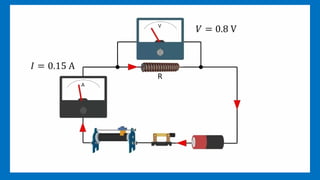
Ohm's Law establishes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit, asserting that voltage is directly proportional to current under constant physical conditions. The law is applicable in determining circuit parameters but does not hold for unilateral elements like diodes and transistors. Key concepts include voltage as the electric potential difference, current as the flow rate of charge, and resistance as the opposition to current flow.