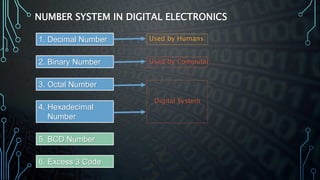
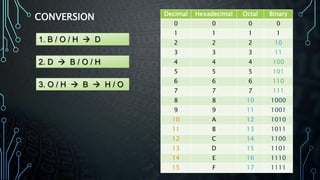
This document discusses different number systems used in digital electronics including decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. It provides examples of numbers represented in each system and methods to convert between the different bases. Conversion methods covered include converting from binary, octal, or hexadecimal to decimal and vice versa, as well as converting between octal and hexadecimal to binary and back. Examples are given to demonstrate each conversion method.