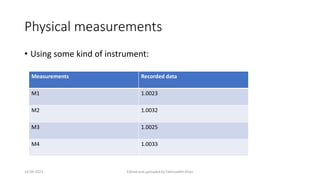
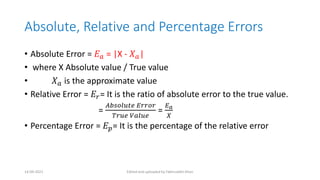
Errors occur in numerical computations due to approximations. Common sources of error include rounding numbers to a certain number of significant figures and truncating infinite series. Absolute error is the difference between the true and approximate values, while relative error is the absolute error divided by the true value. Percentage error expresses relative error as a percentage. Examples show how to calculate absolute, relative, and percentage errors when rounding numbers or truncating functions.