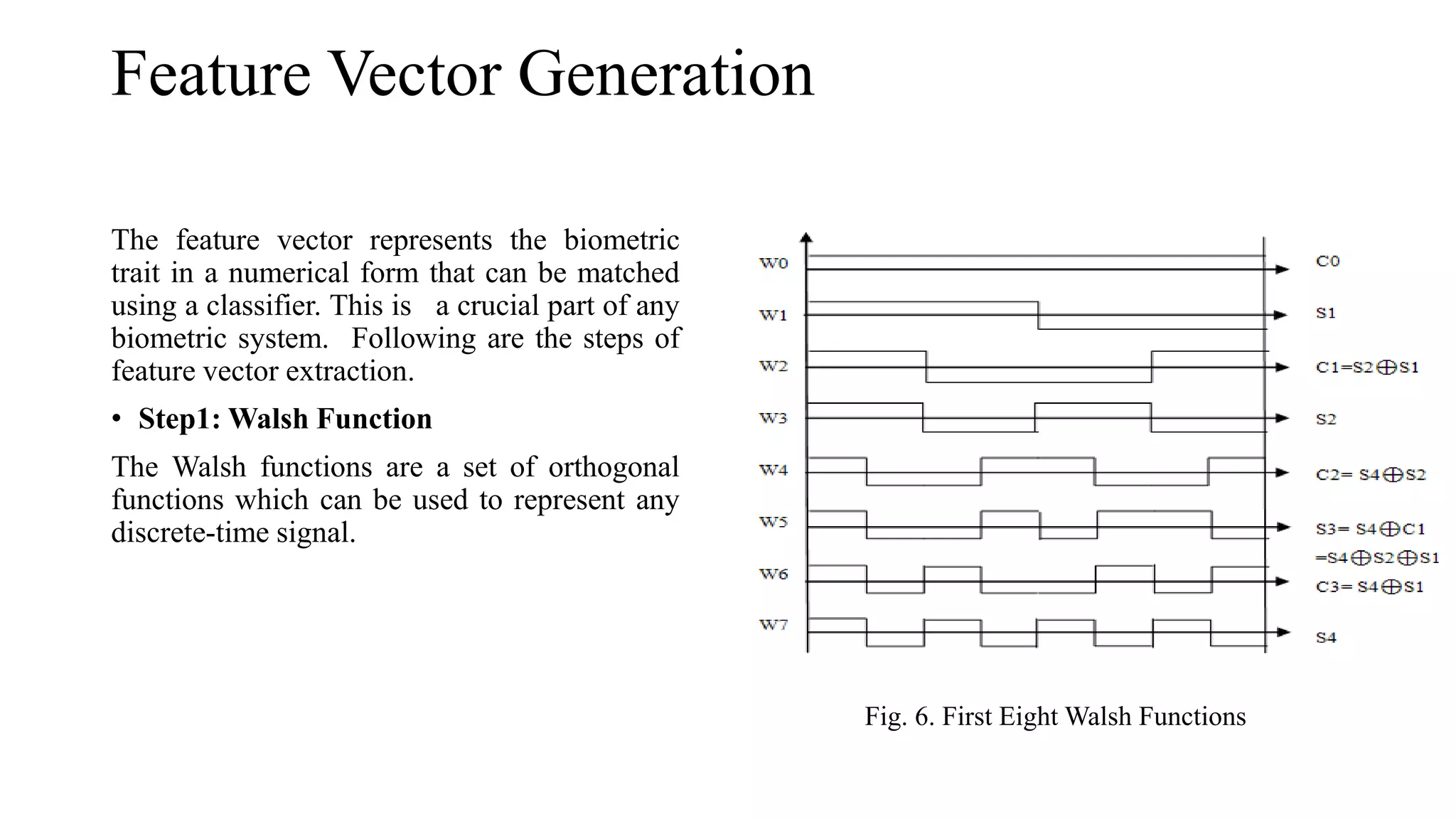

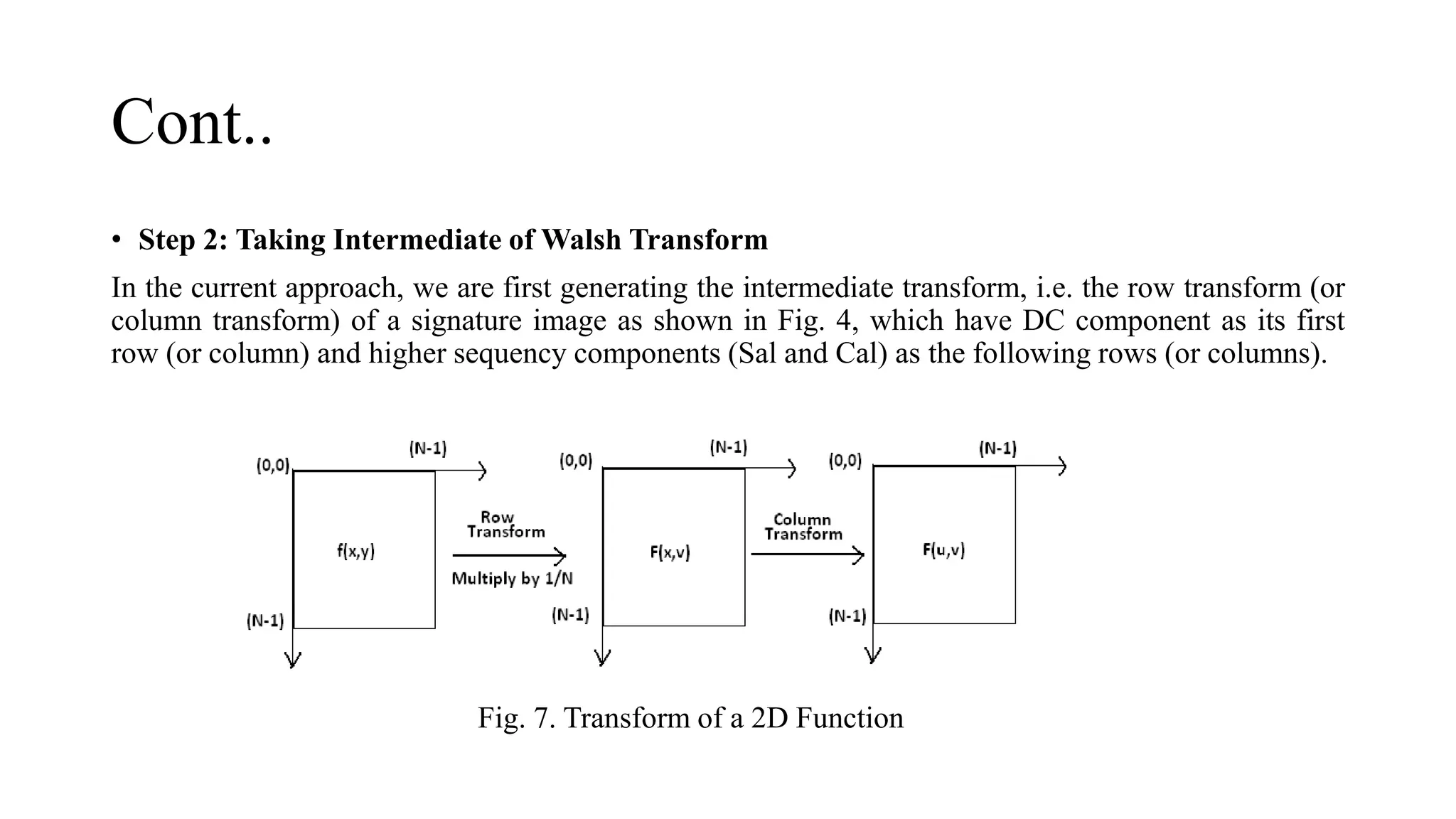

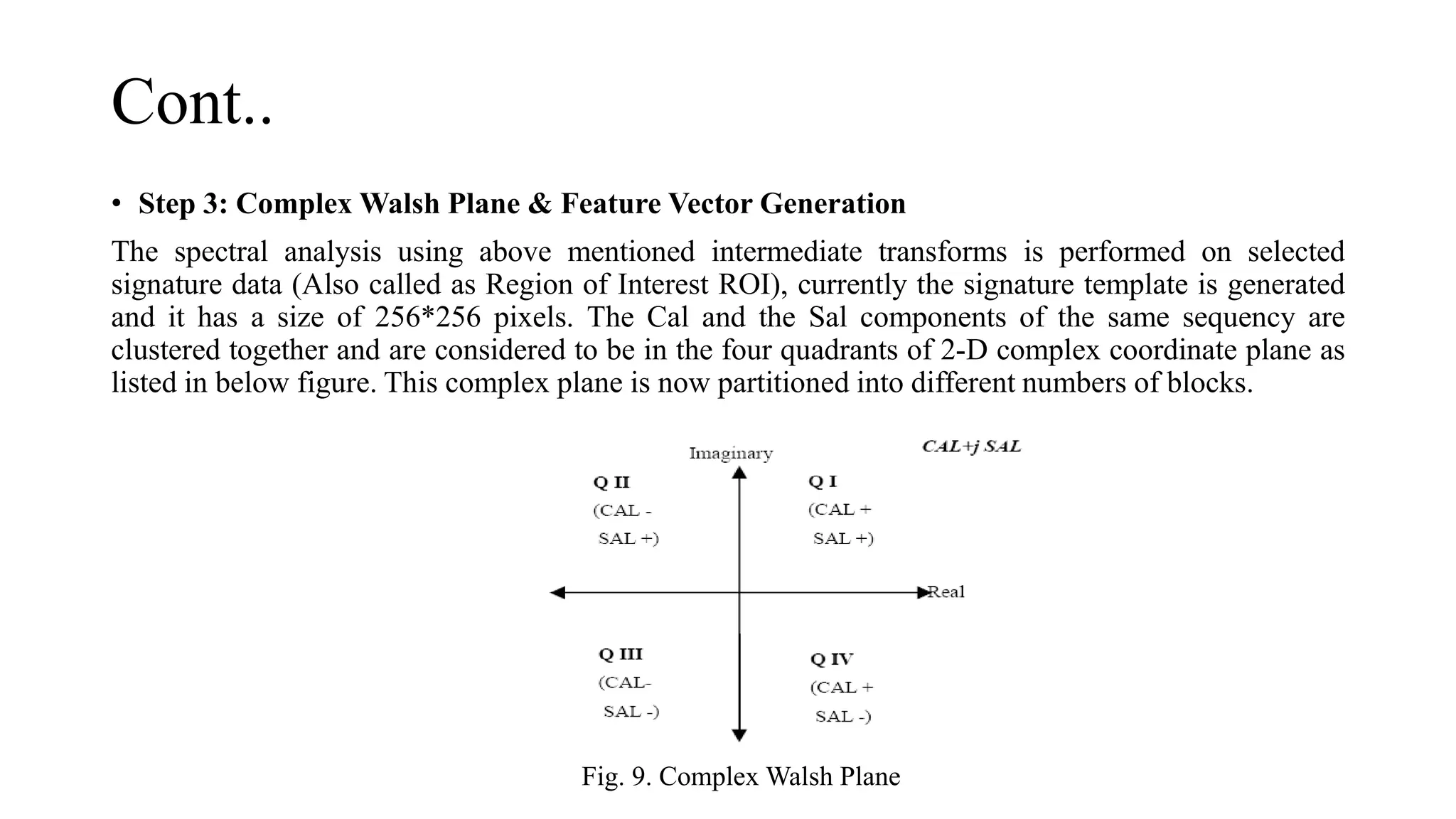
![• The values of Cal & Sal function they plotted in blocks which are square shaped. Feature vectors
generated using sectorization are much less in number and hence the reduction in processing time
and complexity. Currently there are 32*32 = 1024 blocks. For each block in the complex plane the
mean as well as Density of Cal & Sal function is calculated. Beside this DC value of First and Last
Col/Row and the sequency of last row of the intermediate transform is also calculated. Hence total
2S+3 feature points are calculated in all for Cal and Sal plots generated from complex Walsh plane.
Here S = 32, hence total 2051 elements are there in one feature vector. Besides this for actual
evaluation following combinations are tested
[1] Column Mean –CM
[2] Column Density – CD
[3] Row Mean – RM
[4] Row Density – RD
• The mean values of the transform coefficients in each block are calculated as in equation.
𝑀𝑘 =
1
𝑁 𝑁−1
𝑋=0
𝑊𝑖](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onlinesignaturerecognitionusingsectorizationofcomplexwalsh-150115001617-conversion-gate01/75/Online-signature-recognition-using-sectorization-of-complex-walsh-17-2048.jpg)



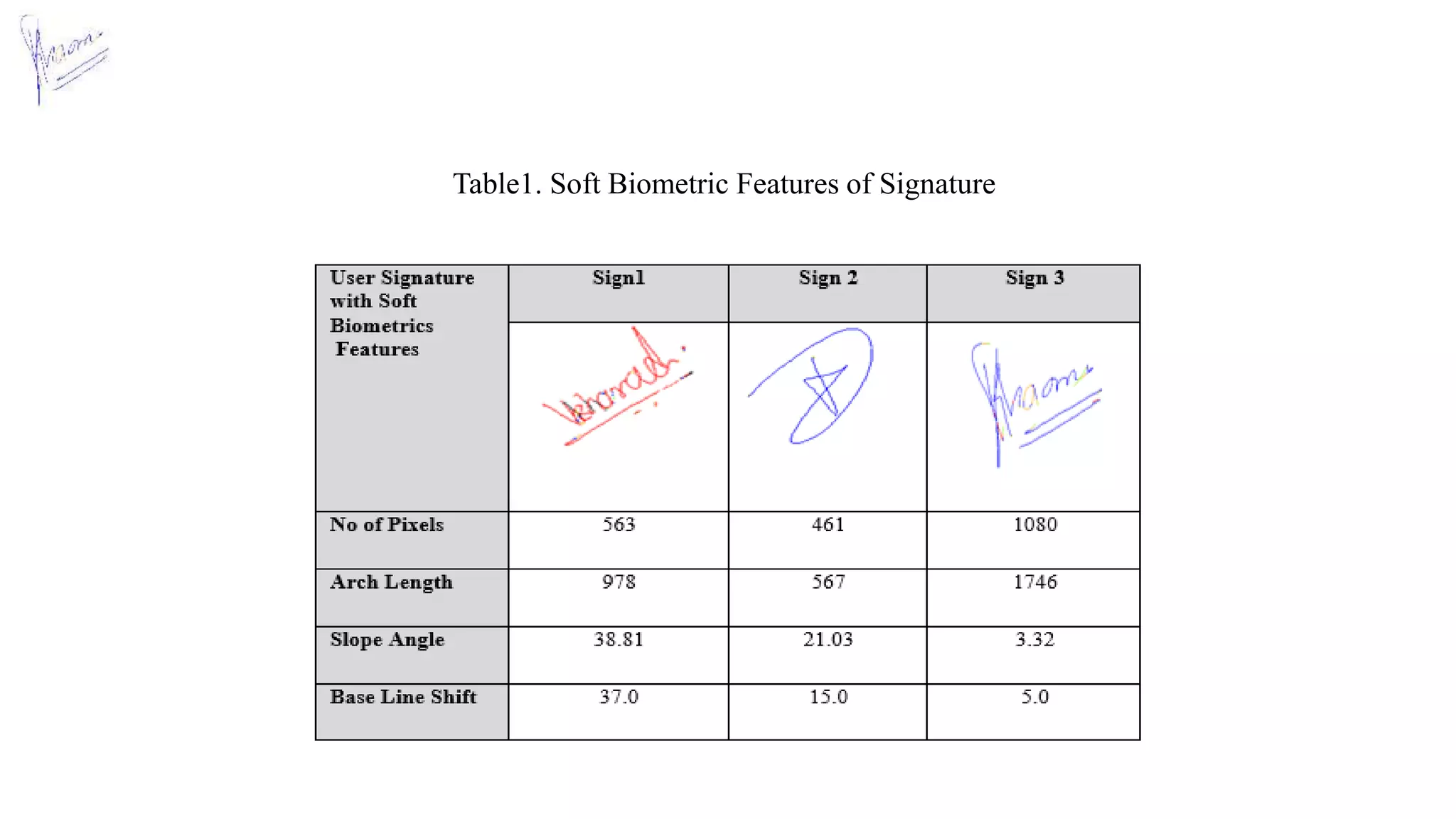

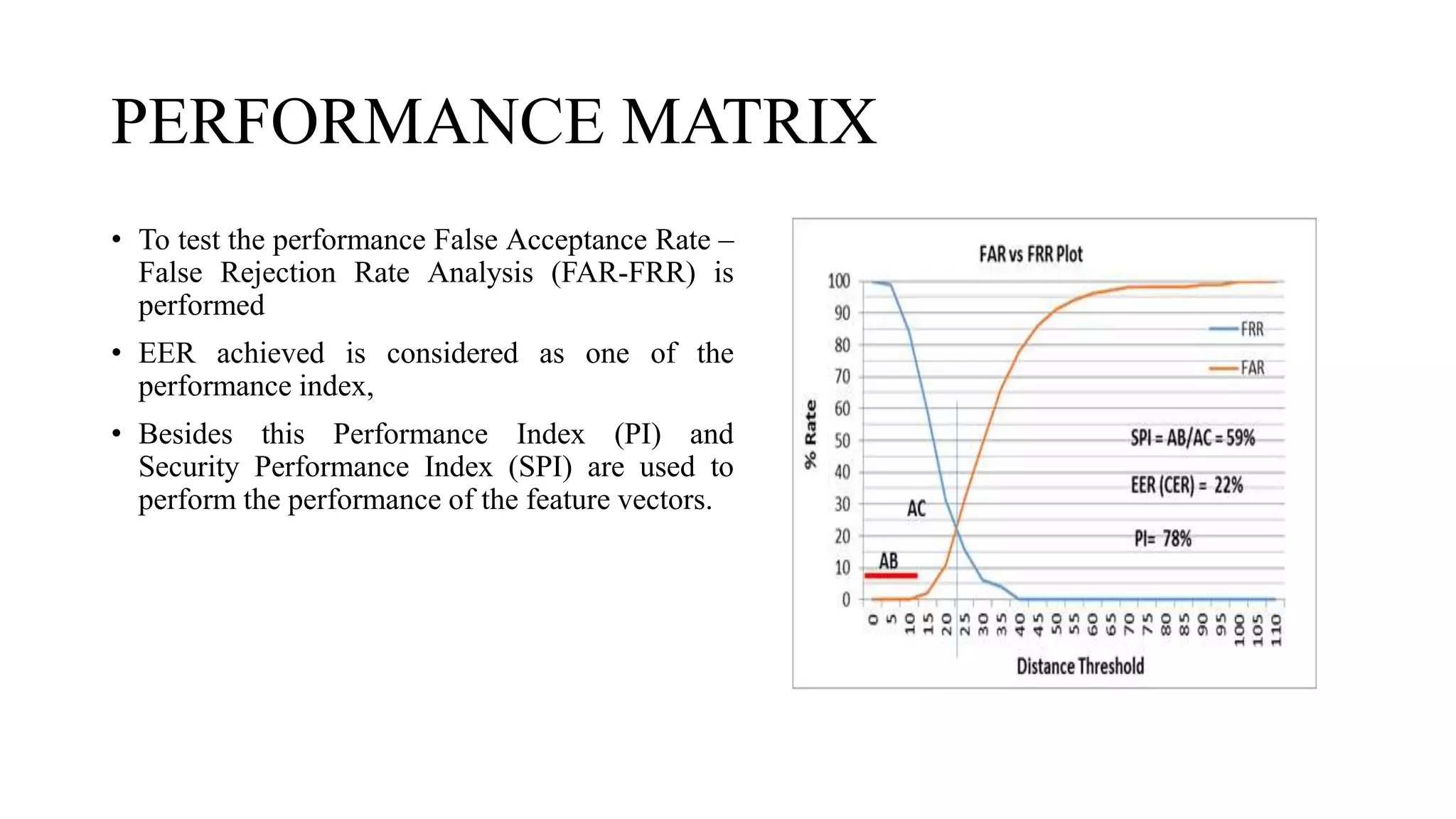
![Result
• 1080 samples are collected from the 108 person (10 signatures of each person) has been used, from
which 1080 five signature used for training and five signatures for testing purpose of individuals.
• Total tests for genuine signatures are 2701 and 288901 for forgery signatures. While testing the
feature vector is generated in following variations:
[1] Column transform mean feature vector (Col TRF)
[2] Row transform mean feature vector (Row TRF)
[3] Column density feature vector (Col Density)
[4] Row density feature vector (Row Density)
[5] Fusion of all above Column & Row feature vector with DC & Sequency components
(Fusion)
[6] Fusion of all above feature vectors with SBF (Soft Biometrics Feature)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/onlinesignaturerecognitionusingsectorizationofcomplexwalsh-150115001617-conversion-gate01/75/Online-signature-recognition-using-sectorization-of-complex-walsh-23-2048.jpg)