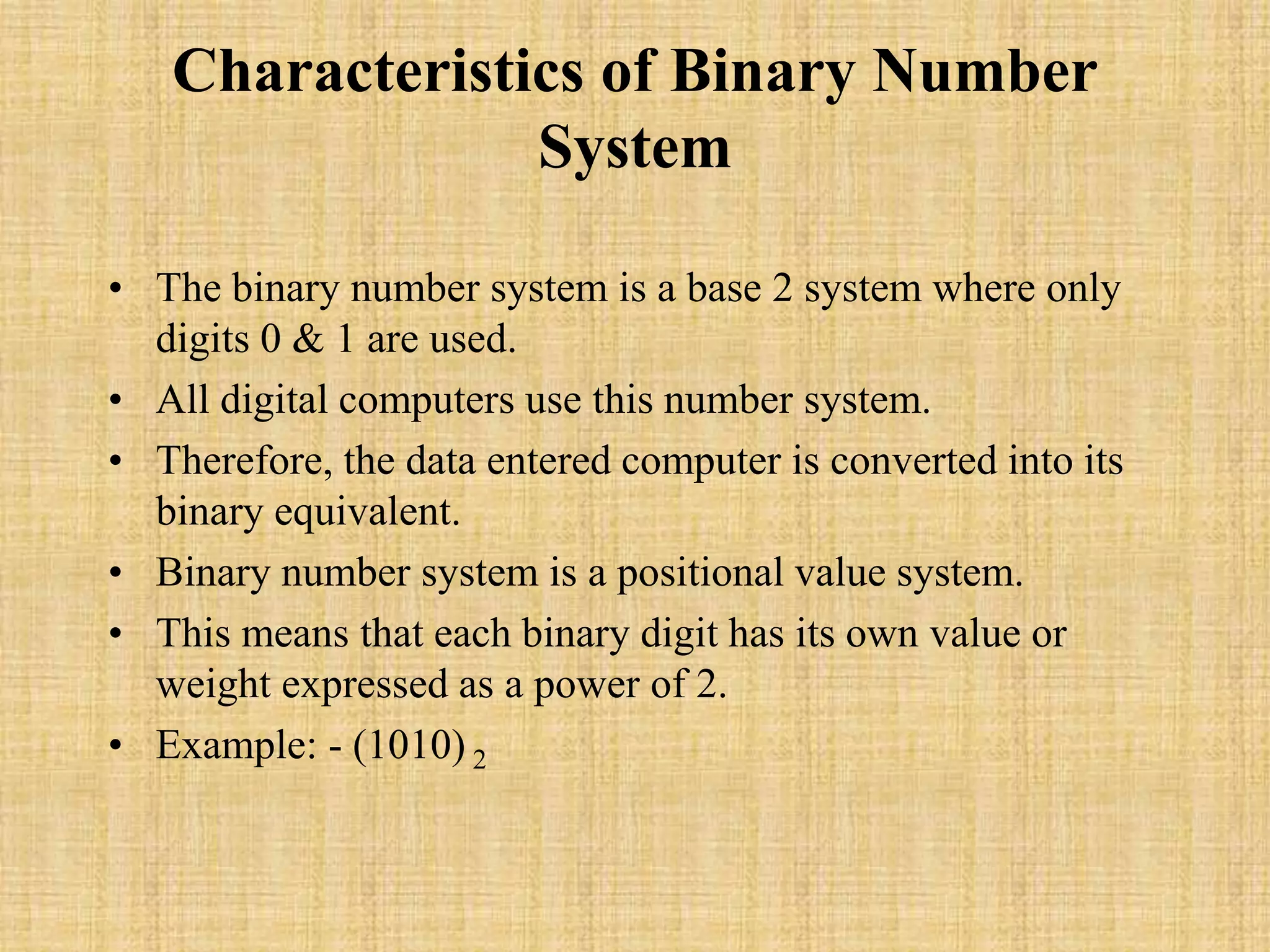
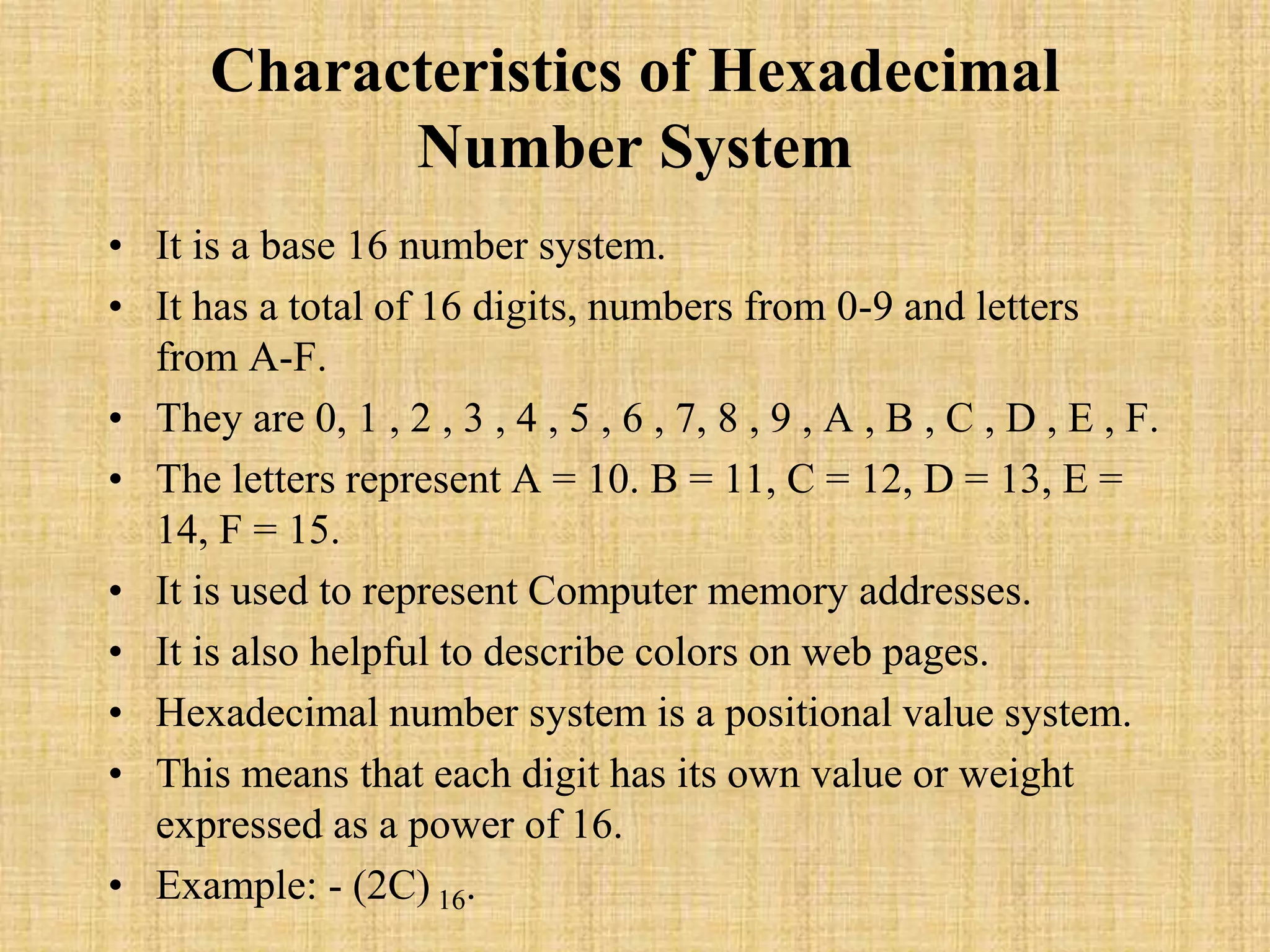
The document discusses different number systems including binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal. It provides characteristics of each system such as the base, digits used, examples, and how position determines value. Binary uses bases 2 with digits 0 and 1. Octal uses base 8 with digits 0-7. Decimal is the common base 10 system with 0-9 and is used for everyday life. Hexadecimal has base 16 and digits 0-9 plus A-F representing values 10-15. Each system is a positional value system where the place of a digit determines its contribution to the number's value.