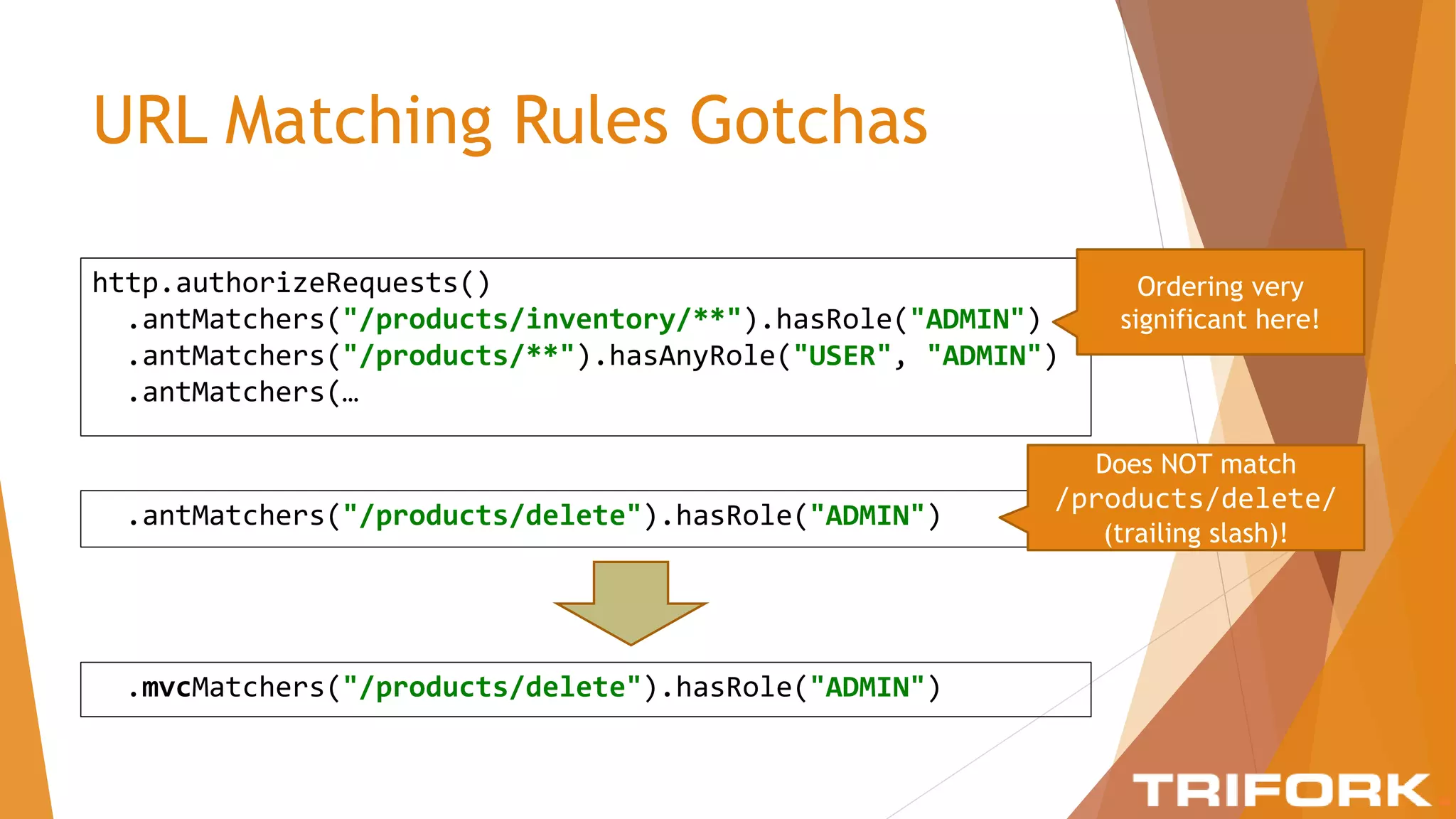
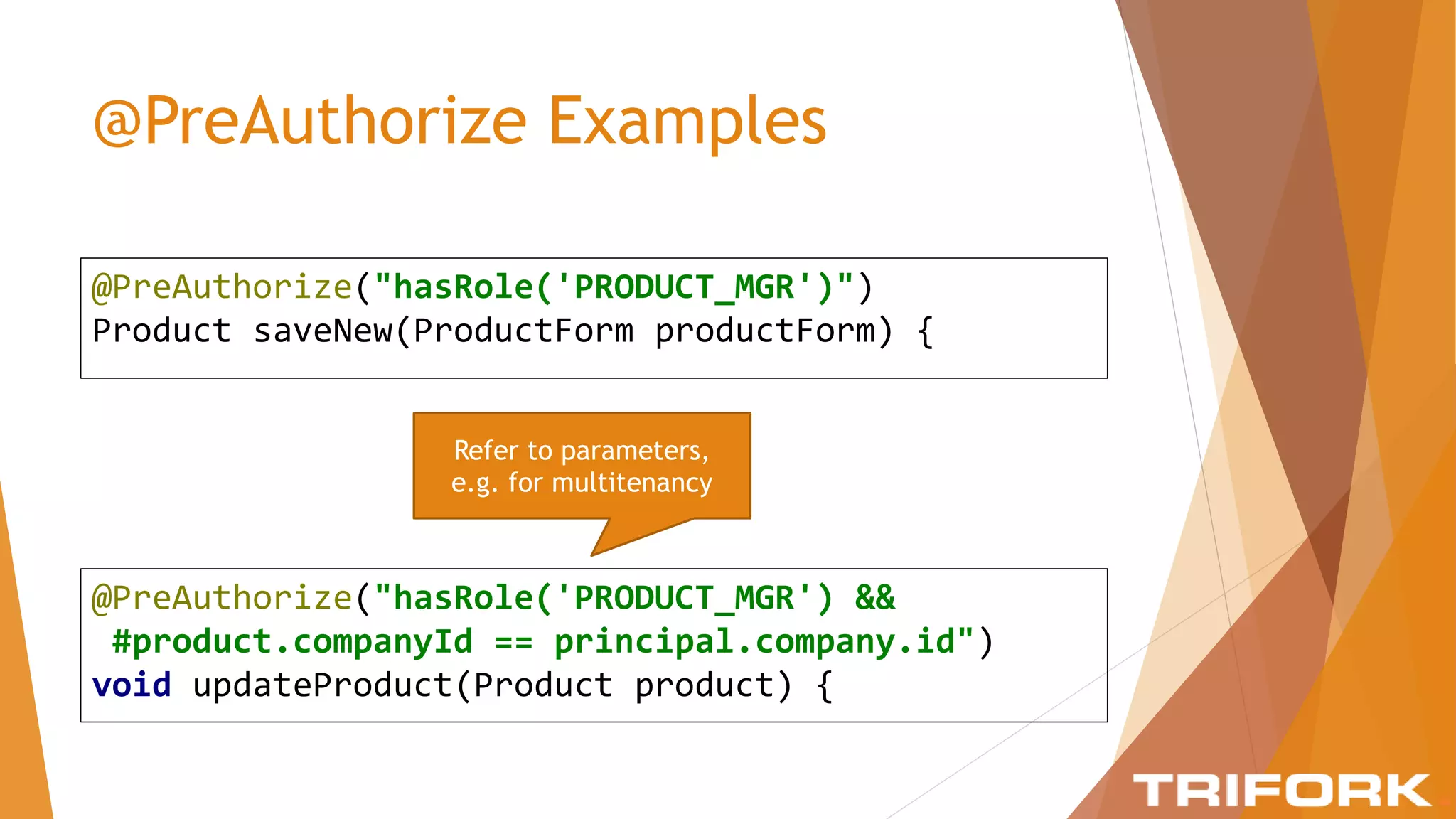
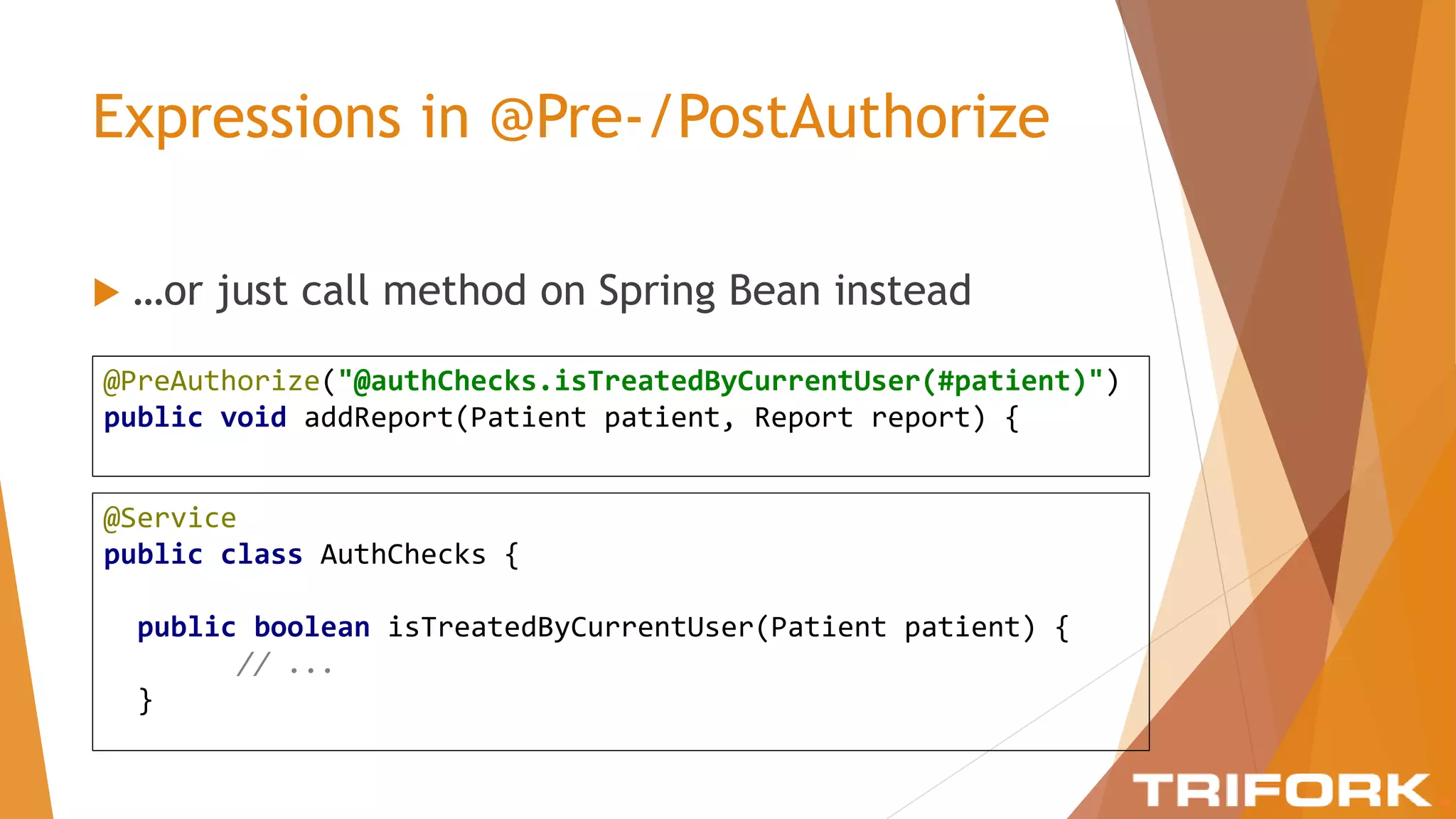
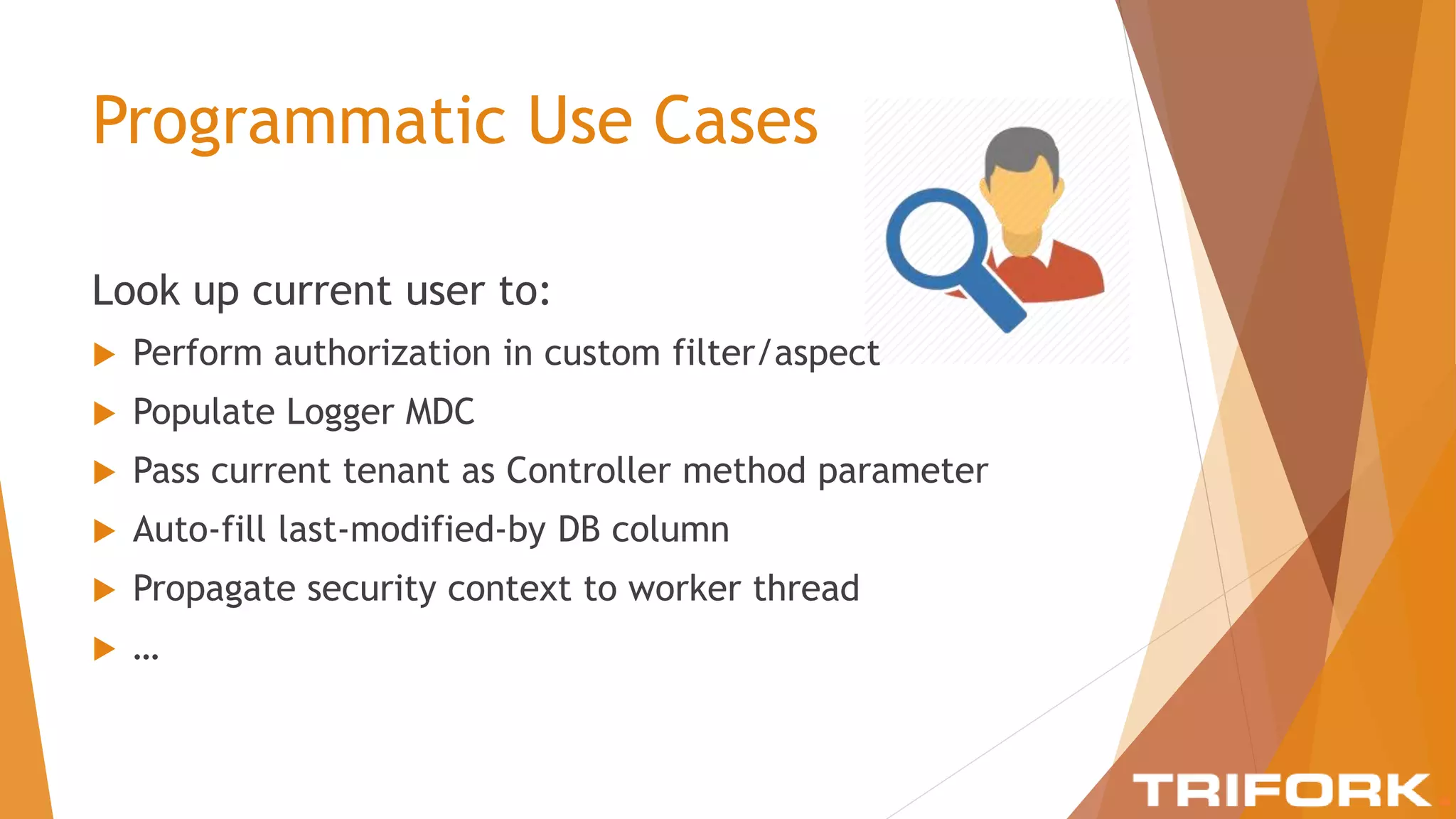
The document discusses implementing layers of defense in web applications using Spring Security, emphasizing the importance of multiple security layers to prevent breaches. It outlines configuration steps, security headers, and methods for authentication and authorization, including CSRF protection and method-level security. The conclusion highlights the need for a comprehensive understanding of security frameworks to enhance application security.