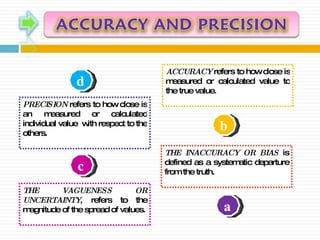
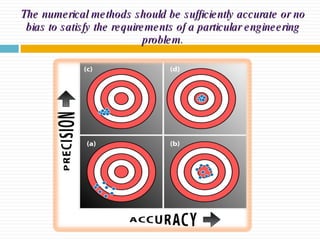
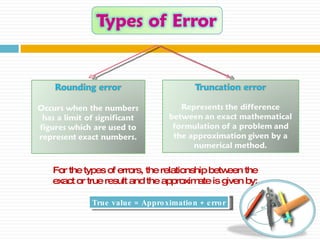
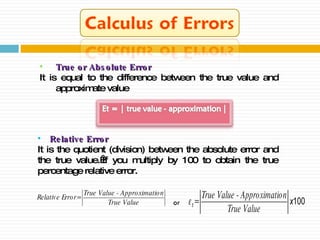
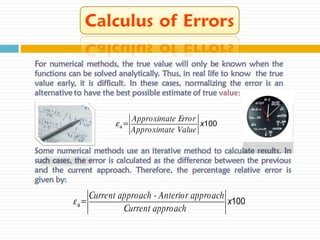
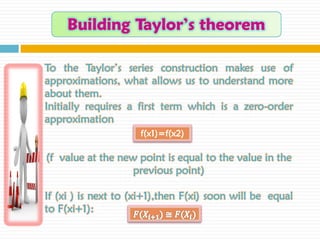
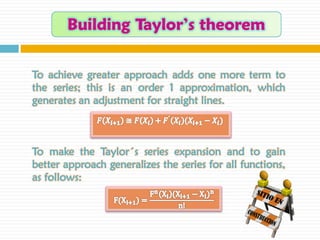
The document discusses significant figures and accuracy in measurements. It explains that:
1) Nonzero digits are always significant, while trailing zeros are only significant if they are after a decimal point.
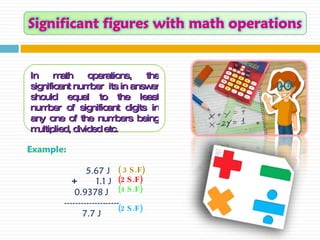
2) In math operations, the answer should be rounded or truncated to the least number of significant figures in the original values.
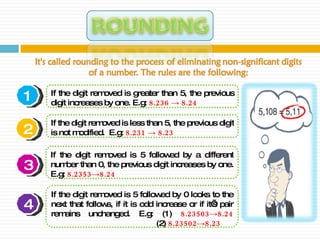
3) There are various rules for rounding numbers during calculations to determine whether the last digit should be rounded up or left unchanged based on the value of the digit removed.