The document discusses the basic steps for configuring Spring Security:
1. Set dependencies and create a WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter configuration class
2. Configure authentication using in-memory, JDBC, or LDAP
3. Ensure the security configuration is loaded by registering WebSecurityConfiguration
4. Configure the springSecurityFilterChain by extending AbstractSecurityWebApplicationInitializer
It provides code examples for configuring different authentication types and securing different URL patterns.







![Spring Security
●
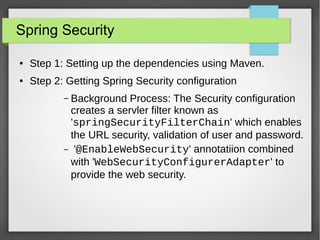
Step 3: Ensuring the Security configuration is loaded. This can be done by
including 'WebSecurityConfiguration' in applicationContext. In other
words register the springSecurityFilterChain with the war.
● In Java: (without Existing Spring)
public class SpringWebMvcInitializer extends
AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return new Class[] { WebSecurityConfiguration.class };
}
...
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/springsecurity-160319091036/85/Spring-Security-11-320.jpg)


