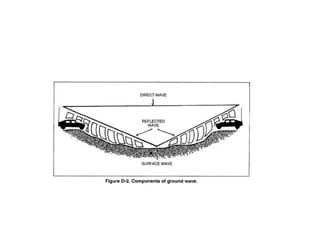
This document discusses three types of radio propagation:
1) Line of sight propagation travels in a straight line up to the visible horizon.
2) Ground wave propagation follows the contour of the Earth and can be reflected by the magnetic field.
3) Sky wave propagation projects waves onto the ionosphere, where they are reflected back to Earth, allowing transmission over longer distances than line of sight. This is useful for broadcasting.