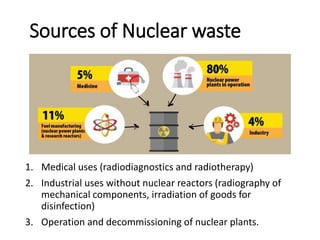
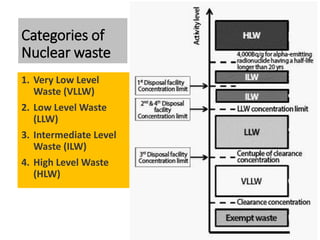
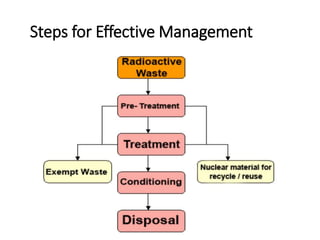
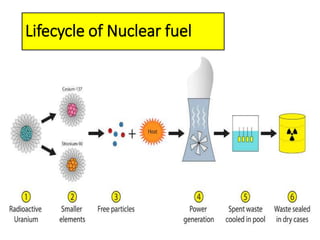
This document summarizes nuclear waste management. It discusses that nuclear waste is a byproduct of nuclear technology and contains radioactive material. The sources of nuclear waste include medical uses, industrial uses without nuclear reactors, and the operation and decommissioning of nuclear plants. Nuclear waste is categorized based on radiation levels and includes very low-level, low-level, intermediate-level, and high-level waste. Storage and disposal methods depend on the category, with low-level waste stored near the surface and high-level waste requiring deep geological disposal.