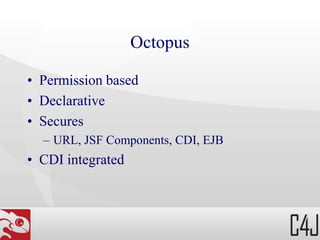
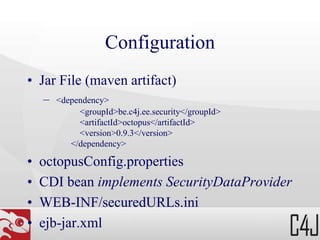
The document outlines the concepts and configurations of the Octopus Java EE Security Framework, focusing on authentication, authorization, and permission management using role-based security. It describes how permissions are assigned to users and groups, how to secure various components such as URLs, JSF components, and EJB methods, and details the implementation of custom voters for enhanced security checks. Configuration specifics are provided, including examples of defining and protecting URLs, roles, and custom security requirements in an application environment.


















![Protect URL
• /pages/department/** = user, namedPermission[xxx]
• Pages requires authentication and the named
permission xxx
– xxx = value of enum class
• np instead of namedPermission also
allowed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/octopusv0-140408070159-phpapp02/85/Octopus-framework-Permission-based-security-framework-for-Java-EE-21-320.jpg)



![Custom annotation for security
• public @interface DemoPermissionCheck {
DemoPermission[] value();
}
• namedPermissionCheck.class =
be.c4j.demo.security.permission.DemoPermissionCheck](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/octopusv0-140408070159-phpapp02/85/Octopus-framework-Permission-based-security-framework-for-Java-EE-25-320.jpg)


![Custom voters and URL
• /pages/updateSalary.xhtml = user,
voter[employeeSalaryUpdateVoter]
• this.hasServletRequestInfo(InvocationContext)
– Called from within URL context?
• this.getURLRequestParameter(InvocationContext, String)
– Get URL parameter](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/octopusv0-140408070159-phpapp02/85/Octopus-framework-Permission-based-security-framework-for-Java-EE-28-320.jpg)

![• this.getAssignableParameter(InvocationContext,
Class<T>[, int])
– Get parameter value of method call
– Optional position can be used if multiple
parameters has same type (0-based)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/octopusv0-140408070159-phpapp02/85/Octopus-framework-Permission-based-security-framework-for-Java-EE-30-320.jpg)


