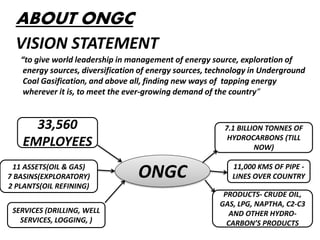
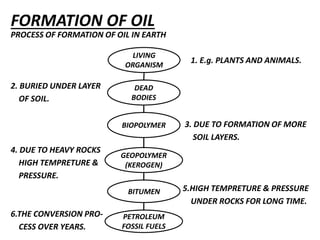
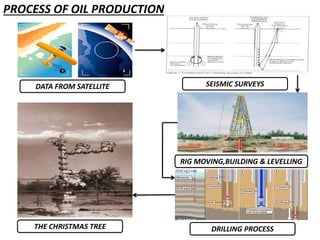
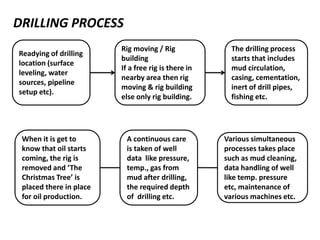
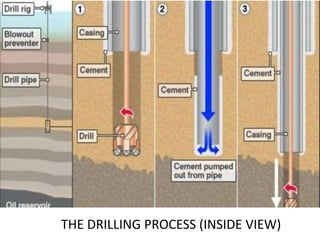
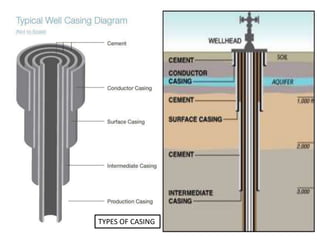
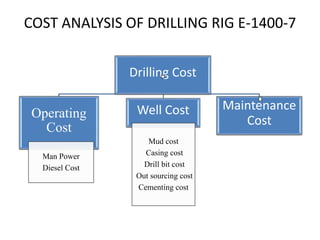
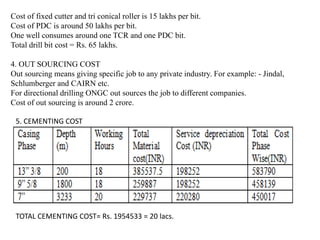
This document provides information about Deepak Chandak's summer industrial training at ONGC Ankleshwar. It includes details about ONGC such as its headquarters, chairman, products, assets, employees, and vision. It then describes ONGC Ankleshwar's fields, infrastructure like rigs, wells drilled, and departments. The document explains the process of oil formation, drilling including rig components and the drilling process, and production. It discusses costs associated with drilling rig E-1400-7 and concludes with thanks after learning about operations through site visits during the training.