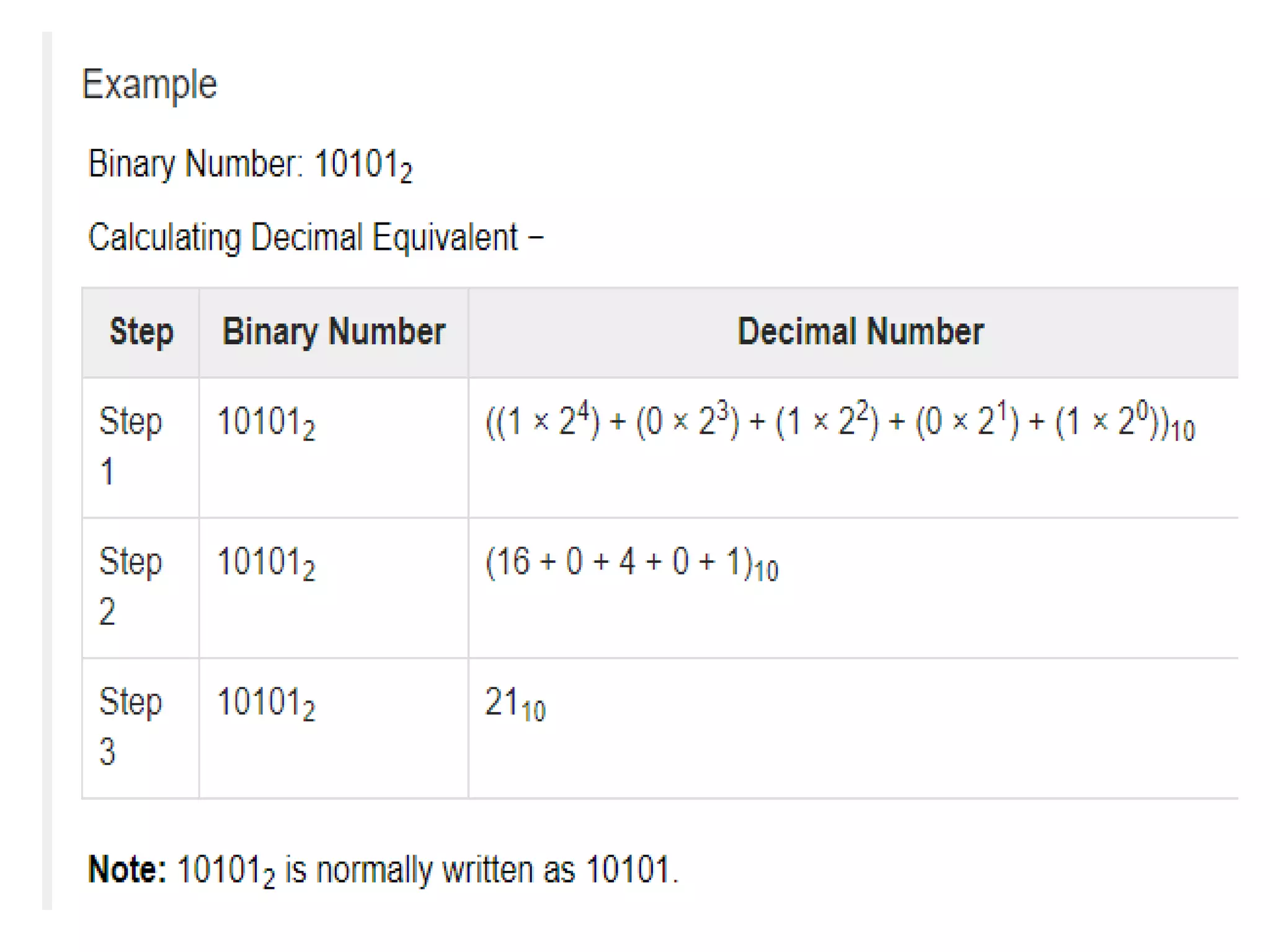
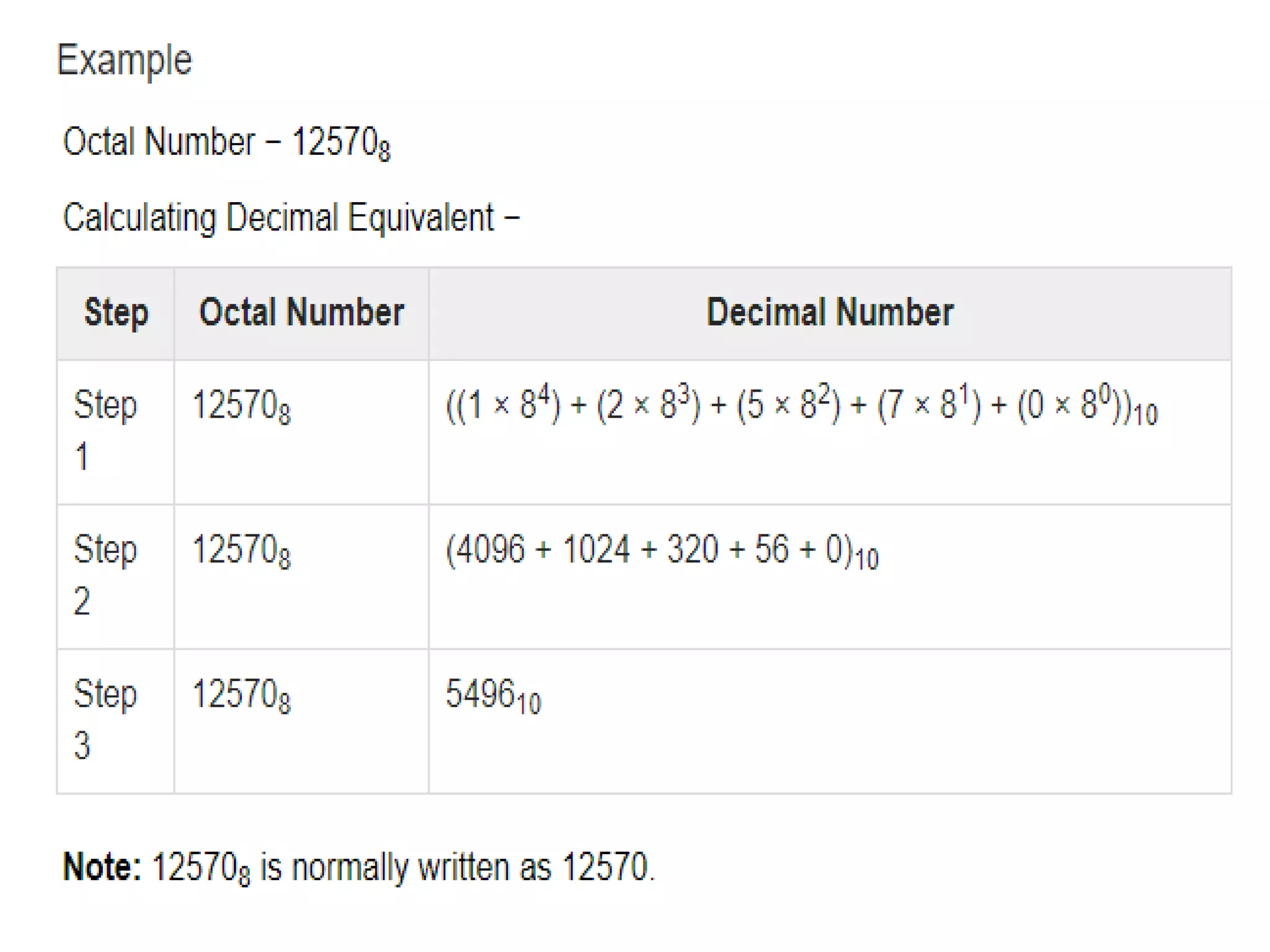
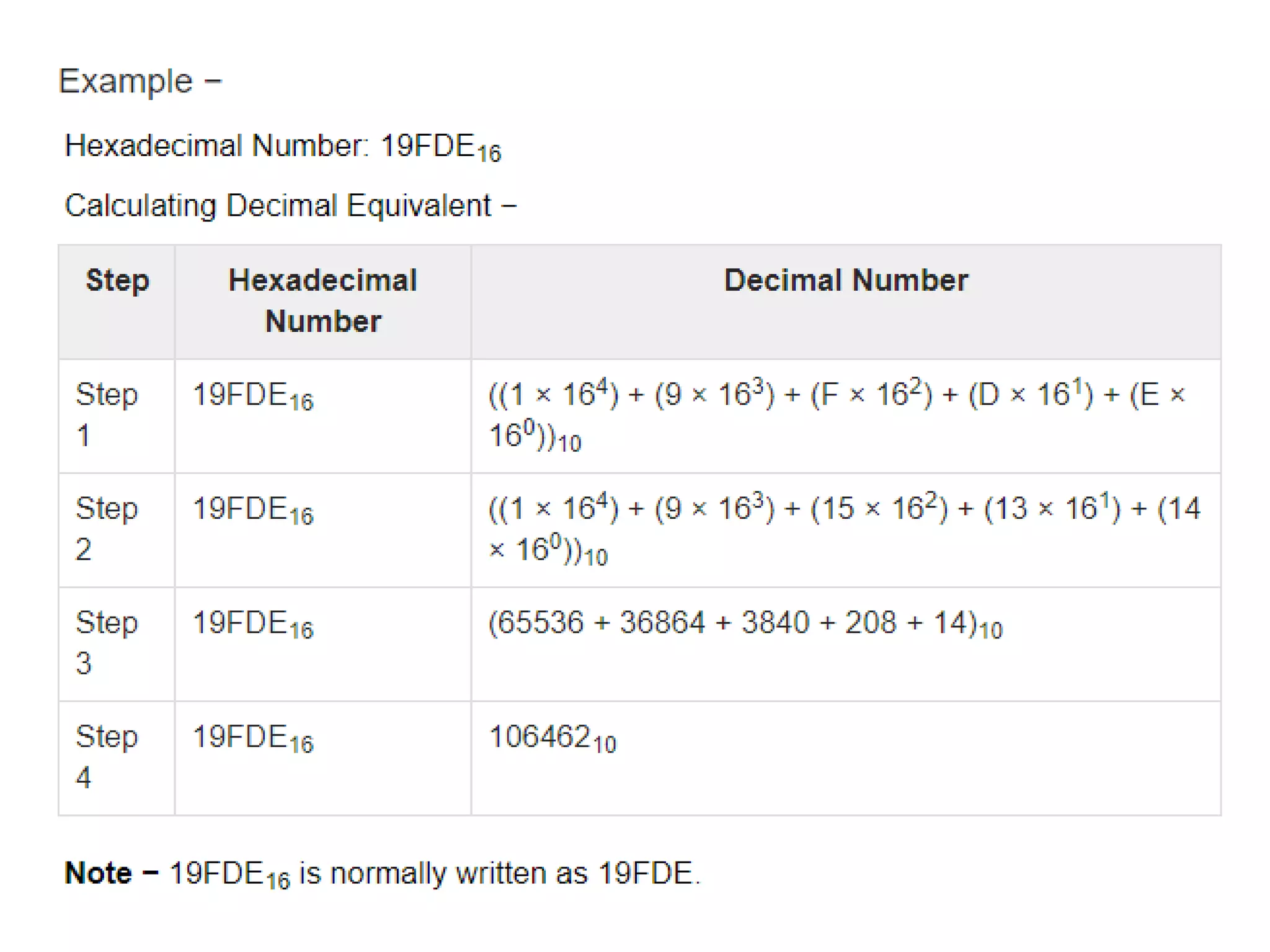
The document discusses different number systems including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. The decimal system uses base 10 with digits 0-9 and is used in everyday life. The binary system uses base 2 with digits 0-1 and each position represents a power of 2. The octal system uses base 8 with digits 0-7 and each position represents a power of 8. Similarly, the hexadecimal system uses base 16 with digits 0-9 and letters A-F, with each position representing a power of 16.