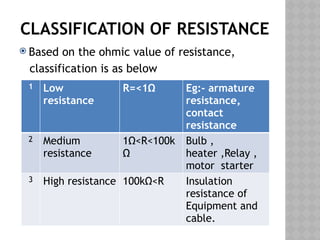
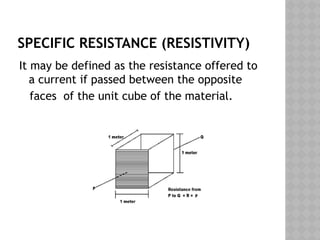
The document covers fundamental concepts of electrical circuits, including definitions of key terms such as current, voltage, and resistance. It explains Ohm's Law, which relates current, voltage, and resistance in a circuit, along with the classification and factors affecting resistance. Additionally, it discusses specific resistance and provides basic circuit calculation examples.