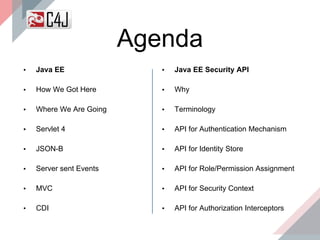
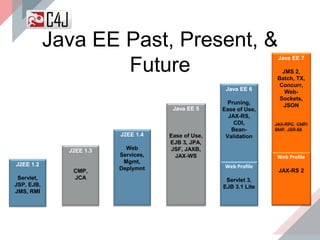
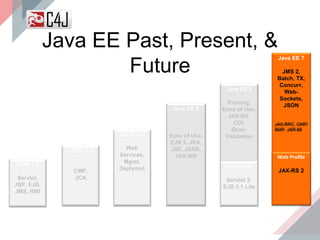
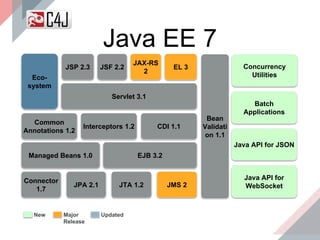
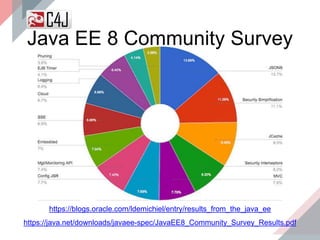
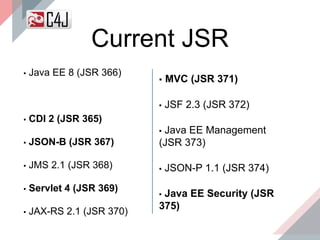
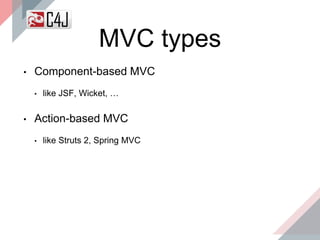
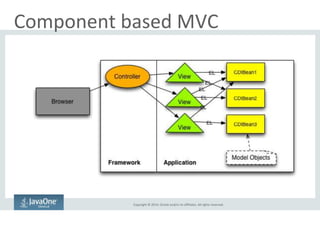
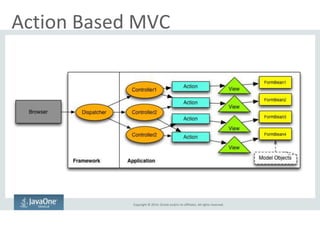
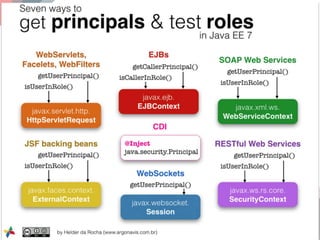
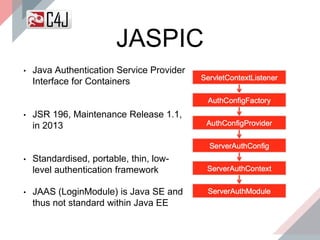
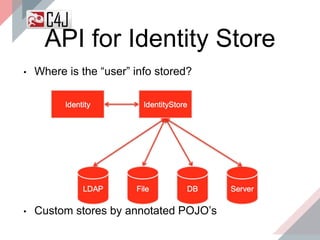
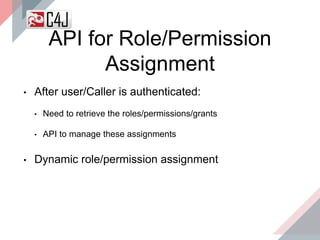
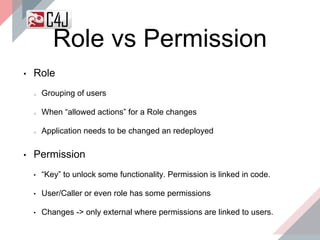
The document outlines the advancements and features in Java EE 8, with a focus on the new Java EE Security API (JSR 375) aimed at modernizing security for cloud applications. It discusses various enhancements such as alignment with web standards, cloud capabilities, improved CDI, and comprehensive security mechanisms that cater to user authentication and role assignment. Overall, it emphasizes a more user-friendly and standardized approach to security without vendor-specific configurations.