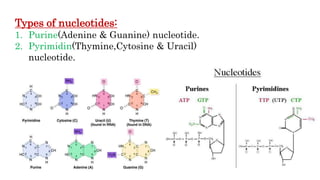
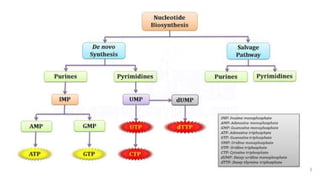
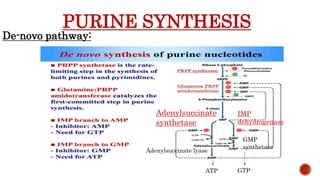
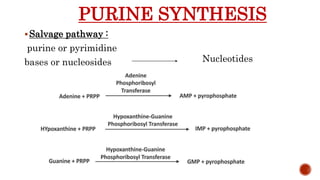
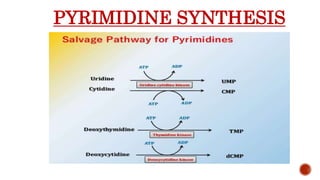
This document discusses nucleotides, which are organic molecules that consist of a nucleoside and one or more phosphate groups. Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA and RNA. It describes the components of nucleotides, including pentose sugars, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases. It also outlines the two pathways for nucleotide biosynthesis in cells: de novo synthesis, where nucleotides are synthesized from simple precursors, and salvage pathways, which recover bases and nucleosides from degraded DNA and RNA. The document provides details on purine and pyrimidine synthesis, including key enzymes and structural analog inhibitors that are used as anticancer drugs.