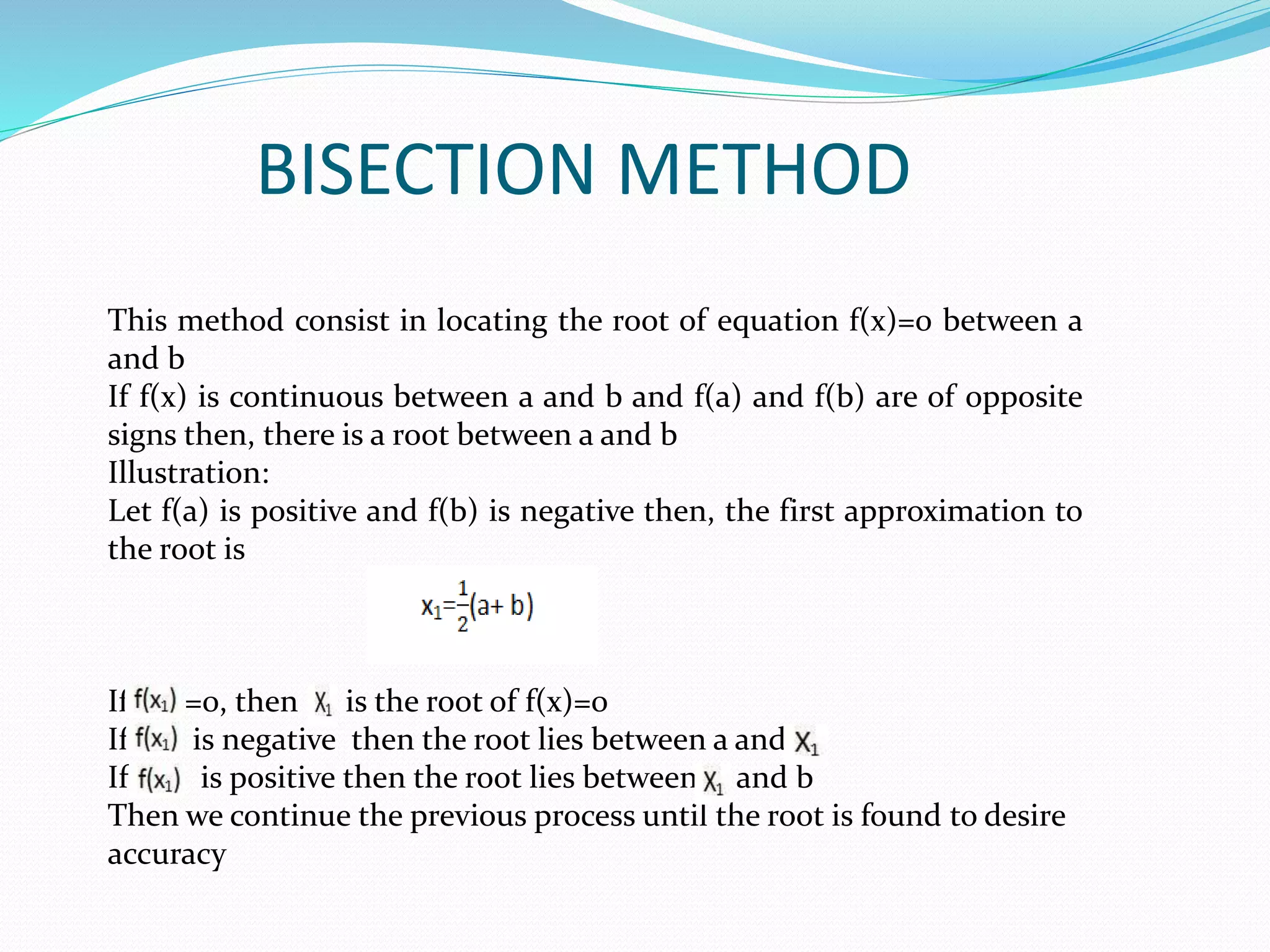
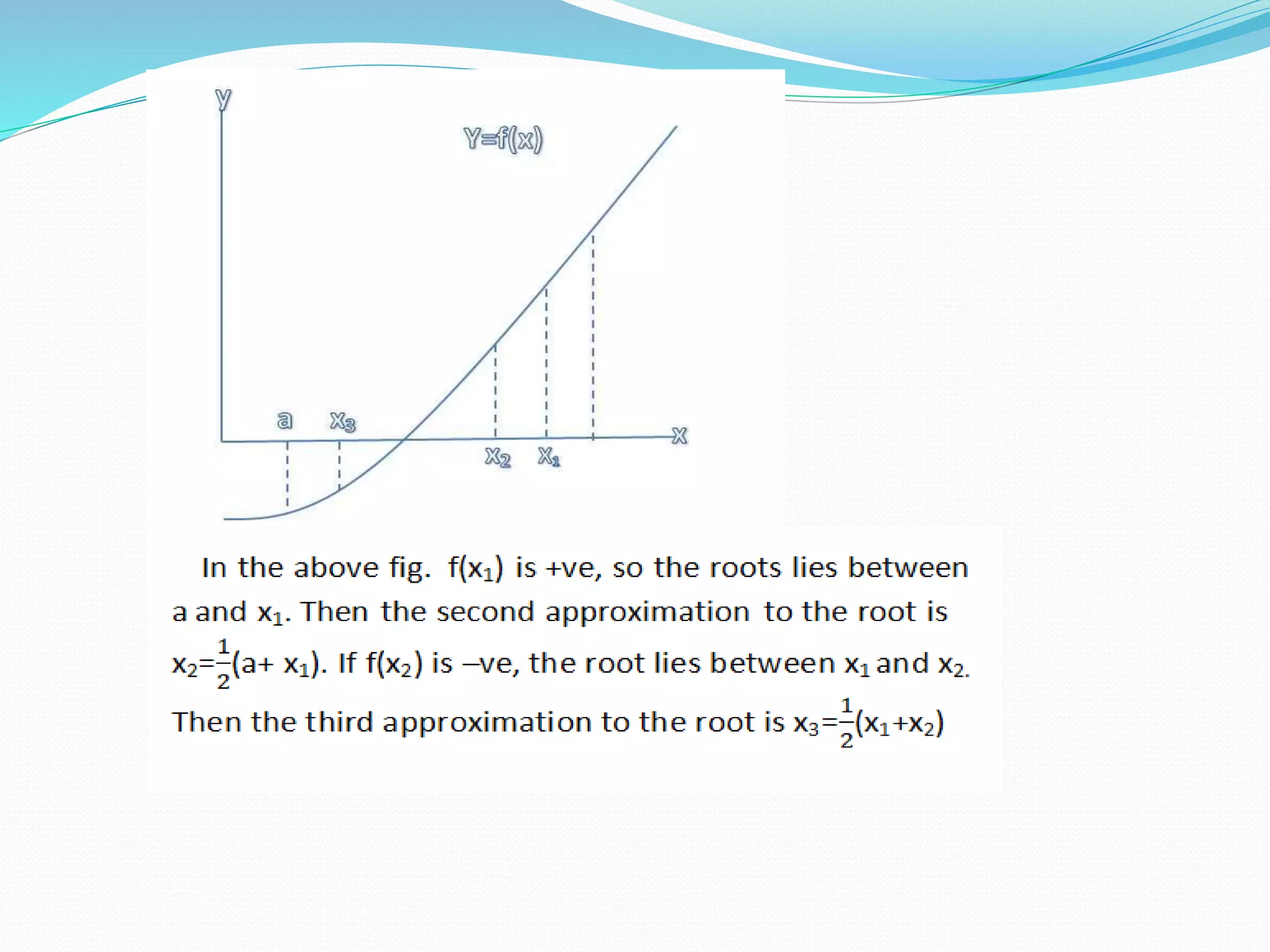
This document discusses numerical methods for solving algebraic and transcendental equations. It introduces the bisection method, regula-falsi method, and Newton-Raphson method. The bisection method locates the root of an equation between two values where the function values have opposite signs. It takes the midpoint of the interval and checks the function value there. If it has the same sign as the left value, the root must lie in the left interval, otherwise it is in the right interval. The process continues iteratively until the root is found to the desired accuracy.