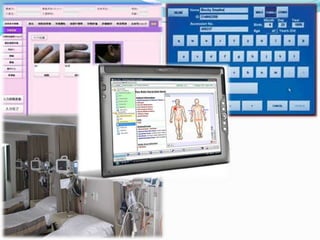
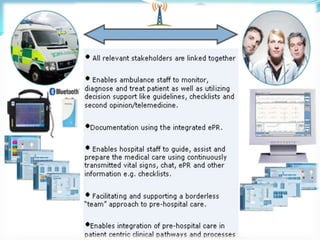
This document discusses the course Nursing Informatics. The course covers the use of information technology and data standards in nursing based on informatics principles. It deals with using clinical information systems to manage patient care and support decision making. The course objectives are to apply informatics concepts to nursing and discuss relevant issues and trends. Various topics are outlined including computers and nursing history, computer systems, issues in informatics, informatics theories, and applying informatics in different nursing practices and internationally. Students are expected to create an online nursing informatics page and do an individual or group presentation to pass the course.