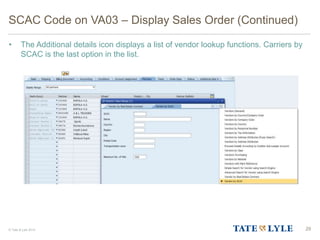
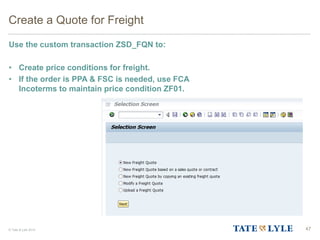
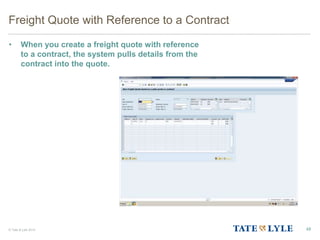
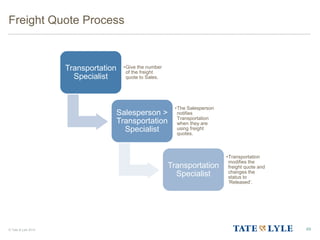
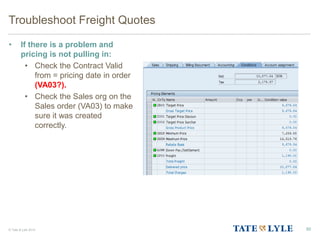
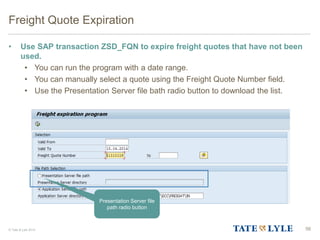
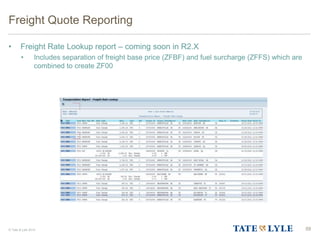
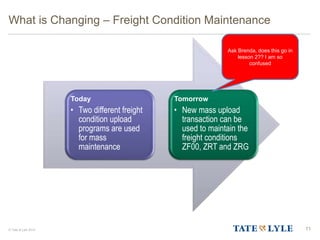
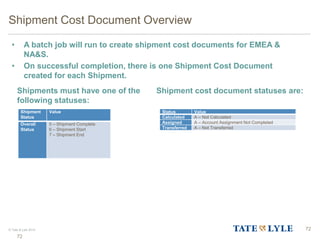
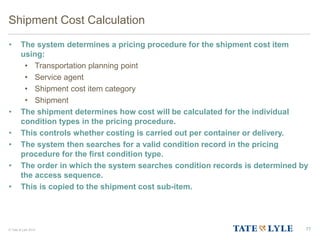
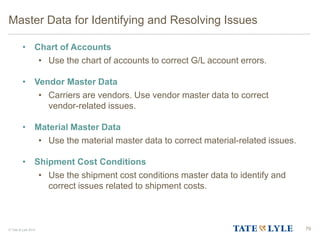
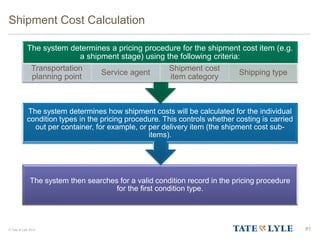
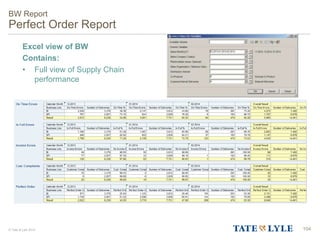
Here are the key points about changes to fuel surcharges:
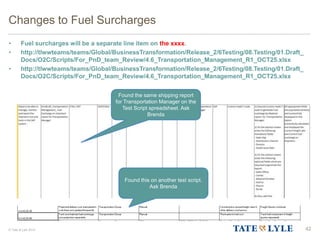
- Fuel surcharges will be calculated and maintained as shipment cost conditions in SAP ECC.
- Transportation will be responsible for maintaining the fuel surcharge shipment cost conditions on a monthly basis or as needed.
- When a shipment is invoiced, the applicable fuel surcharge shipment cost condition will accrue as a separate line item on the invoice.
- This allows fuel surcharges to be tracked and analyzed separately from the base freight charges.
- The fuel surcharge shipment cost condition can be applied to either customer invoices or carrier invoices, depending on who is responsible for paying the fuel surcharge.
So in summary, the changes standard