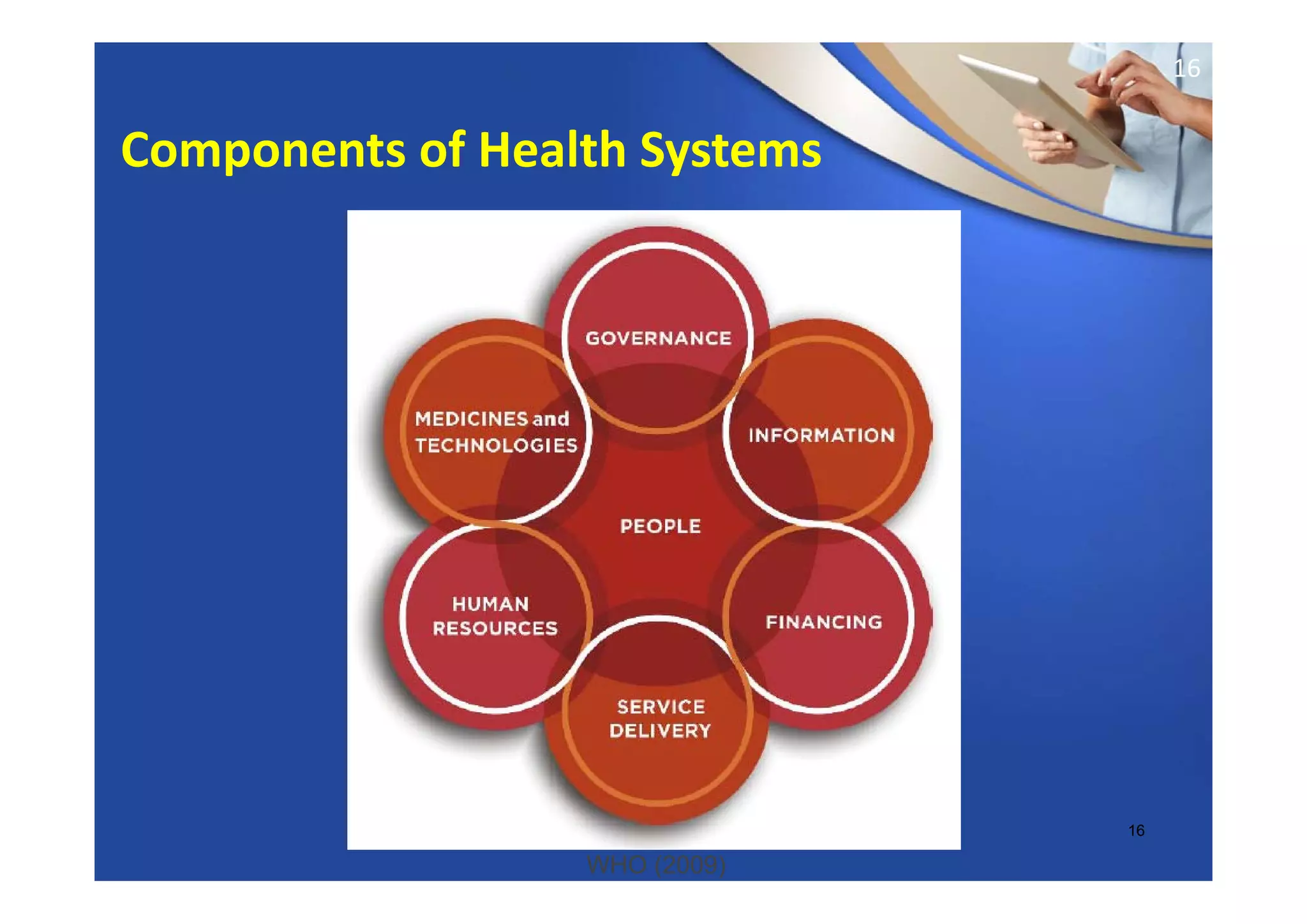
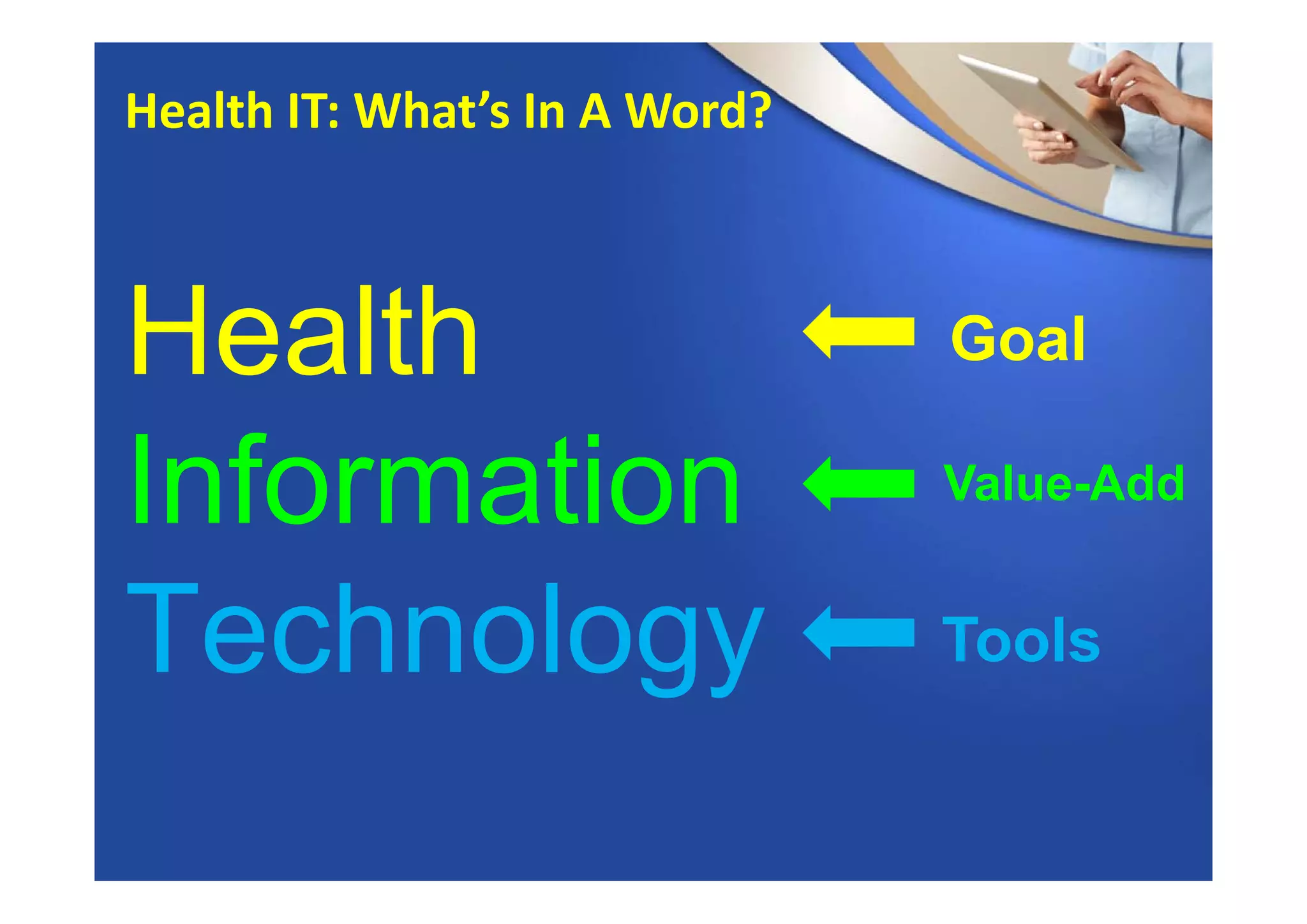
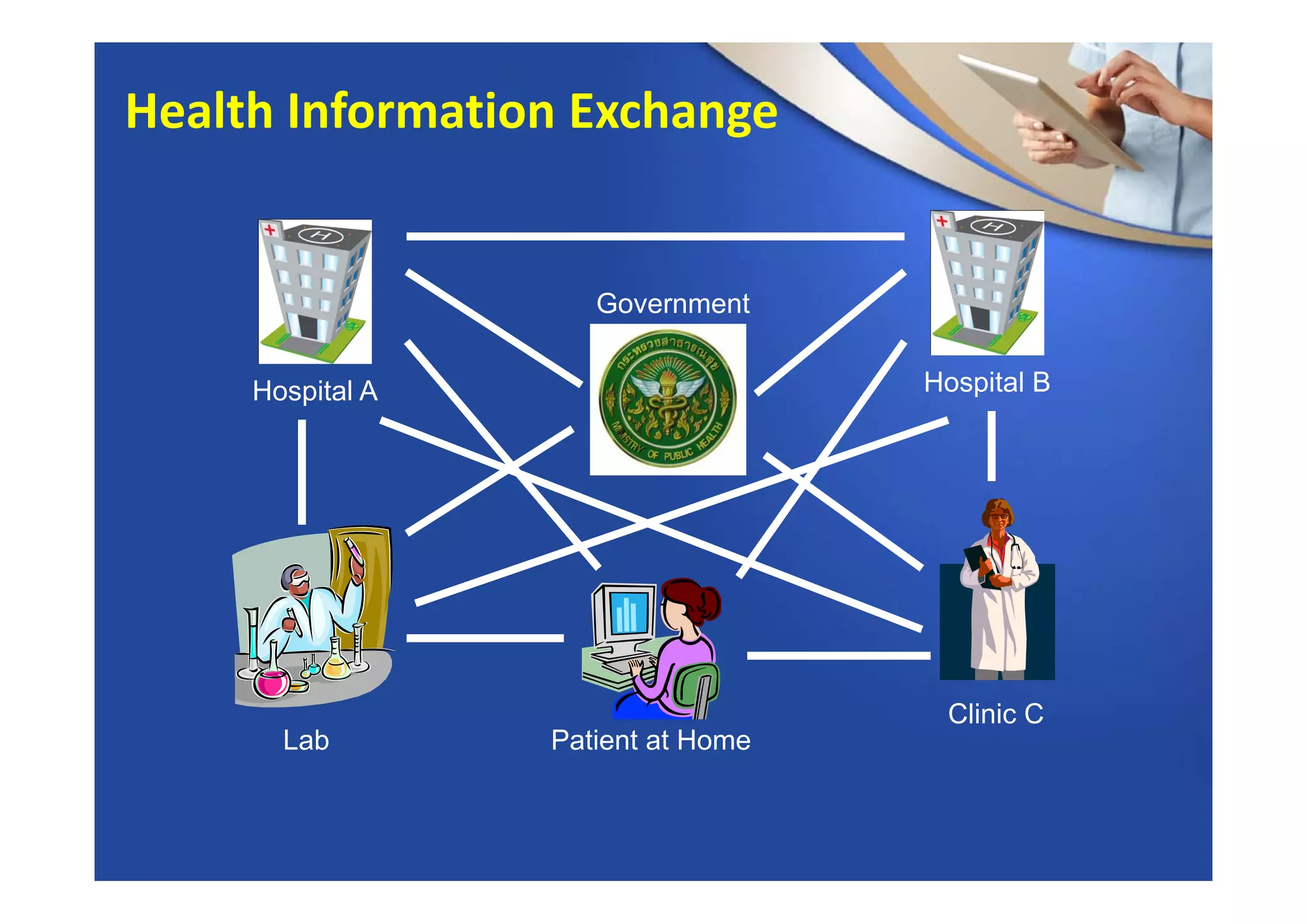
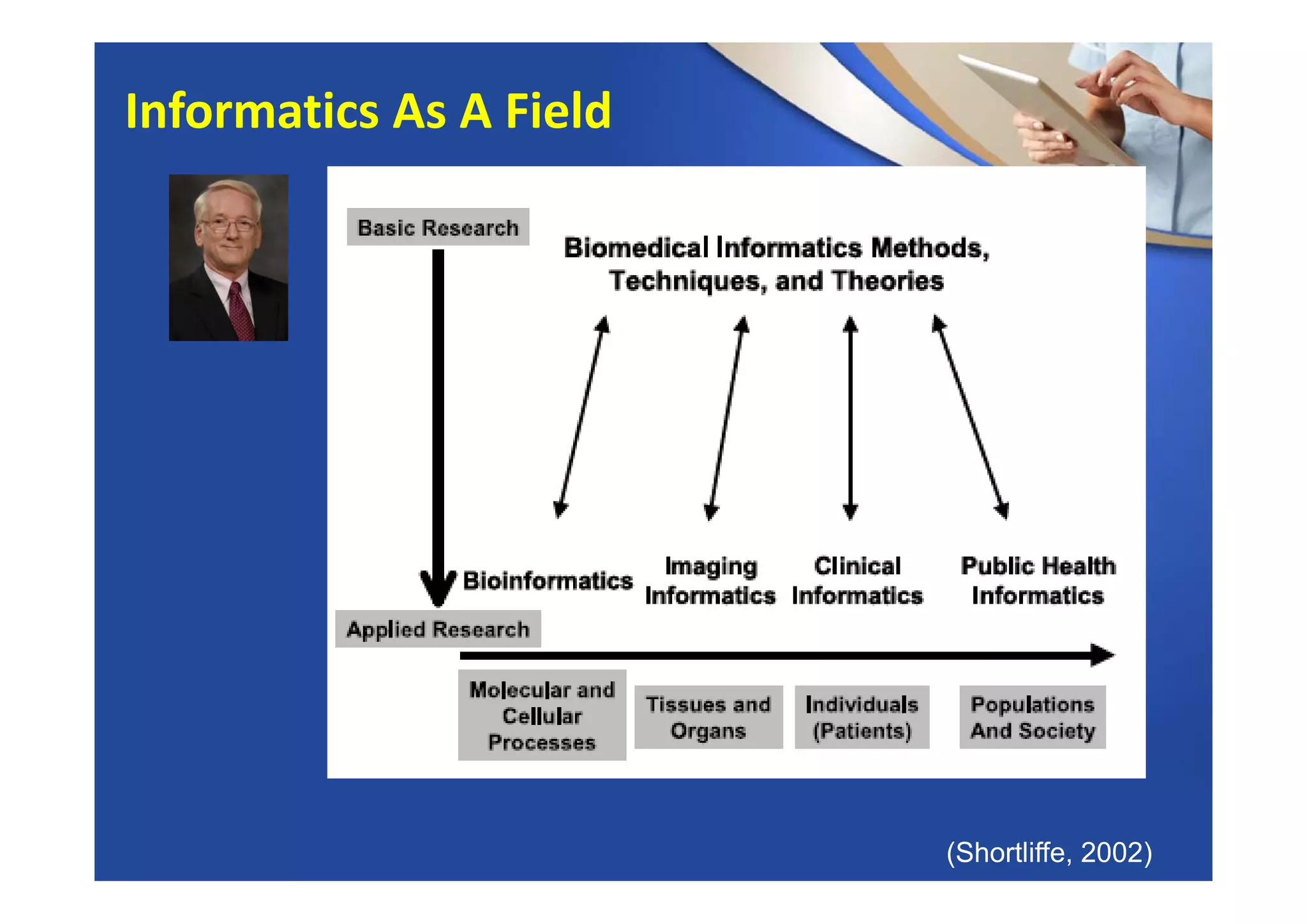
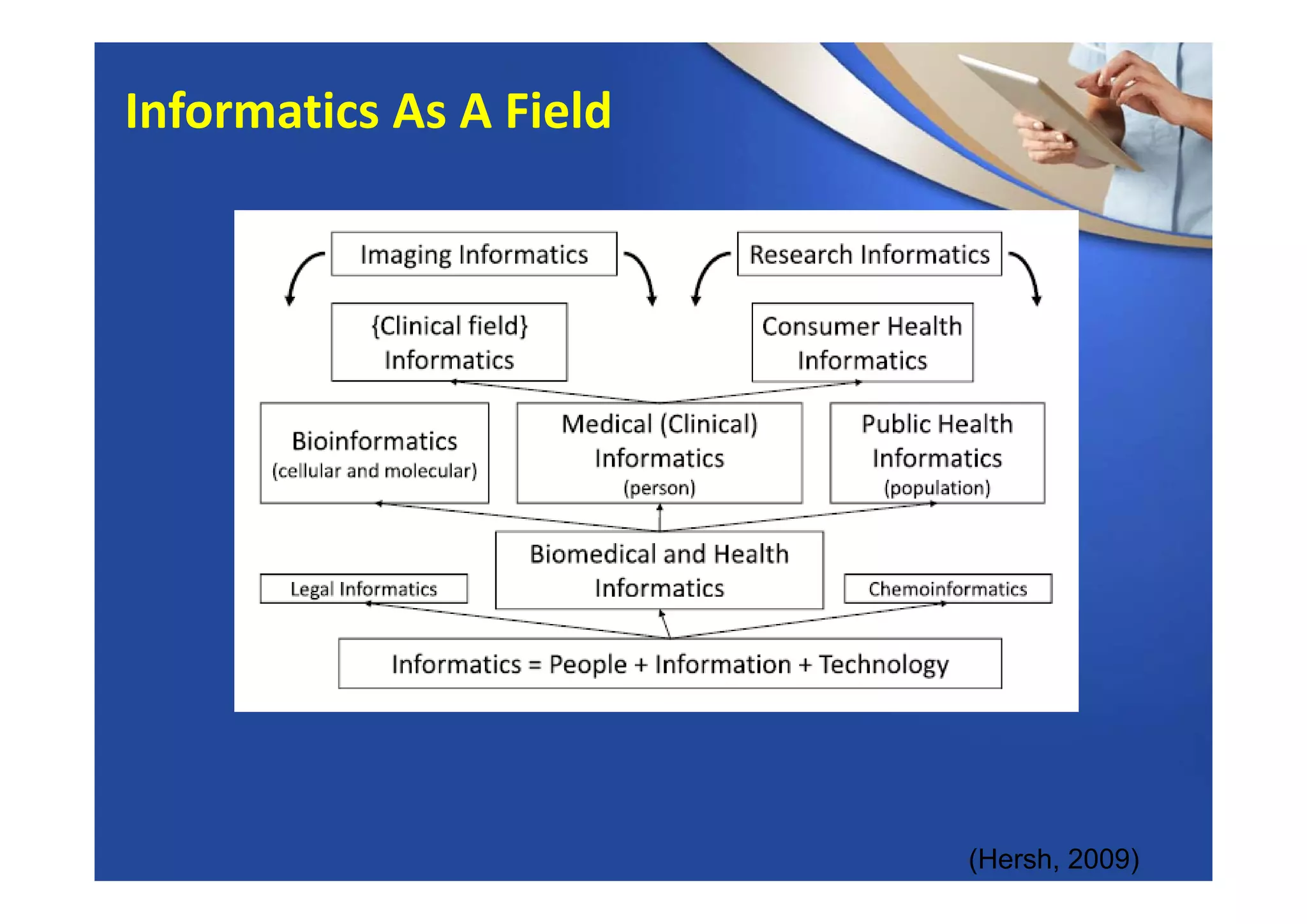
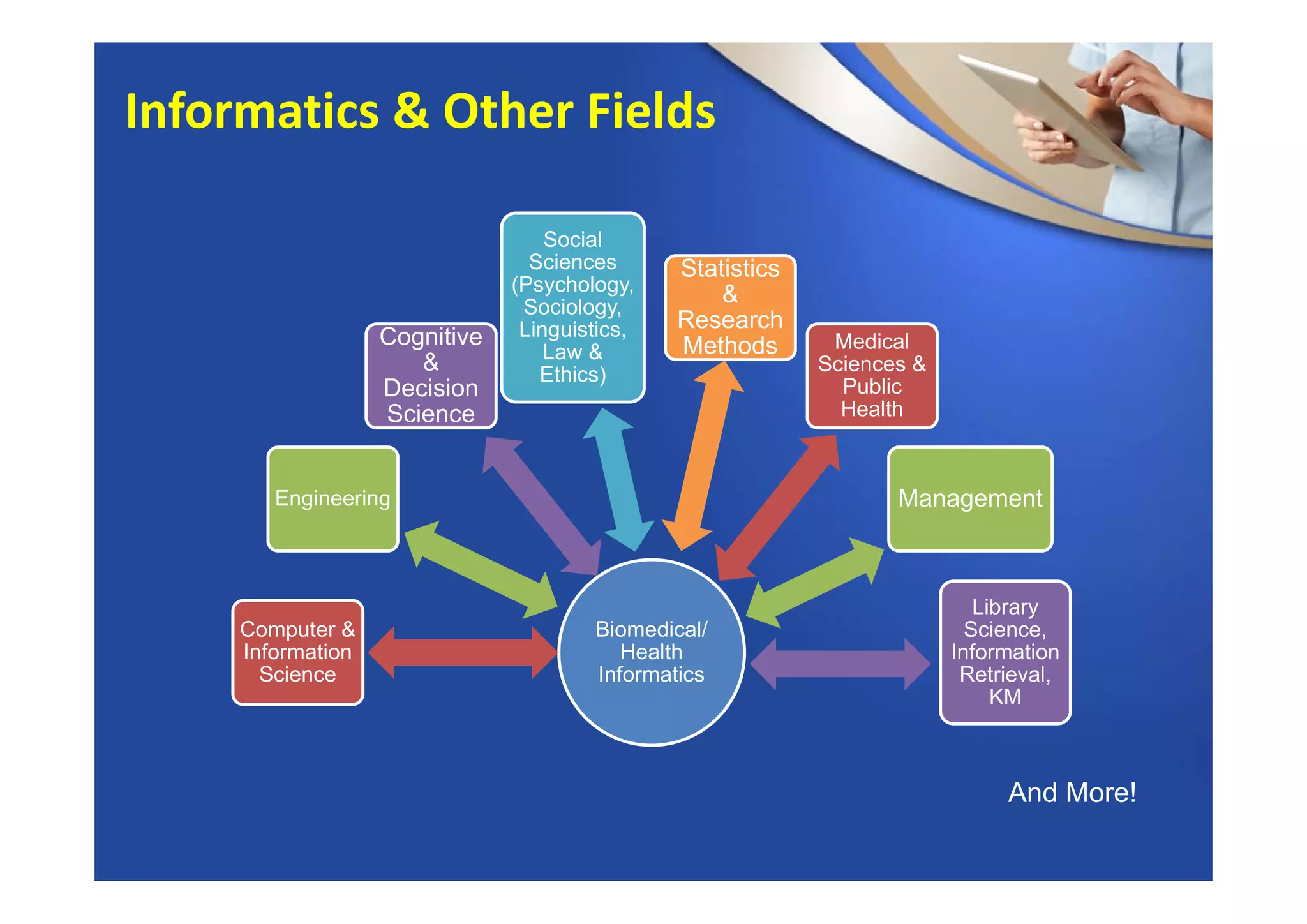
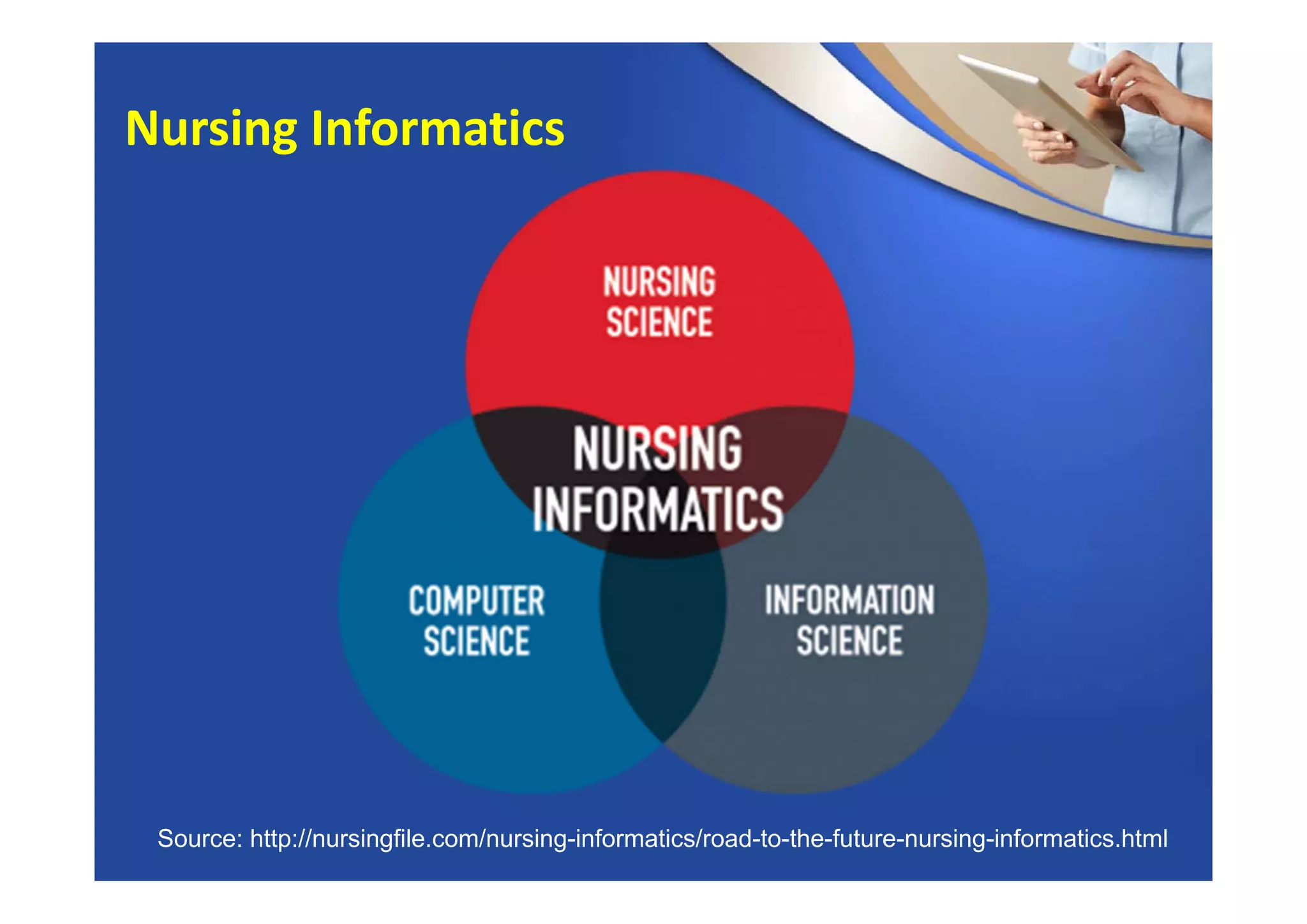
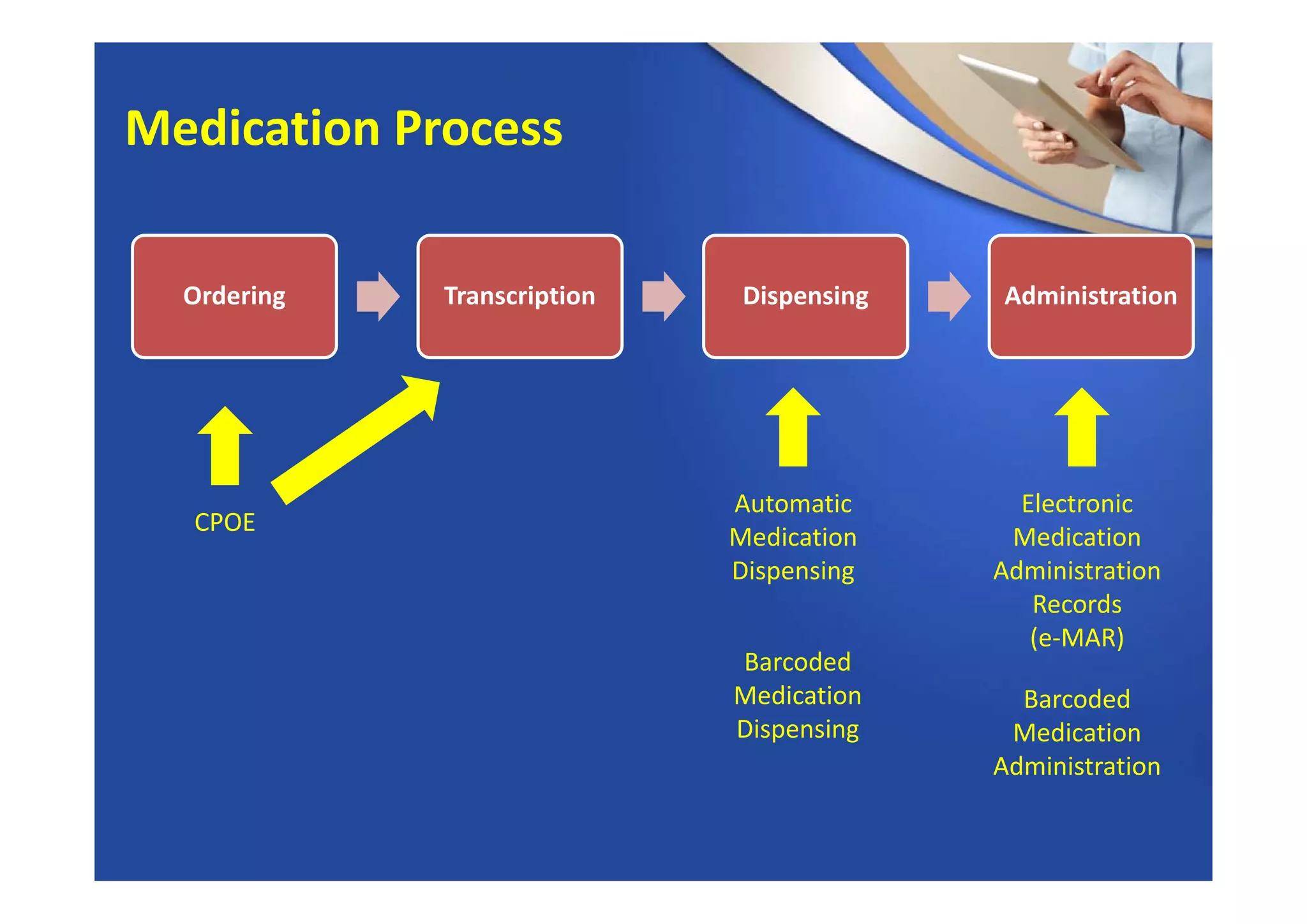
This document provides an overview of informatics and technology in nursing. It discusses how health information and health IT can help improve care delivery and reduce errors. Informatics is presented as an interdisciplinary field that draws from areas like computer science, nursing, and other health disciplines. Nursing informatics applies informatics principles and technologies to support evidence-based practice, standards, research, and tools that promote safe and effective nursing care.