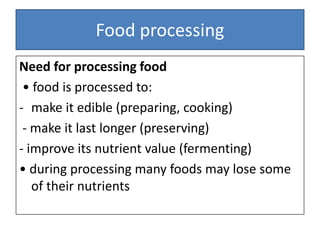
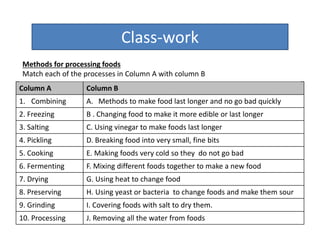
This document discusses food processing and related methods. It explains that food is processed to make it edible, last longer through preservation, and improve nutrient value. Common processing methods include combining foods, cooking, freezing, pickling using vinegar, fermenting using bacteria or yeast, drying by removing water, and salting to draw out water. The document provides examples of how each method processes foods and notes that processing can reduce a food's nutrient content.