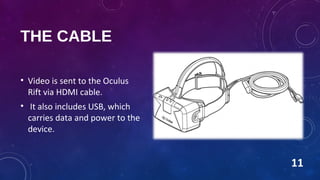
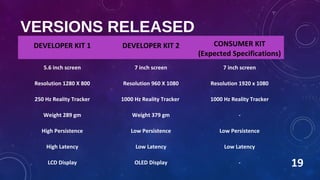
The Oculus Rift is a virtual reality head-mounted display developed by Oculus VR. It uses lenses and a split screen to display stereoscopic 3D graphics with a 110 degree field of view. Tracking of the user's head position is enabled by infrared LEDs on the headset and a camera. The Rift is connected to a PC via an HDMI cable that provides video and a USB cable for data and power. It has progressed through developer kits with improved screens and tracking technology in preparation for a consumer version.