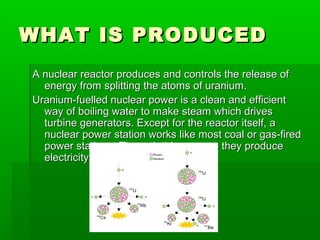
The first commercial nuclear power stations began operating in the 1950s. Currently, there are over 435 nuclear power reactors operating in 31 countries, providing over 11% of the world's electricity through clean, reliable base-load power without carbon dioxide emissions. Nuclear power plants produce electricity by using uranium fuel to boil water and create steam that drives turbine generators, similar to fossil fuel power plants. Nuclear power is important because it can help solve air pollution problems through reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, and nuclear waste is being dealt with through improved management.