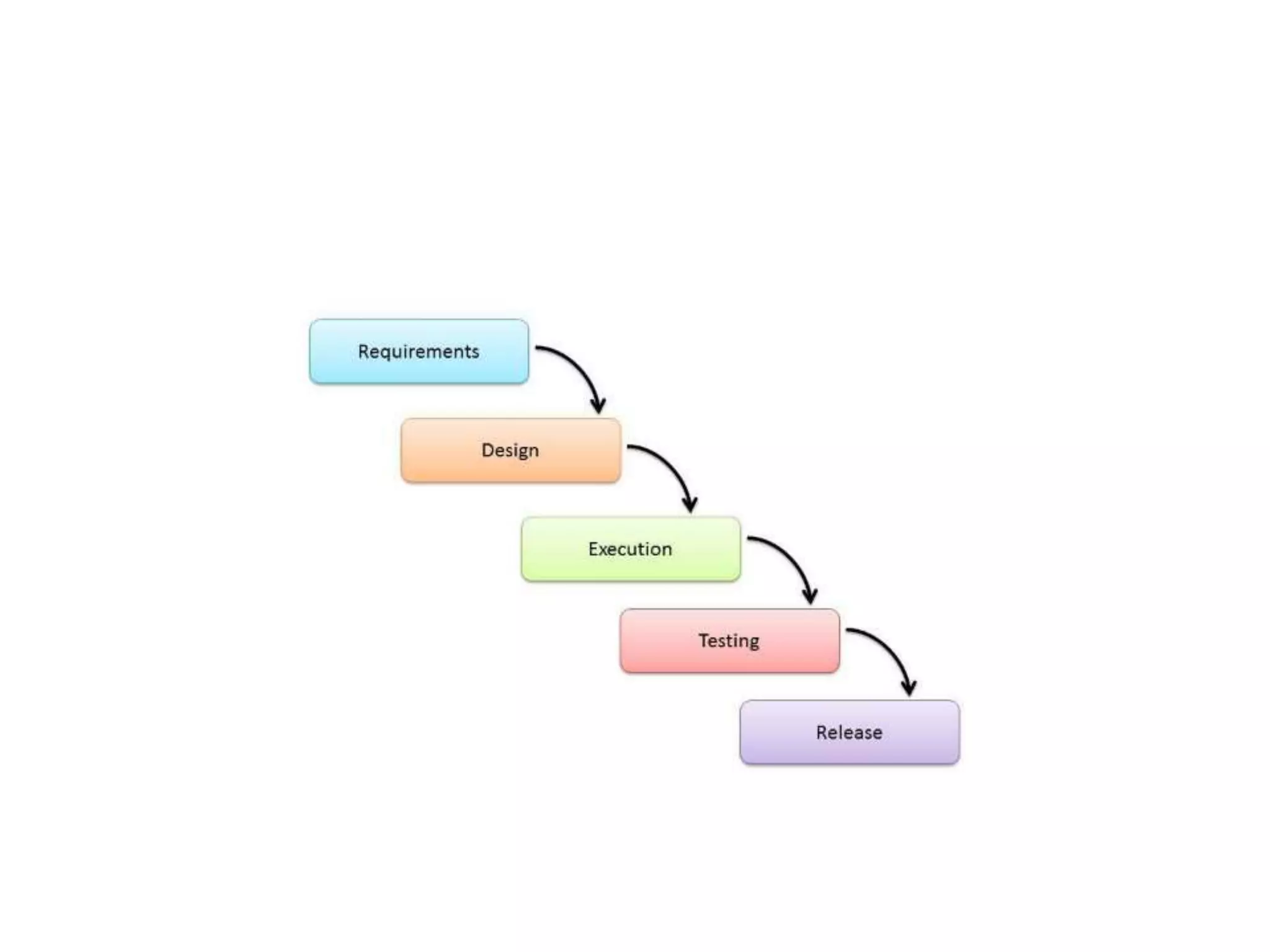
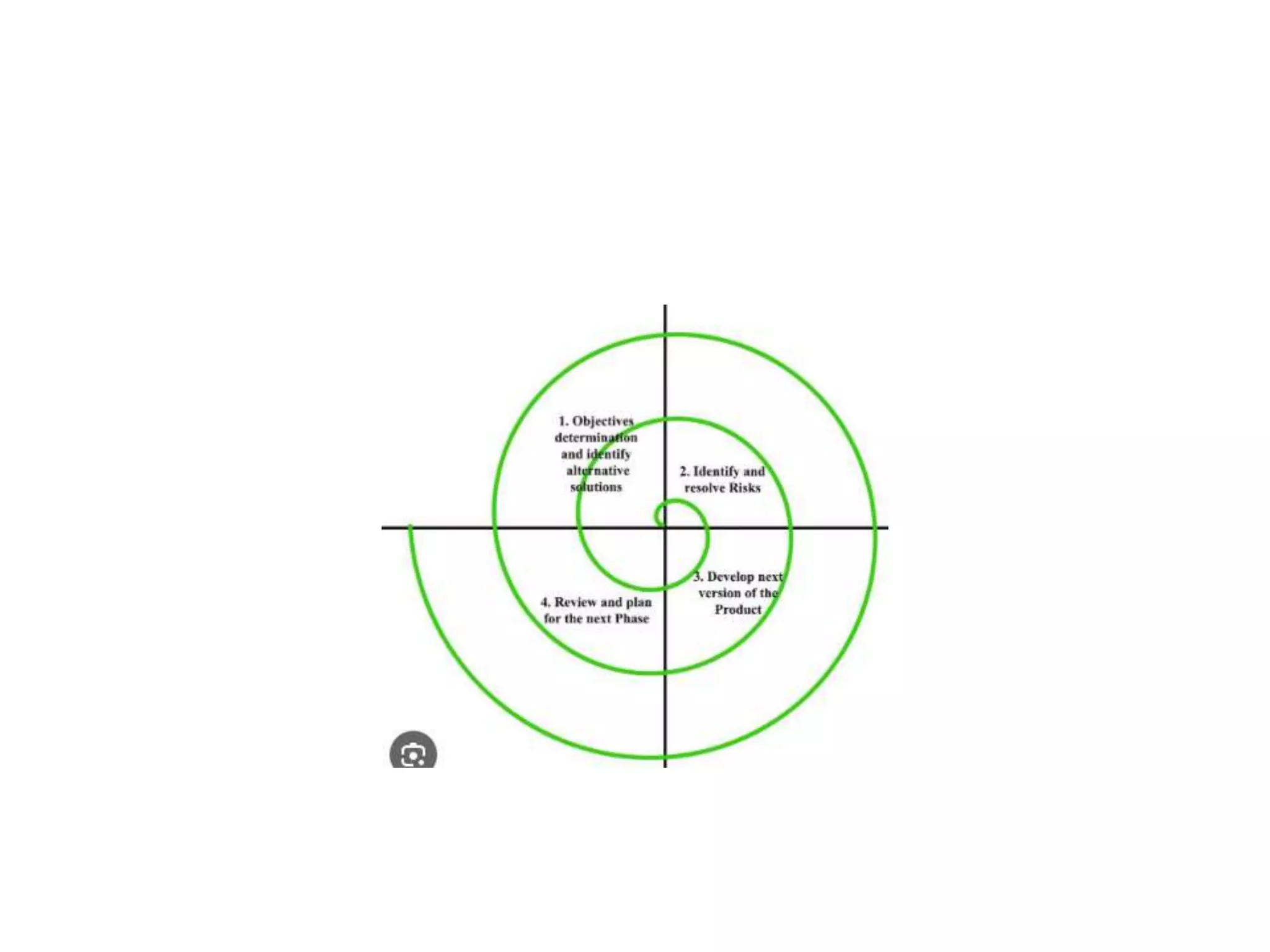
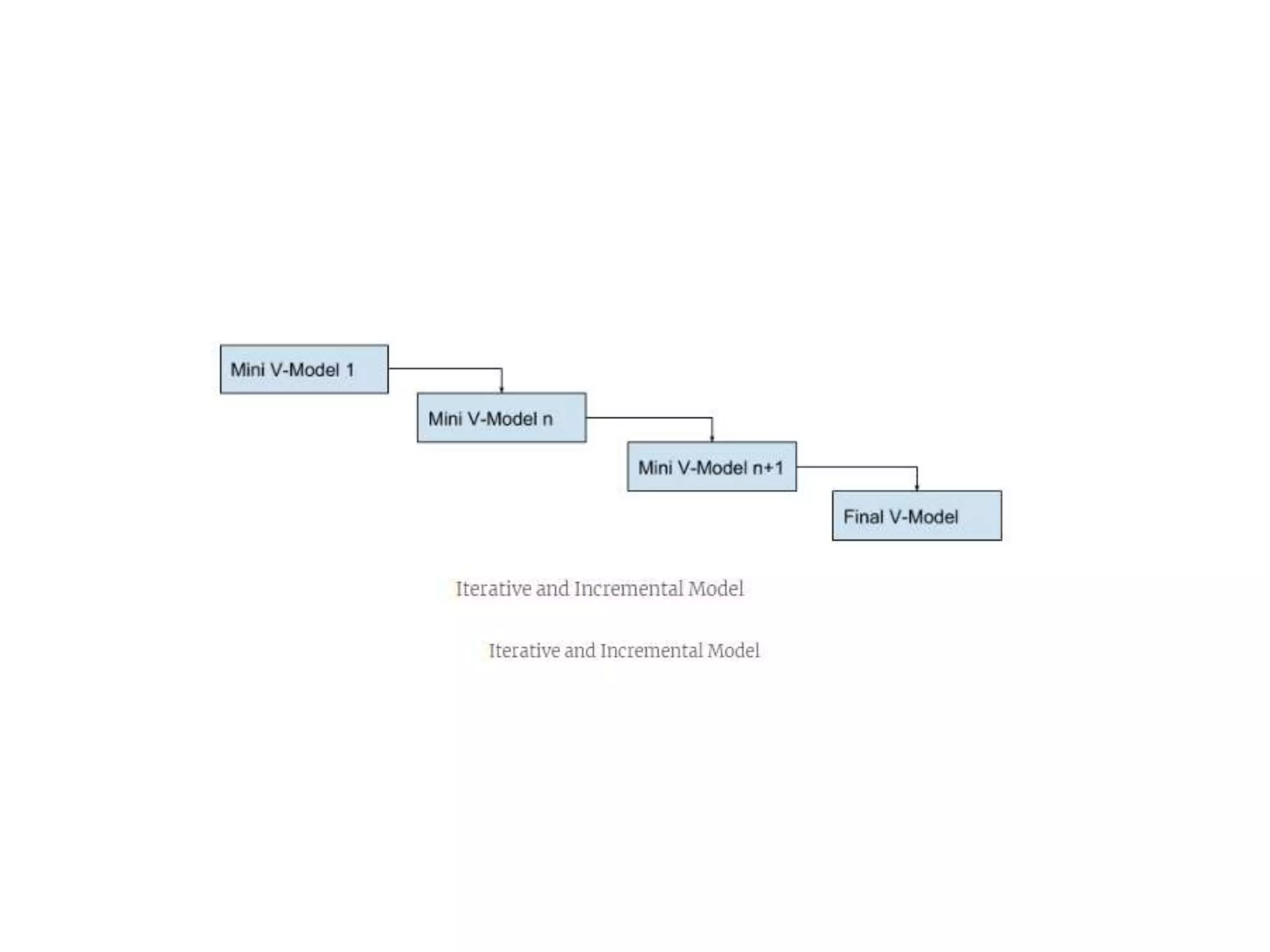
The document discusses several software development lifecycle models including waterfall, V-shaped, spiral, evolutionary prototyping, iterative and incremental. It provides details on the waterfall, spiral and iterative incremental models. For each it describes their usage, advantages and disadvantages. The waterfall model is linear and sequential while spiral combines prototyping and waterfall features. The iterative model develops the system through repeated cycles and smaller portions to overcome weaknesses of waterfall.