Embed presentation
Downloaded 22 times
![DNA REPLICATION of [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleicacid-replication-english-version-1229459138282834-1/75/Nucleic-Acid-Replication-English-Version-1-2048.jpg)



![THE END [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleicacid-replication-english-version-1229459138282834-1/85/Nucleic-Acid-Replication-English-Version-14-320.jpg)

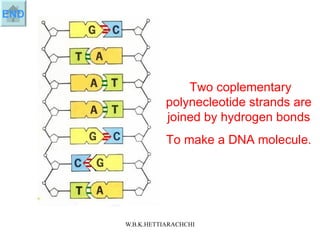
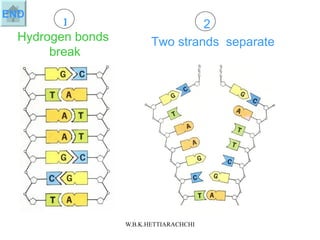
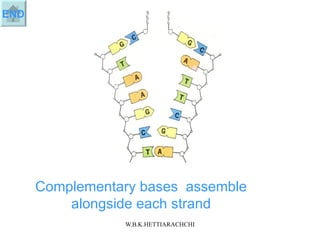
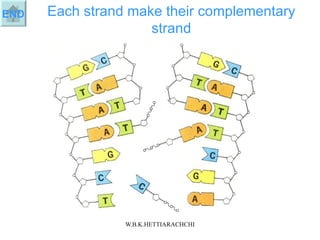
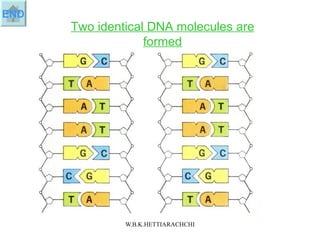
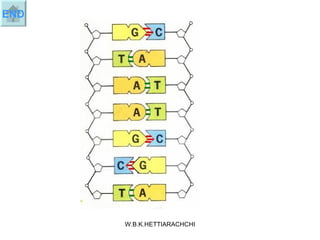
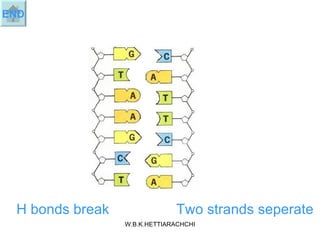
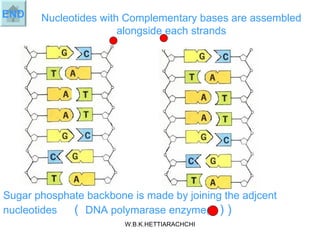
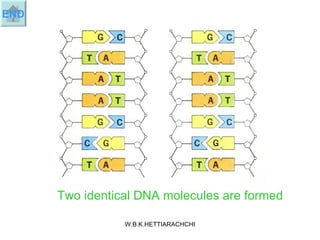
DNA replication produces two identical DNA molecules from one original DNA molecule through unwinding and separating the strands, using each single strand as a template to assemble complementary nucleotides to form new strands, and resulting in two identical DNA daughter molecules. During replication, the hydrogen bonds between the DNA strands break, the strands separate, each single strand acts as a template for assembly of complementary nucleotides to form new strands along the backbone, and eventually two identical DNA molecules are formed.
![DNA REPLICATION of [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleicacid-replication-english-version-1229459138282834-1/75/Nucleic-Acid-Replication-English-Version-1-2048.jpg)












![THE END [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nucleicacid-replication-english-version-1229459138282834-1/85/Nucleic-Acid-Replication-English-Version-14-320.jpg)