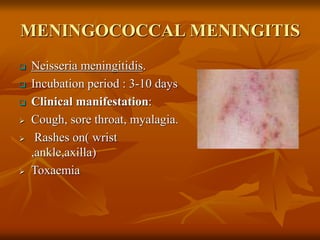
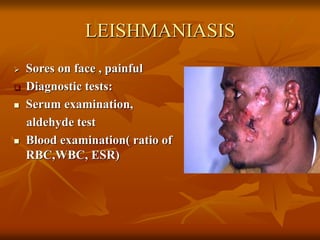
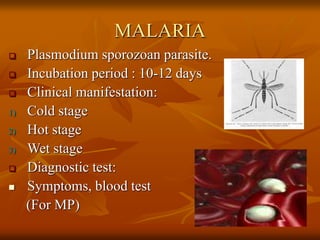
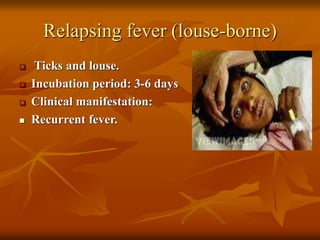
This document provides an overview of nursing management of communicable diseases in emergency situations. It discusses the major causes of morbidity and mortality in emergencies like diarrheal diseases, respiratory infections, measles, and malaria. It outlines the fundamental principles of communicable disease control, including rapid assessment, prevention, surveillance, outbreak control, and disease management. It also summarizes the prevention and control of specific communicable diseases like respiratory infections, tuberculosis, measles, cholera, and diarrhea.